Team,
Two questions:
1) Can you provide the maximum operating supply current for TPS50601A-SP? as well as the maximum output voltage. A note from the manufacturer on these two items is needed for WCA documentation for an end customer.
I realize that it is a 7V in 6A out device, which could provide the theoretical max input current and output voltage of a DC/DC buck reg. however a calculation is not sufficient for the end customer and a spec is being asked for.
in addition:
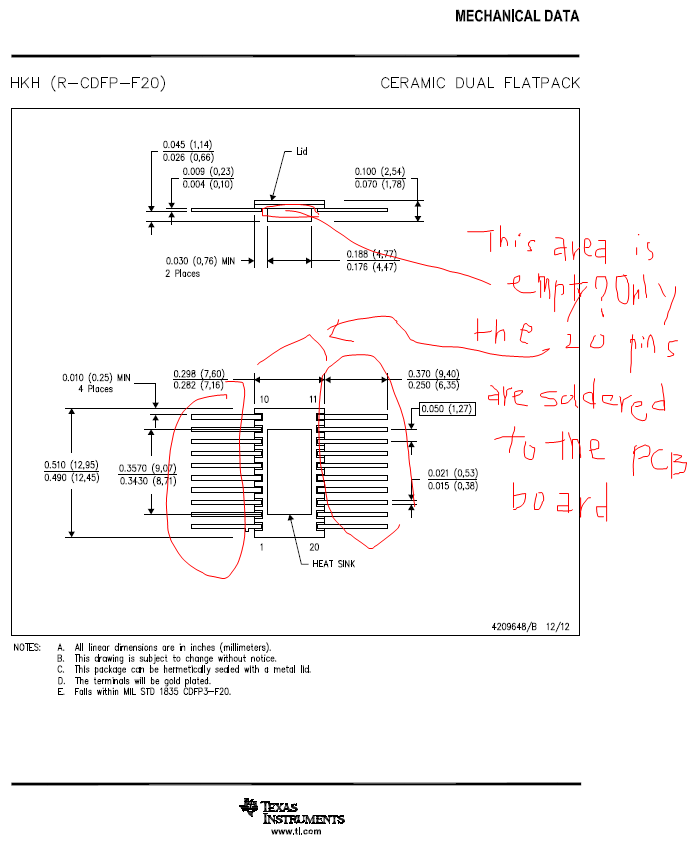
2) When the 20 pins of the TPS50601A-SP device is soldered to the PCB board, I believe the bottom case of the 50601A-SP device is floating in the air, and the area which I circled is empty , and when there is 1W loss in the TPS50601A-SP device itself, the worst case temperature rise of the internal junction of the TPS50601A-SP device will only have 0.514 deg. C temperature rise above the ambient temperature ? i.e. this is the absolute worst case temp rise per watt the device will encounter. and this can be used in the WCA effort to bound the temp rise.