Other Parts Discussed in Thread: IWR1443
hello i have some problem about mmwave sensor
already i learned TI trainning of 'fundamentals of mmwave sensor'.
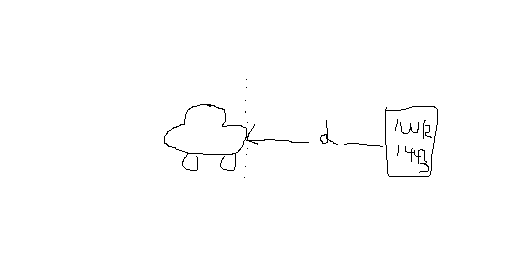
i wondering about range estimation. i want show the example about estimate the distance from rader to object
please show me the example about range estimation
Thank you listening