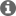Other Parts Discussed in Thread: SIMPLELINK-CC13XX-CC26XX-SDK, SYSCONFIG
Hello,
I'm experiencing an issue very similar to the following link but there was no response in this link: https://e2e.ti.com/support/wireless-connectivity/sub-1-ghz-group/sub-1-ghz/f/sub-1-ghz-forum/989368/cc1312r-cc1312-to-cc1310-spi-transfer-issue/3662432?tisearch=e2e-sitesearch&keymatch=SPI%2525252520transfer%2525252520preappends%2525252520byte#3662432
I have the SPI slave setup as:
spiParams.transferMode = SPI_MODE_CALLBACK;
spiParams.transferTimeout = (uint32_t)SPI_WAIT_FOREVER;
spiParams.transferCallbackFxn = (SPI_CallbackFxn)FSL_SPICallback;
spiParams.mode = SPI_SLAVE;
spiParams.bitRate = 4000000;
spiParams.dataSize = 8;
spiParams.frameFormat = SPI_POL0_PHA1;
spiParams.custom = NULL;
I have the tx and rx buffers sized at 262 bytes.
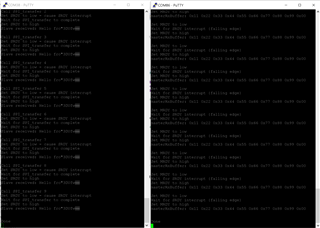
When I call SPI_Transfer, the tx buffer is set as 0xB1 0x00 0x01 0x27 0xE0 0x00 0x40 0xBF with the rest filled with 0x00
However, on the master side, I receive 0x00 0xB1 0x00 0x01 0x27 0xE0 0x00 0x40 0xBF
The master is clocking 263 bytes when this happens. If I set the master to clock 262 bytes, then the master receives the correct data with no pre-appended 0x00 (0xB1 0x00 0x01 0x27 0xE0 0x00 0x40 0xBF 0x00 0x00). The master is configured for the same bit rate and frame format.
Shouldn't the slave spi driver be able to handle any amount of clock cycles from the master?
Thanks,
Dawn