Tool/software:
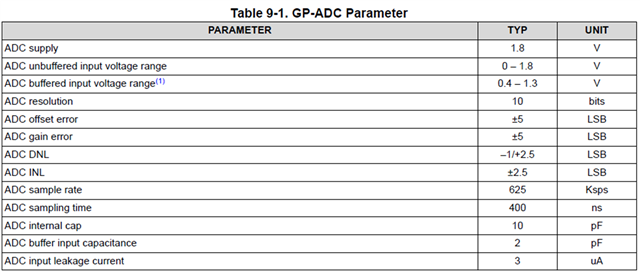
We are planning to use ADC pins 5 and 6 for voltage monitoring. Could you please advise on the recommended input current specification and input capacitance? The leakage current is expected to be designed below 5 µA.
Please check unbuffered condition and buffered condition.