Other Parts Discussed in Thread: MMWAVE-SDK, , IWR1443,
Tool/software: Code Composer Studio
Hi,
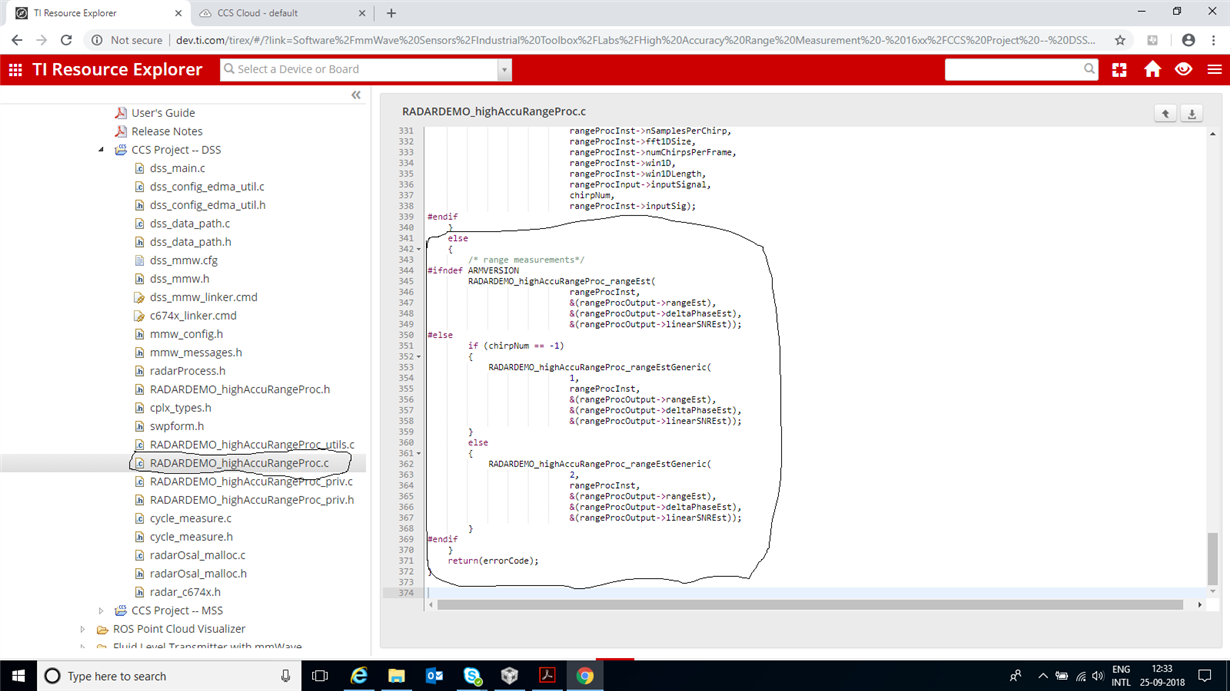
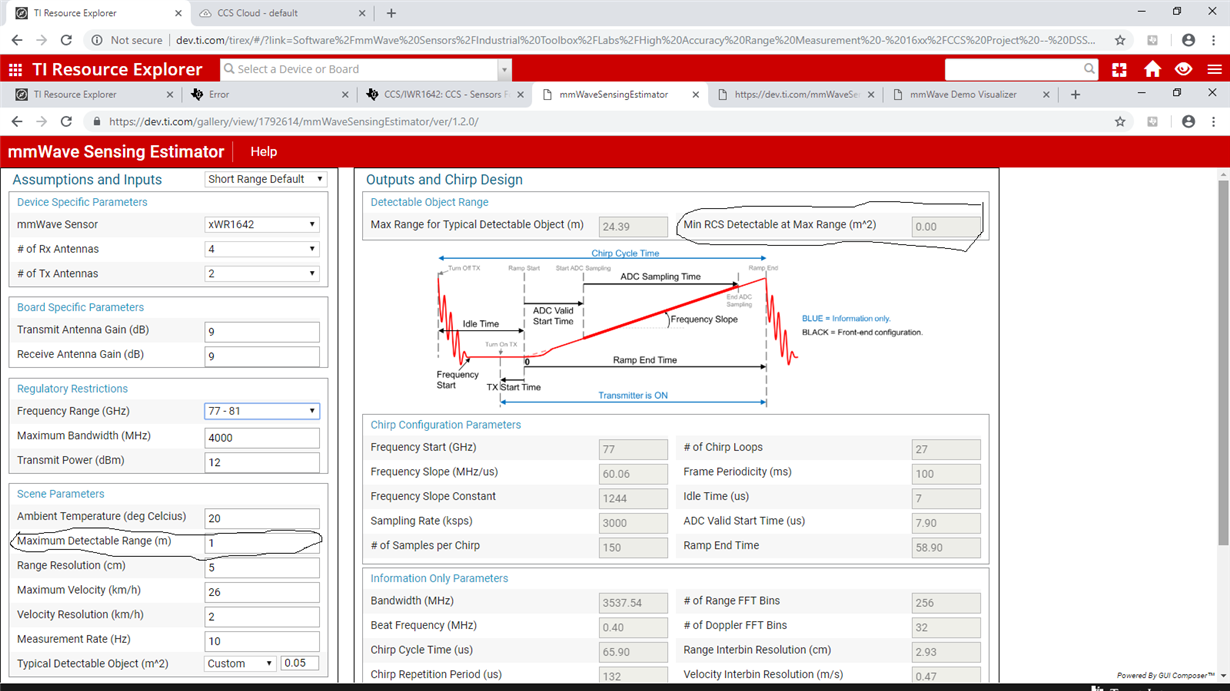
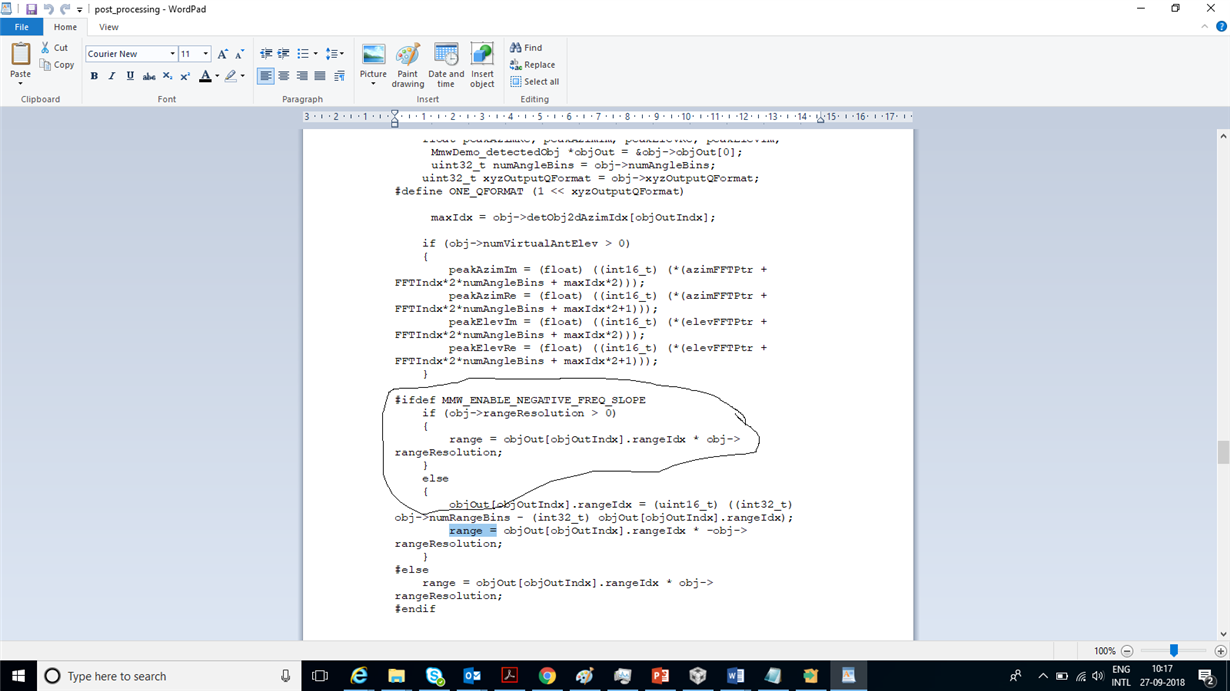
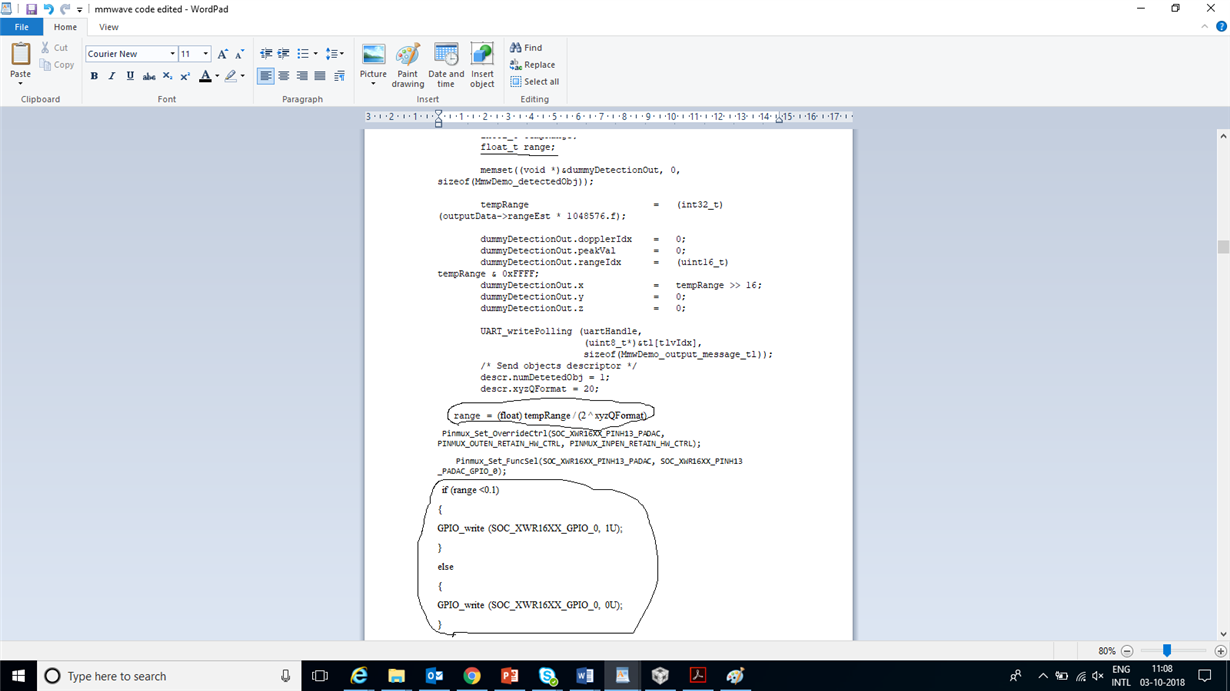
My application is like: I want to detect an object which is at a distance of few cm from the mmWave radar. I want to compare the range of this detected object and if it is less than some threshold (I will decide the threshold), one GPOI pin should be made high.
Please help me with any demo where do I need to modify to get this done.
Went through some lab examples, but not able to understand complete code.
Regrads
Karthik S