Other Parts Discussed in Thread: IWR1843BOOST, IWR6843ISK
Hi Zigang Yang and others,
I would like to continue our conversation from the thread (https://e2e.ti.com/support/sensors-group/sensors/f/sensors-forum/1311419/iwr6843isk-ods-iwr6843isk-ods-chirp-order-and-virtual-antenna-configuration/4994814#4994814).
I will ask my question again,
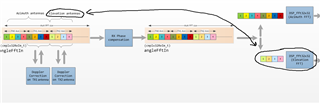
If I understood correctly, you are mentioning about peak grouping on 2D angle FFT as mentioned in aoa2dproc index.html file documentation. But I couldn't understand how integrating 2D angle spectrum over azimuth will give elevation and vice-versa. Could you please explain this more for me to understand this?
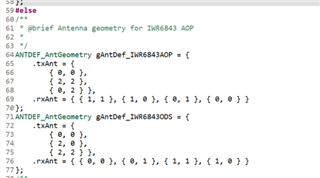
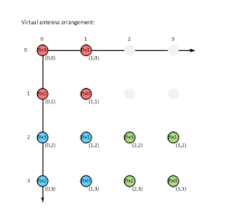
For IWR6843ISK-ODS, across which channels shall I perform fft on angle FFT to get the required azimuth and elevation angles? Requesting you to please explain this in detail on finding angles for ODS antenna. arrangement
I am using the below function to get the azimuth and elevation angles. The input to function is 2D angle spectrum. Will it possible to look into it?
def naive_xyz(virtual_ant, num_tx=3, num_rx=4, fft_size=64): #
assert num_tx > 2, "need a config for more than 2 TXs"
num_detected_obj = virtual_ant.shape[1]
azimuth_ant = virtual_ant[:2 * num_rx, :]
azimuth_ant_padded = np.zeros(shape=(fft_size, num_detected_obj), dtype=np.complex_)
azimuth_ant_padded[:2 * num_rx, :] = azimuth_ant
# Process azimuth information
azimuth_fft = np.fft.fft(azimuth_ant_padded, axis=0)
k_max = np.argmax(np.abs(azimuth_fft), axis=0)
peak_1 = np.zeros_like(k_max, dtype=np.complex_)
for i in range(len(k_max)):
peak_1[i] = azimuth_fft[k_max[i], i]
k_max[k_max > (fft_size // 2) - 1] = k_max[k_max > (fft_size // 2) - 1] - fft_size
wx = 2 * np.pi / fft_size * k_max
x_vector = wx / np.pi
# Zero pad elevation
elevation_ant = virtual_ant[2 * num_rx:, :]
elevation_ant_padded = np.zeros(shape=(fft_size, num_detected_obj), dtype=np.complex_)
elevation_ant_padded[:num_rx, :] = elevation_ant
# Process elevation information
elevation_fft = np.fft.fft(elevation_ant, axis=0)
elevation_max = np.argmax(np.log2(np.abs(elevation_fft)), axis=0) # shape = (num_detected_obj, )
peak_2 = np.zeros_like(elevation_max, dtype=np.complex_)
for i in range(len(elevation_max)):
peak_2[i] = elevation_fft[elevation_max[i], i]
# Calculate elevation phase shift
wz = np.angle(peak_1 * peak_2.conj() * np.exp(1j * 2 * wx))
z_vector = wz / np.pi
ypossible = 1 - x_vector ** 2 - z_vector ** 2
y_vector=ypossible
x_vector[ ypossible<0 ] = 0
z_vector[ ypossible<0 ] = 0
y_vector[ ypossible<0 ] = 0
y_vector = np.sqrt(y_vector)
return x_vector, y_vector, z_vector
This function is for IWR1843BOOST keeping in mind its virtual antenna arrangement and chirp order Tx0, Tx1 and Tx2.
Best regards,
Pushkar