Tool/software:
Hello,
In our app, we need 4 way joystick + rotary position + push button. Is it possible to implement all these functions combined using TI Hall ICs such as TMAG5173?
Best regards,
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
Tool/software:
Hello,
In our app, we need 4 way joystick + rotary position + push button. Is it possible to implement all these functions combined using TI Hall ICs such as TMAG5173?
Best regards,
Hi Egemen,
Thank you for posting to the Sensors forum!
By 4-way joystick, I assume you mean being able to move the joystick up, down, left, and right. If this assumption is incorrect, please let me know.
To clarify, is it the case that a single magnet would be the one that the TMAG5173-Q1 is supposed to track for the joystick, rotary position, and push button? If so, with the TMAG5173-Q1's internal CORDIC, it is able to make both angle calculations, which you can use for rotary position, and calculate the magnitude, which would be useful to detect a button push. Regarding the joystick movement, as the magnetic fields will change as the magnet gets rotated, you may need to constantly calibrate the joystick every time a rotation occurs which will add some complexity to the firmware.
Best,
~Alicia
Hello,
Thank you for your reply.
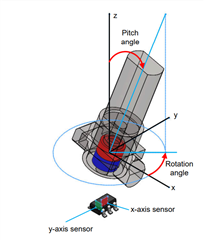
In case of single magnet, how can we do the calibration is there any example?
We can use additional magnet and/or additional TMAG5173-Q1 to make software less complex. In this case how we can implement design to reliable control?
Best regards,
Hi Egemen,
Apologies, I believe that I may have misunderstood what you were initially asking.
To help make sure that I understand your application, is the image that you have shared an accurate representation what you are trying to achieve? Where the angle rotation of the joystick correlates to the joystick position (up/down/left/right)?
Best,
~Alicia
Hello Alicia,
Yes attached images represents our application.
How can we achieve this application?
Do you have any recommendations?
Best regards.
Hi Egemen,
To help determine if the joystick has been tilted up/down/left/right, one option would be to look at the magnetic results of the X and Y-axis, namely the zero-crossings. See the quick TIMSS simulations that I made to demonstrate this below:
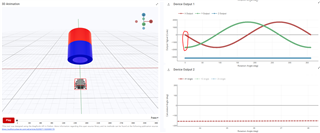
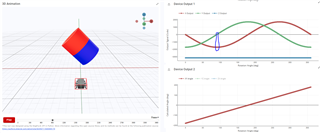
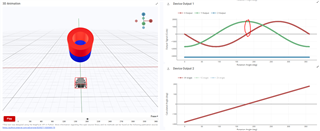
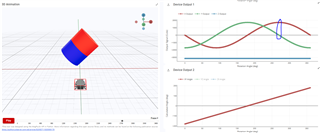
For more specific joystick positioning, you can use the XY angle calculation, shown in the Device Output 2 plots above.
I have attached the JSON file below for the joystick example that I made so that you can play around with some of the parameters to see how different inputs affect the results. For the below simulation, I have the sensor lined up so that the center of the magnet is centered with the sensing element.
{
"version": "3.4.0",
"design_name": "Joystick Example",
"magnet_id": 5,
"poles": 2,
"material_id": 1,
"grade_id": 1,
"select_remanence": "br_average",
"remanence": 1200,
"temperature": 20,
"temperature_coefficient": -0.12,
"coercivity": 10.9,
"function_id": 4,
"magnet_geometry": {
"outer_diameter": 5,
"inner_diameter": 3,
"height": 6
},
"magnet_position": {
"x_position": 0,
"y_position": 0,
"z_position": 5
},
"magnet_angle": {
"x_angle": -45,
"y_angle": 0,
"z_angle": 0
},
"magnet_movement": {
"arc_length": 360
},
"sim_setting": {
"angular_step_size": 0.1
},
"sensor": [
{
"sensor_id": "TMAG5173-Q1",
"sensor_position": {
"x_position": 0.12,
"y_position": 0.4,
"z_position": -5
},
"sensor_angle": {
"x_angle": 0,
"y_angle": 0,
"z_angle": 0
},
"custom_inputs": {
"variant": "TMAG5173D2QDBVRQ1",
"applied_vcc": 3.3,
"temperature_compensation": 0,
"averaging": 32,
"maximum_input": 133
},
"id": 28681,
"user_design": 41221
}
],
"parametric_sweep": [
{
"sweep_values": {
"values": "-45,-35,-25,-15,-5,5,15,25,35,45",
"from": -45,
"to": 45,
"step_size": 10
},
"is_combination": false,
"parameter": "magnet_angle:y_angle",
"sweep_type": "Range",
"user_design": 41221,
"id": 12501
}
]
}
To determine whether a button press has occurred, I would recommend using the device's calculated magnitude results and checking to see if the magnitude exceeds some set value which would equal a button press.
Best,
~Alicia
Hello Alicia,
When the handle is in exactly vertical (perpendicular) position, 360-degree rotation movement will also be applied. With this configuration, is it possible to detect full 360-degree rotation? If not, would adding an additional magnet help solve this issue?
Best regards.
Egemen,
Since an axially polarized magnet has radial symmetry, the field will not change when twisted 0-360° at any joystick position, so there will not be a measurable change in the magnetic field.
Typically for rotation a diametric magnet is used.
However, this magnet type is less ideal for joystick functionality. If you are able to track the 0-360° rotation, it might be possible to derive a calculation to determine the joystick tilt, but this will be more computationally difficult than the original alignment with an axially polarized magnet. The observed joystick tilt will be directly dependent on the rotation angle applied.
It may be possible to add a second magnet on the shaft that could be used to track the rotation, but you would likely need a second sensor placed to measure the field from this magnet. The two magnets may interact with each other depending on how you intended to place them. The tilt this magnet experiences may also impact the linearity of the angle measurement performed by the second sensor.
Thanks,
Scott