Part Number: EVMK2GX
Other Parts Discussed in Thread: 66AK2G01, 66AK2G02, , 66AK2G12
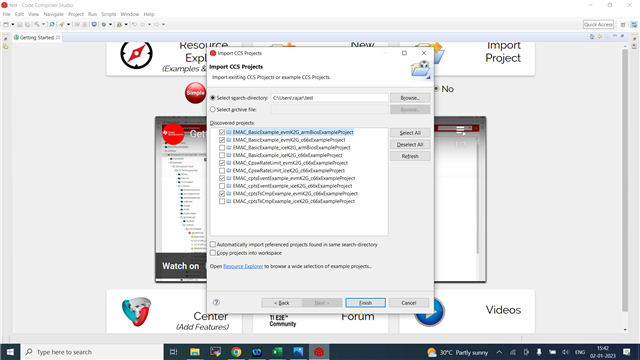
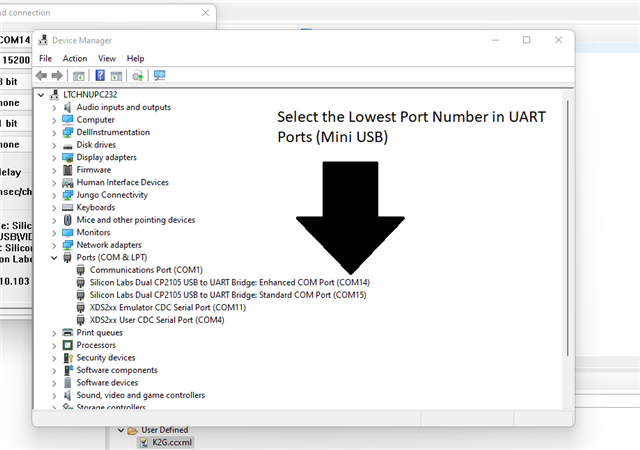
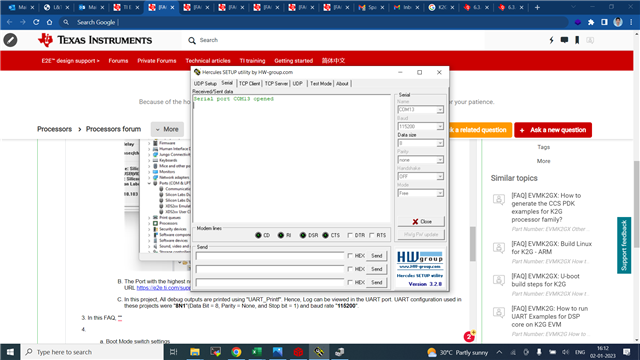
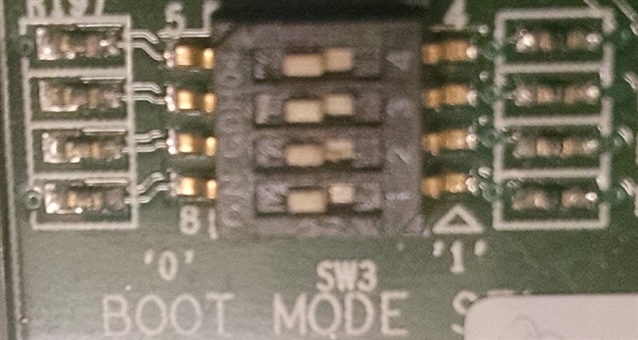
How to build, run and test the EMAC example from TI-RTOS PDK for the K2G family processors (EVMK2G, EVMK2GX, EVMK2GX, 66AK2G01, 66AK2G02, 66AK2G12 and K2GICE) on its DSP core?