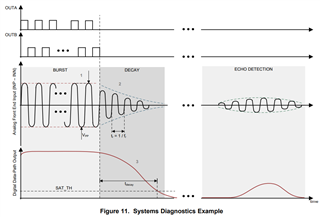
This post talk about Transducer disconnect diagnostics.
I think only monostatic mode can do diagnostics,bi-static mode can not.
Is this right?
I use bi-static mode, i do diagnostics when there is no object in front of transducer,the result is wrong.
So when use bi-static mode,we can not do diagnostics if no obstacle.