Other Parts Discussed in Thread: AWR1843, IWR1642
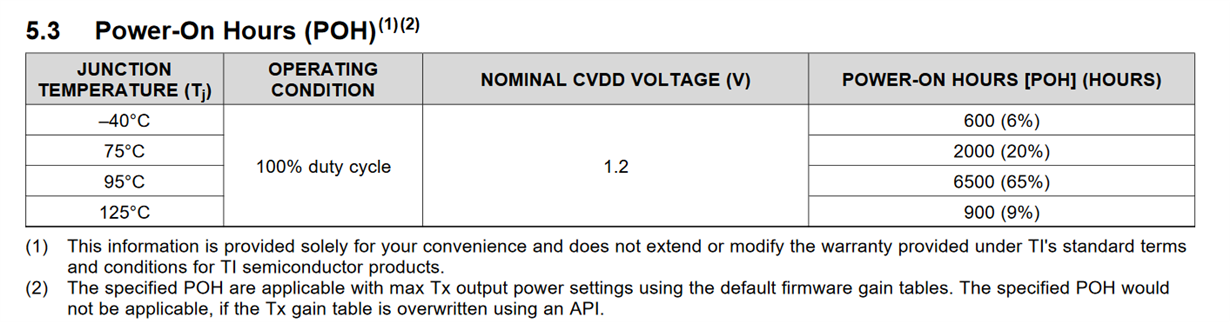
The AWR2243 and AWR1843 datasheets both specify POH as the following:
1. Is 100% duty cycle defined as continuous-wave transmission (i.e. no chirp idle time)?
2. What kind of POH can we expect at 50% duty cycle for both AWR2243 and AWR1843 (accounting for chirp idle time)?
3. Is it correct that the IC has lower lifetime at 75C Tj compared to 95C Tj?
4. What is the degradation criteria that limits POH? Will the chip still function with degraded performance (e.g. SNR, TX power, etc)?
5. For comparison, IWR1642 specifies 50% duty cycle POH as the following (100,000 hours at 50% duty cycle, 85C Tj). Is this performance representative of other TI radar sensors with the same 45nm RFCMOS technology?
Thanks,
David