Hello Champs,
Customer has some questions about AWR6843 DMA controller.
1. Can the DMA Port B read and write simultaneously? Or it can only read or write at a time?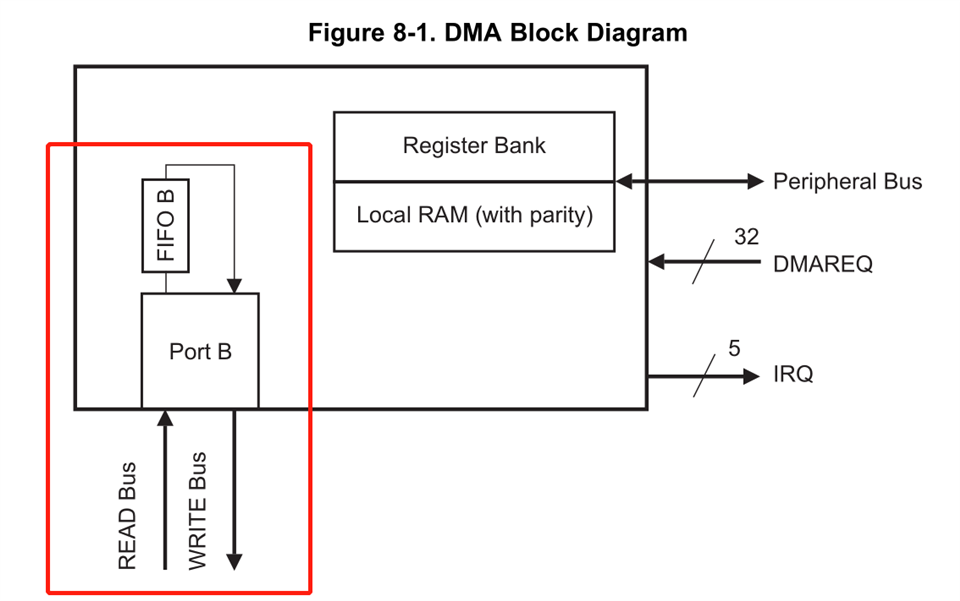
2. What does "Peripheral Bus" refer to? Does it refer to APB or AHB or other bus?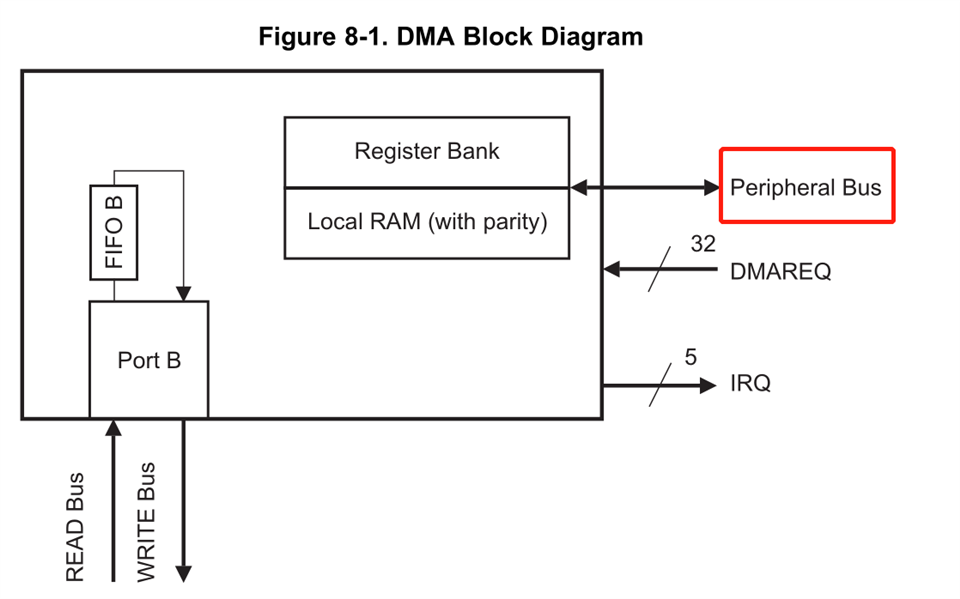

3. How does the GCTRL. DEBUG MODE bit work with CPU? Or is it only controlled by DMA hardware?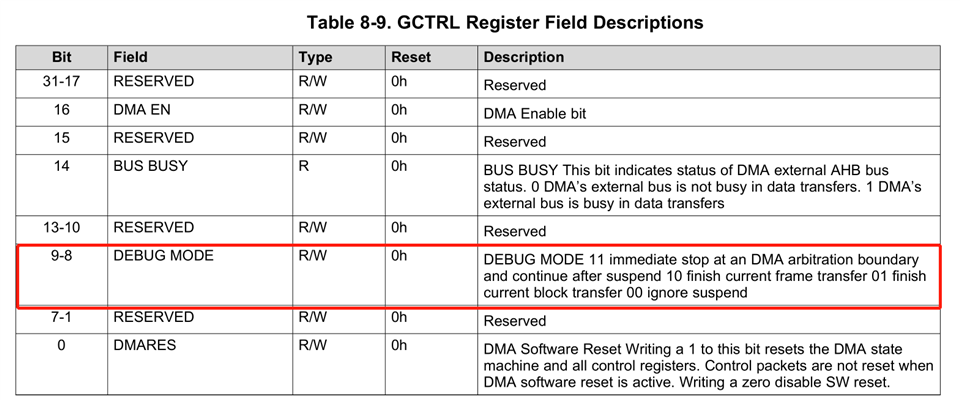
4. When is the PEND bit in channel PEND register set to "1"?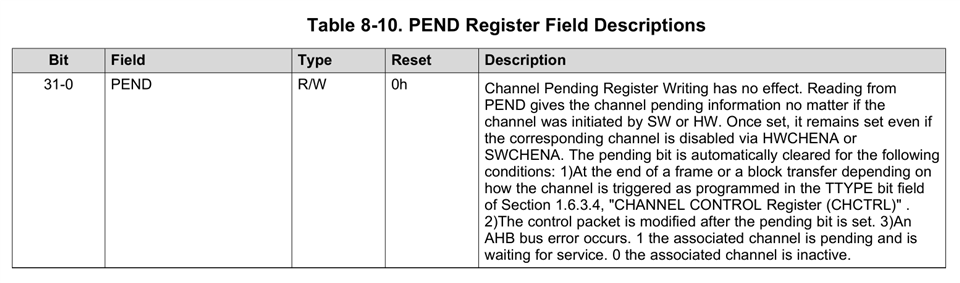
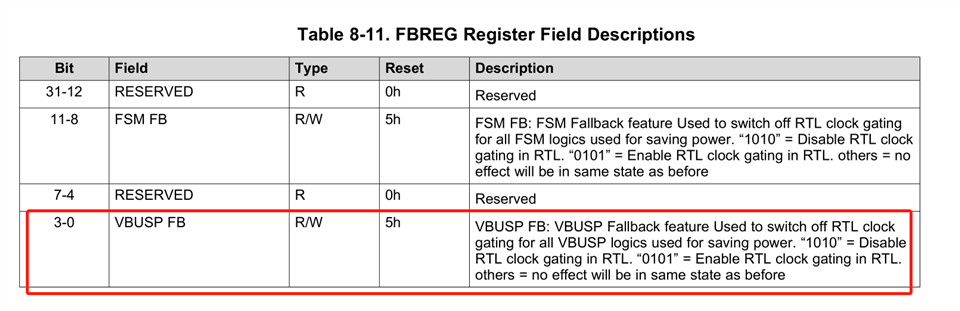
5. What is the working scheme for VBUSP FB clocking gating? Is there some relationship between FSM FB and VBUS FB clock gating?
Thanks
Regards
Shine

