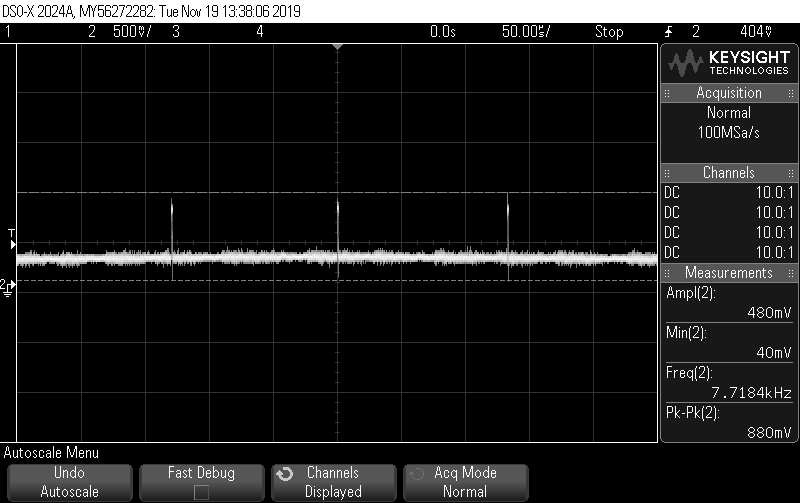
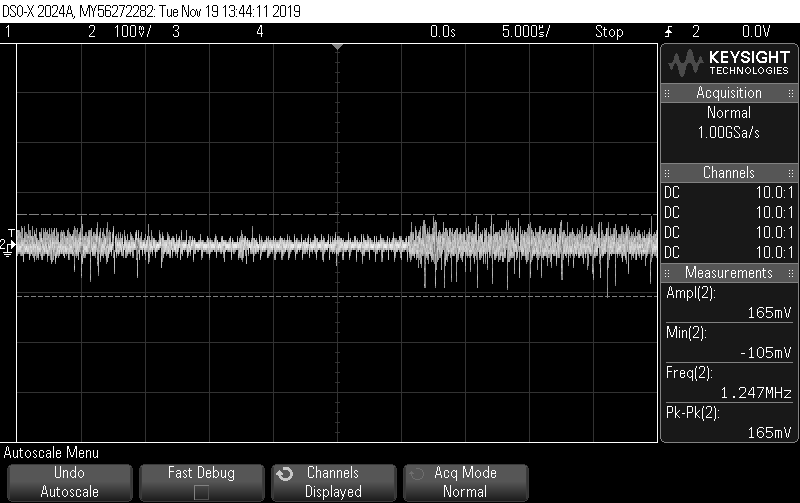
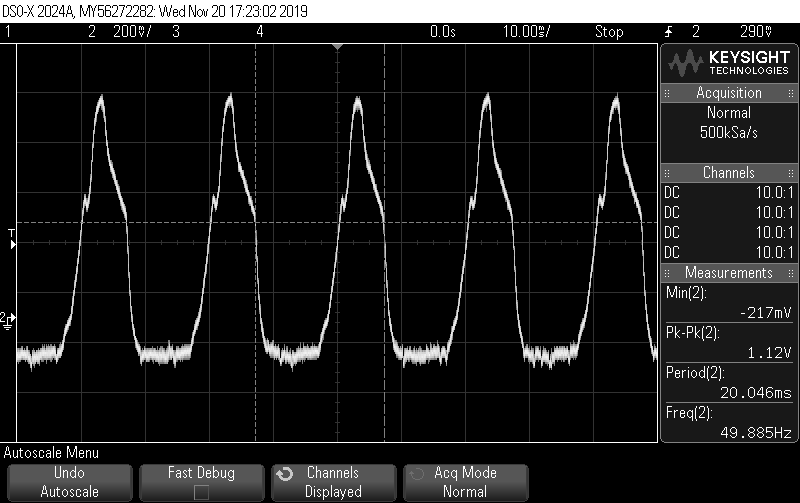
Other Parts Discussed in Thread: EK-TM4C1294XL, TM4C1290NCPDT, , EK-TM4C129EXL
Tool/software: Code Composer Studio
Experience Level: Beginner
Trying to establish communication between ADC and controller via SPI.
Data sheet of the ADC - https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/AD7177-2.pdf
As per the data sheet, the command should be given to Communications register and its given that the best way to check if both the devices are communicating is by reading the ID Register ( Reference: Pg- 49,55)
According to that, I'm expecting to read 0x4FDX (Please correct me I'm wrong)
But I'm reading random values like : "128", "0", "255".
(Tried ways like using GPIO Interuppt, changing the filter configuration etc)
Struck here for over a week now. Not able to understand where I'm going wrong. Any help so as how I move forward is highly appreciated. Thanks!
Following is the source code:
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "driverlib/ssi.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/uart.h"
#include "utils/uartstdio.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "inc/hw_ints.h"
#include "driverlib/adc.h"
#include "driverlib/interrupt.h"
#include "driverlib/rom.h"
#include "driverlib/rom_map.h"
#include "driverlib/fpu.h"
#include "driverlib/debug.h"
#include "drivers/pinout.h"
//*****************************************************************************
//
//! \addtogroup ssi_examples_list
//! <h1>SPI Master (spi_master)</h1>
//!
//! This example shows how to configure the SSI0 as SPI Master. The code will
//! send three characters on the master Tx then polls the receive FIFO until
//! 3 characters are received on the master Rx.
//!
//! This example uses the following peripherals and I/O signals. You must
//! review these and change as needed for your own board:
//! - SSI0 peripheral
//! - GPIO Port A peripheral (for SSI0 pins)
//! - SSI0Clk - PA2
//! - SSI0Fss - PA3 (Tried connecting it to ground as well)
//! - SSI0Rx - PA4
//! - SSI0Tx - PA5
//!
//! The following UART signals are configured only for displaying console
//! messages for this example. These are not required for operation of SSI0.
//! - UART0 peripheral
//! - GPIO Port A peripheral (for UART0 pins)
//! - UART0RX - PA0
//! - UART0TX - PA1
//!
//! This example uses the following interrupt handlers. To use this example
//! in your own application you must add these interrupt handlers to your
//! vector table.
//! - None.
//
//*****************************************************************************
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Number of bytes to send and receive.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#define NUM_SSI_DATA 4
uint32_t g_ui32SysClock;
uint32_t pui32DataRx[2];
uint32_t pui32DataRx_1[NUM_SSI_DATA];
uint32_t pui32DataTx_1[NUM_SSI_DATA];
uint32_t ui32Index;
uint32_t *temp;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This function sets up UART0 to be used for a console to display information
// as the example is running.
//
//*****************************************************************************
//void IntSR();
void ConfigureUART(void)
{
//
// Enable the GPIO Peripheral used by the UART.
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
//
// Enable UART0
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART0);
//
// Configure GPIO Pins for UART mode.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA0_U0RX);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA1_U0TX);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
//
// Initialize the UART for console I/O.
//
UARTStdioConfig(0, 115200, g_ui32SysClock);
UARTprintf("UART configured successfully\n");
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Configure SSI0 in master Freescale (SPI) mode. This example will send out
// 3 bytes of data, then wait for 3 bytes of data to come in. This will all be
// done using the polling method.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
main(void)
{
ConfigureUART();
/*
#if defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA0) || \
defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA1) || \
defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA2)
uint32_t ui32SysClock;
#endif
*/
g_ui32SysClock = MAP_SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ |
SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_USE_PLL |
SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_480), 120000000);//Sets the clock Frequency
// PinoutSet(false, false);//enables the GPIO modules and configures the device pins for standard usages
// Display the setup on the console.
// UARTprintf("SSI ->\n");
// UARTprintf(" Mode: SPI\n");
// UARTprintf(" Data: 8-bit\n\n");
//
// The SSI0 peripheral must be enabled for use.
//
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_SSI0);
//
// For this example SSI0 is used with PortA[5:2]. The actual port and pins
// used may be different on your part, consult the data sheet for more
// information. GPIO port A needs to be enabled so these pins can be used.
// TODO: change this to whichever GPIO port you are using.
//
// SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
//
// Configure the pin muxing for SSI0 functions on port A2, A3, A4, and A5.
// This step is not necessary if your part does not support pin muxing.
// TODO: change this to select the port/pin you are using.
//
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA2_SSI0CLK);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA3_SSI0FSS);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA5_SSI0XDAT1);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA4_SSI0XDAT0);
// //GPIOIntRegisterPin(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3, ISR);
// GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3);
// GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE,GPIO_PIN_3, 0);
//GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2);
//
// Configure the GPIO settings for the SSI pins. This function also gives
// control of these pins to the SSI hardware. Consult the data sheet to
// see which functions are allocated per pin.
// The pins are assigned as follows:
// PA5 - SSI0Tx
// PA4 - SSI0Rx
// PA3 - SSI0Fss
// PA2 - SSI0CLK
// TODO: change this to select the port/pin you are using.
//
GPIOPinTypeSSI(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5 | GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_3 |
GPIO_PIN_2);
//
// Configure and enable the SSI port for SPI master mode. Use SSI0,
// system clock supply, idle clock level low and active low clock in
// freescale SPI mode, master mode, 1MHz SSI frequency, and 8-bit data.
// For SPI mode, you can set the polarity of the SSI clock when the SSI
// unit is idle. You can also configure what clock edge you want to
// capture data on. Please reference the datasheet for more information on
// the different SPI modes.
//
#if defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA0) || \
defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA1) || \
defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA2)
SSIConfigSetExpClk(SSI0_BASE, g_ui32SysClock, SSI_FRF_MOTO_MODE_1,
SSI_MODE_MASTER, 300000, 8);
#else
SSIConfigSetExpClk(SSI0_BASE,g_ui32SysClock , SSI_FRF_MOTO_MODE_1,
SSI_MODE_MASTER, 300000, 8);
#endif
//UARTprintf("Test print \n");
//
// Enable the SSI0 module.
//
//SSIAdvModeSet(SSI0_BASE, SSI_ADV_MODE_QUAD_WRITE);
SSIAdvModeSet(SSI0_BASE, SSI_ADV_MODE_READ_WRITE);
SSIEnable(SSI0_BASE);
SSIDataPut(SSI0_BASE,0x47);//Command word To read ID register
while(SSIDataGetNonBlocking(SSI0_BASE, &pui32DataRx[0]))
{
}
// SSIDataPut(SSI0_BASE,0x8274);
//
//ox29 -> Fliter Config 1
//Filter - Sinc3 -> Bit word= 1000001001101000 = 0x8268
//Filter - Sinc3 -> Bit word= 1000001001110100 =
int a=1;
SSIDataPut(SSI0_BASE,0x0047);
while(SSIBusy(SSI0_BASE))
{
}
// for(ui32Index = 0; ui32Index < 2; ui32Index++)
// {
//
// //
// // Receive the data using the "blocking" Get function. This function
// // will wait until there is data in the receive FIFO before returning.
// //
// SSIDataGet(SSI0_BASE, &pui32DataRx[ui32Index]);
// //UARTprintf("Test print\n");
// //
// // Since we are using 8-bit data, mask off the MSB.
// //
// pui32DataRx[ui32Index] &= 0x000000FF;
//
// //
// // Display the data that SSI0 received.
// //
// // UARTprintf("Received = ");
// // UARTprintf("'%d' ", pui32DataRx[ui32Index]);
// while(SSIBusy(SSI0_BASE))
// {
// }
//
// }
// while(SSIBusy(SSI0_BASE))
// {
// }
//
// Read any residual data from the SSI port. This makes sure the receive
// FIFOs are empty, so we don't read any unwanted junk. This is done here
// because the SPI SSI mode is full-duplex, which allows you to send and
// receive at the same time. The SSIDataGetNonBlocking function returns
// "true" when data was returned, and "false" when no data was returned.
// The "non-blocking" function checks if there is any data in the receive
// FIFO and does not "hang" if there isn't.
//
// GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0);
// GPIOIntTypeSet(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0, GPIO_FALLING_EDGE);
// GPIOIntEnable(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0);
// IntEnable(INT_GPIOP0);
// GPIOIntTypeSet(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4, GPIO_FALLING_EDGE);
// GPIOIntEnable(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4);
// IntEnable(INT_GPIOA);
//IntTrigger(INT_GPIOP0);
//UARTprintf("Interrupt configured successfully\n");
//
// Display indication that the SSI is transmitting data.
//
//UARTprintf("'%d' ", *temp);
//UARTprintf("Sent:\n ");
//SSIDataGet(SSI0_BASE, &pui32DataRx[ui32Index]);
//
// Wait until SSI0 is done transferring all the data in the transmit FIFO.
//
//
// Display indication that the SSI is receiving data.
//
// UARTprintf("\nInterrupt not occurred\n ");
//
// Receive 3 bytes of data.
//
for(ui32Index = 0; ui32Index < NUM_SSI_DATA; ui32Index++)
{
//
// Receive the data using the "blocking" Get function. This function
// will wait until there is data in the receive FIFO before returning.
//
SSIDataGet(SSI0_BASE, &pui32DataRx[ui32Index]);
//
// Since we are using 8-bit data, mask off the MSB.
//
pui32DataRx[ui32Index] &= 0x000000FF;
//
// Display the data that SSI0 received.
//
UARTprintf("'%d' ", pui32DataRx[ui32Index]);
while(SSIBusy(SSI0_BASE))
{
}
}
while(1)
{
//UARTprintf("Idle state\n");
}
//
// Return no errors
//
//return(0);*/
}
/*
void ISR()
{
GPIOIntClear(GPIO_PORTA_BASE,GPIO_PIN_4);
//UARTprintf("Interrupt Occurred\n");
//SSIDataGet(SSI0_BASE, &pui32DataRx[ui32Index]);
// while(SSIDataGetNonBlocking(SSI0_BASE, &pui32DataRx_1[0]))
// {
// }
// SSIDataPut(SSI0_BASE,0x00);
// while(SSIBusy(SSI0_BASE))
// {
// }
SSIDataPut(SSI0_BASE,0x44);
while(SSIBusy(SSI0_BASE))
{
}
for(ui32Index = 0; ui32Index < NUM_SSI_DATA; ui32Index++)
{
//
// Receive the data using the "blocking" Get function. This function
// will wait until there is data in the receive FIFO before returning.
//
SSIDataGet(SSI0_BASE, &pui32DataRx_1[ui32Index]);
//UARTprintf("Test print\n");
//
// Since we are using 8-bit data, mask off the MSB.
//
pui32DataRx_1[ui32Index] &= 0x000000FF;
//
// Display the data that SSI0 received.
//
// UARTprintf("Received = ");
// UARTprintf("'%d' ", pui32DataRx[ui32Index]);
while(SSIBusy(SSI0_BASE))
{
}
}
}
*/