Tool/software:
Hello TI experts,
While testing the vital sign lab, we found vibrating nonhuman object, such as plastic bag, paper, or a cloth glove, make Vital Sign.
Following videos are experiment making plastic/paper/cloth vibrating by a handheld fan, we can see vital sign is detected in TI mmWave industrial Visualizer
I tried to explain the phenomenon, according to TI Radome Design document page 4: Electromagnetic wave reflection of an object is related to its dielectric constant(ε_r) . The more dielectric constant(ε_r) close to 1, the less reflection.
Base on the reflection coefficient formula below:
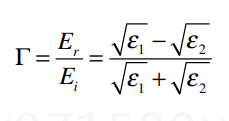

- PE(ε_r=2), Γ=-0.17. means 17% electric filed is reflected
- Cotton (ε_r=1.6), Γ=-0.117, means 11.7% electric filed is reflected.
- Paper (ε_r=1.4), Γ=-0.083, means 8.3% electric filed is reflected.
- Metal (ε_r=∞), Γ=-1, means 100% electric filed is reflected.
So for paper, the 8.3% reflection electric field reflection is sufficient for mmWave Radar to detect, then it makes the vital Sign in TI mmWave industrial Visualizer.
Is my above understanding correct?

