Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TPS25924,
Hi
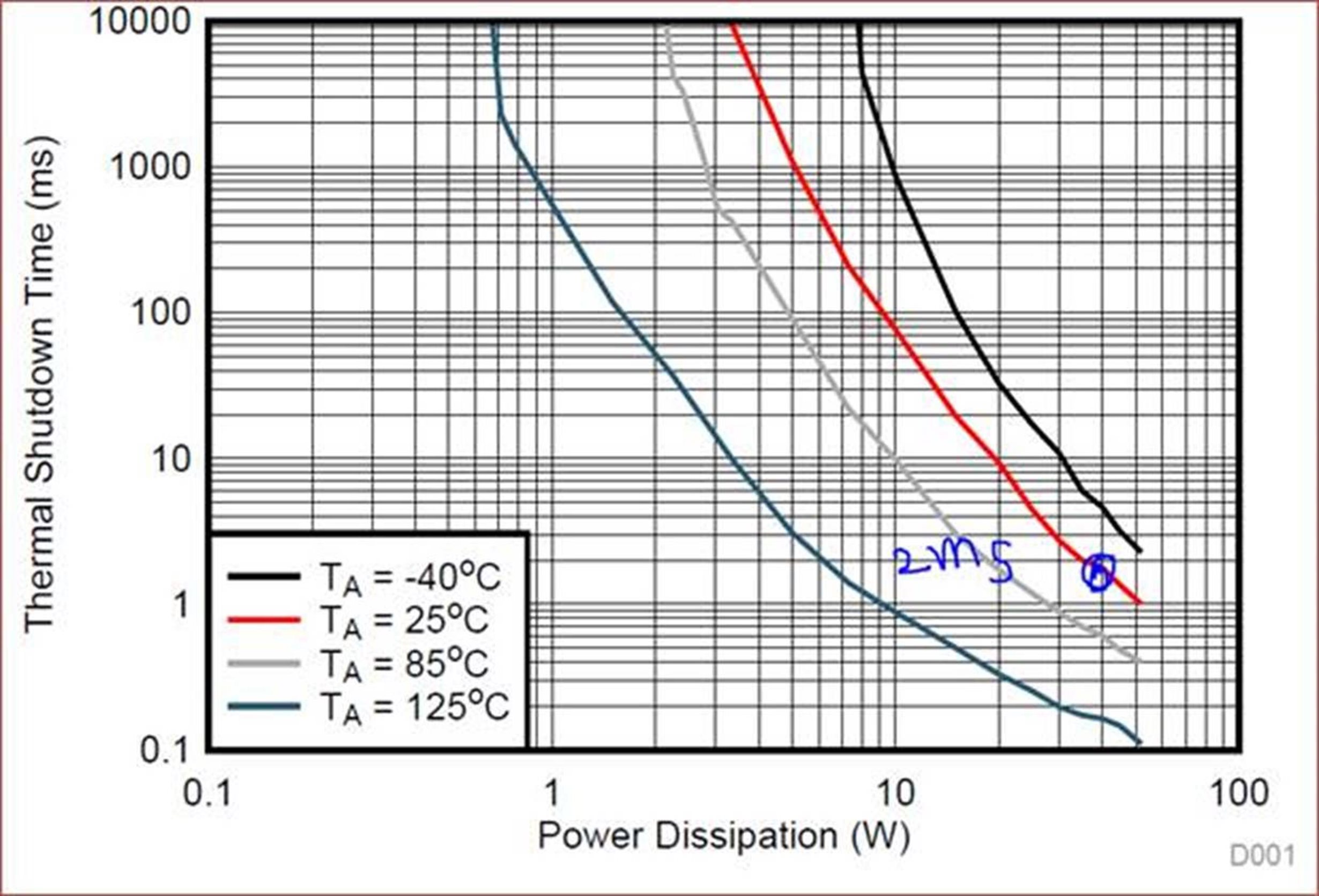
How can we estimate the thermal shutdown time ?
In the case of configured that RLIM is 200mA, if Rdson = 150mohm, PD would be around 6mW.
If the current was inputted over the RLIM, how customer can estimate the thermal shutdown time in the above case ?
Thank you and best regards,
Michiaki