Other Parts Discussed in Thread: SYSBIOS, SIMPLELINK-CC13XX-CC26XX-SDK
I have followed the instructions on TI-RTOS Basics for the board, starting from the "hello"-example. The contents of "hello.c" was replaced. In "hello.cfg", the entire ROM block was removed, BIOS logs enabled, and the 3 lines with loggingSetup was added at the end.
Here is the "hello.cfg" file content:
/*
* Copyright (c) 2015-2021, Texas Instruments Incorporated
* All rights reserved.
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
* are met:
*
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
*
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
* documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
*
* * Neither the name of Texas Instruments Incorporated nor the names of
* its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
* AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
* THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
* PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR
* CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL,
* EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
* PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS;
* OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY,
* WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR
* OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE,
* EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*/
/* ================ Boot configuration ================ */
var Boot = xdc.useModule('ti.sysbios.family.arm.cc26xx.Boot');
/*
* This module contains family specific Boot APIs and configuration settings.
* See the SYS/BIOS API guide for more information.
*/
/* ================ Clock configuration ================ */
var Clock = xdc.useModule('ti.sysbios.knl.Clock');
/*
* When using Power and calibrateRCOSC is set to true, this should be set to 10.
* The timer used by the Clock module supports TickMode_DYNAMIC. This enables us
* to set the tick period to 10 us without generating the overhead of additional
* interrupts.
*
* Note: The calibrateRCOSC parameter is set within the Power configuration
* structure in the "Board.c" file.
*/
Clock.tickPeriod = 10;
/* ================ Defaults (module) configuration ================ */
var Defaults = xdc.useModule('xdc.runtime.Defaults');
/*
* A flag to allow module names to be loaded on the target. Module name
* strings are placed in the .const section for debugging purposes.
*
* Pick one:
* - true (default)
* Setting this parameter to true will include name strings in the .const
* section so that Errors and Asserts are easier to debug.
* - false
* Setting this parameter to false will reduce footprint in the .const
* section. As a result, Error and Assert messages will contain an
* "unknown module" prefix instead of the actual module name.
*
* When using BIOS in ROM:
* This option must be set to false.
*/
//Defaults.common$.namedModule = true;
Defaults.common$.namedModule = false;
/* ================ Error configuration ================ */
var Error = xdc.useModule('xdc.runtime.Error');
/*
* This function is called to handle all raised errors, but unlike
* Error.raiseHook, this function is responsible for completely handling the
* error with an appropriately initialized Error_Block.
*
* Pick one:
* - Error.policyDefault (default)
* Calls Error.raiseHook with an initialized Error_Block structure and logs
* the error using the module's logger.
* - Error.policySpin
* Simple alternative that traps on a while(1) loop for minimized target
* footprint.
* Using Error.policySpin, the Error.raiseHook will NOT called.
*/
//Error.policyFxn = Error.policyDefault;
Error.policyFxn = Error.policySpin;
/*
* If Error.policyFxn is set to Error.policyDefault, this function is called
* whenever an error is raised by the Error module.
*
* Pick one:
* - Error.print (default)
* Errors are formatted and output via System_printf() for easier
* debugging.
* - null
* Errors are not formatted or logged. This option reduces code footprint.
* - non-null function
* Errors invoke custom user function. See the Error module documentation
* for more details.
*/
//Error.raiseHook = Error.print;
Error.raiseHook = null;
//Error.raiseHook = "&myErrorFxn";
/*
* If Error.policyFxn is set to Error.policyDefault, this option applies to the
* maximum number of times the Error.raiseHook function can be recursively
* invoked. This option limits the possibility of an infinite recursion that
* could lead to a stack overflow.
* The default value is 16.
*/
Error.maxDepth = 2;
/* ================ Hwi configuration ================ */
var halHwi = xdc.useModule('ti.sysbios.hal.Hwi');
var m3Hwi = xdc.useModule('ti.sysbios.family.arm.m3.Hwi');
/*
* Checks for Hwi (system) stack overruns while in the Idle loop.
*
* Pick one:
* - true (default)
* Checks the top word for system stack overflows during the idle loop and
* raises an Error if one is detected.
* - false
* Disabling the runtime check improves runtime performance and yields a
* reduced flash footprint.
*/
//halHwi.checkStackFlag = true;
halHwi.checkStackFlag = false;
/*
* The following options alter the system's behavior when a hardware exception
* is detected.
*
* Pick one:
* - Hwi.enableException = true
* This option causes the default m3Hwi.excHandlerFunc function to fully
* decode an exception and dump the registers to the system console.
* This option raises errors in the Error module and displays the
* exception in ROV.
* - Hwi.enableException = false
* This option reduces code footprint by not decoding or printing the
* exception to the system console.
* It however still raises errors in the Error module and displays the
* exception in ROV.
* - Hwi.excHandlerFunc = null
* This is the most aggressive option for code footprint savings; but it
* can difficult to debug exceptions. It reduces flash footprint by
* plugging in a default while(1) trap when exception occur. This option
* does not raise an error with the Error module.
*/
//m3Hwi.enableException = true;
//m3Hwi.enableException = false;
m3Hwi.excHandlerFunc = null;
/*
* Enable hardware exception generation when dividing by zero.
*
* Pick one:
* - 0 (default)
* Disables hardware exceptions when dividing by zero
* - 1
* Enables hardware exceptions when dividing by zero
*/
m3Hwi.nvicCCR.DIV_0_TRP = 0;
//m3Hwi.nvicCCR.DIV_0_TRP = 1;
/*
* Enable hardware exception generation for invalid data alignment.
*
* Pick one:
* - 0 (default)
* Disables hardware exceptions for data alignment
* - 1
* Enables hardware exceptions for data alignment
*/
m3Hwi.nvicCCR.UNALIGN_TRP = 0;
//m3Hwi.nvicCCR.UNALIGN_TRP = 1;
/*
* Assign an address for the reset vector.
*
* Default is 0x0, which is the start of Flash. Ordinarily this setting should
* not be changed.
*/
m3Hwi.resetVectorAddress = 0x0;
/*
* Assign an address for the vector table in RAM.
*
* The default is the start of RAM. This table is placed in RAM so interrupts
* can be added at runtime.
*
* Note: To change, verify address in the device specific datasheets'
* memory map.
*/
m3Hwi.vectorTableAddress = 0x20000000;
/* ================ Idle configuration ================ */
var Idle = xdc.useModule('ti.sysbios.knl.Idle');
/*
* The Idle module is used to specify a list of functions to be called when no
* other tasks are running in the system.
*
* Functions added here will be run continuously within the idle task.
*
* Function signature:
* Void func(Void);
*/
//Idle.addFunc("&myIdleFunc");
Idle.addFunc('&Power_idleFunc'); /* add the Power module's idle function */
/* ================ Kernel (SYS/BIOS) configuration ================ */
var BIOS = xdc.useModule('ti.sysbios.BIOS');
/*
* Enable asserts in the BIOS library.
*
* Pick one:
* - true (default)
* Enables asserts for debugging purposes.
* - false
* Disables asserts for a reduced code footprint and better performance.
*
* When using BIOS in ROM:
* This option must be set to false.
*/
//BIOS.assertsEnabled = true;
BIOS.assertsEnabled = false;
/*
* Specify default CPU Frequency.
*/
BIOS.cpuFreq.lo = 48000000;
/*
* A flag to determine if xdc.runtime sources are to be included in a custom
* built BIOS library.
*
* Pick one:
* - false (default)
* The pre-built xdc.runtime library is provided by the respective target
* used to build the application.
* - true
* xdc.runtime library sources are to be included in the custom BIOS
* library. This option yields the most efficient library in both code
* footprint and runtime performance.
*/
//BIOS.includeXdcRuntime = false;
BIOS.includeXdcRuntime = true;
/*
* The SYS/BIOS runtime is provided in the form of a library that is linked
* with the application. Several forms of this library are provided with the
* SYS/BIOS product.
*
* Pick one:
* - BIOS.LibType_Custom
* Custom built library that is highly optimized for code footprint and
* runtime performance.
* - BIOS.LibType_Debug
* Custom built library that is non-optimized that can be used to
* single-step through APIs with a debugger.
*
*/
BIOS.libType = BIOS.LibType_Custom;
//BIOS.libType = BIOS.LibType_Debug;
/*
* Runtime instance creation enable flag.
*
* Pick one:
* - true (default)
* Allows Mod_create() and Mod_delete() to be called at runtime which
* requires a default heap for dynamic memory allocation.
* - false
* Reduces code footprint by disallowing Mod_create() and Mod_delete() to
* be called at runtime. Object instances are constructed via
* Mod_construct() and destructed via Mod_destruct().
*
* When using BIOS in ROM:
* This option must be set to true.
*/
BIOS.runtimeCreatesEnabled = true;
//BIOS.runtimeCreatesEnabled = false;
/*
* Enable logs in the BIOS library.
*
* Pick one:
* - true (default)
* Enables logs for debugging purposes.
* - false
* Disables logging for reduced code footprint and improved runtime
* performance.
*
* When using BIOS in ROM:
* This option must be set to false.
*/
BIOS.logsEnabled = true;
//BIOS.logsEnabled = false;
/* ================ Memory configuration ================ */
var Memory = xdc.useModule('xdc.runtime.Memory');
/*
* The Memory module itself simply provides a common interface for any
* variety of system and application specific memory management policies
* implemented by the IHeap modules(Ex. HeapMem, HeapBuf).
*/
/*
* Use HeapMem primary heap instance to use linker-defined memory region
*/
var HeapMem = xdc.useModule('ti.sysbios.heaps.HeapMem');
HeapMem.primaryHeapBaseAddr = "&__primary_heap_start__";
HeapMem.primaryHeapEndAddr = "&__primary_heap_end__";
var heapMemParams = new HeapMem.Params();
heapMemParams.usePrimaryHeap = true;
Program.global.heap0 = HeapMem.create(heapMemParams);
Memory.defaultHeapInstance = Program.global.heap0;
/* ================ Program configuration ================ */
/*
* Program.stack must be set to 0 to allow the setting
* of the system stack size to be determined in the example's
* linker command file.
*/
Program.stack = 0;
/*
* Uncomment to enable Semihosting for GNU targets to print to the CCS console.
* Please read the following TIRTOS Wiki page for more information on Semihosting:
* http://processors.wiki.ti.com/index.php/TI-RTOS_Examples_SemiHosting
*/
if (Program.build.target.$name.match(/gnu/)) {
//var SemiHost = xdc.useModule('ti.sysbios.rts.gnu.SemiHostSupport');
}
/* ================ ROM configuration ================ */
/*
* To use BIOS in flash, comment out the code block below.
*/
/*
* CC13X1 and CC26X1 devices do not contain ROM; therefore, we do not include
* the ROM module unless needed.
*/
/* ================ Semaphore configuration ================ */
var Semaphore = xdc.useModule('ti.sysbios.knl.Semaphore');
/*
* Enables global support for Task priority pend queuing.
*
* Pick one:
* - true (default)
* This allows pending tasks to be serviced based on their task priority.
* - false
* Pending tasks are services based on first in, first out basis.
*
* When using BIOS in ROM:
* This option must be set to false.
*/
//Semaphore.supportsPriority = true;
Semaphore.supportsPriority = false;
/*
* Allows for the implicit posting of events through the semaphore,
* disable for additional code saving.
*
* Pick one:
* - true
* This allows the Semaphore module to post semaphores and events
* simultaneously.
* - false (default)
* Events must be explicitly posted to unblock tasks.
*
* When using BIOS in ROM:
* This option must be set to false.
*/
//Semaphore.supportsEvents = true;
Semaphore.supportsEvents = false;
/* ================ Swi configuration ================ */
var Swi = xdc.useModule('ti.sysbios.knl.Swi');
/*
* A software interrupt is an object that encapsulates a function to be
* executed and a priority. Software interrupts are prioritized, preempt tasks
* and are preempted by hardware interrupt service routines.
*
* This module is included to allow Swi's in a users' application.
*/
/*
* Reduce the number of swi priorities from the default of 16.
* Decreasing the number of swi priorities yields memory savings.
*/
Swi.numPriorities = 6;
/* ================ System configuration ================ */
var System = xdc.useModule('xdc.runtime.System');
/*
* The Abort handler is called when the system exits abnormally.
*
* Pick one:
* - System.abortStd (default)
* Call the ANSI C Standard 'abort()' to terminate the application.
* - System.abortSpin
* A lightweight abort function that loops indefinitely in a while(1) trap
* function.
* - A custom abort handler
* A user-defined function. See the System module documentation for
* details.
*/
//System.abortFxn = System.abortStd;
System.abortFxn = System.abortSpin;
//System.abortFxn = "&myAbortSystem";
/*
* The Exit handler is called when the system exits normally.
*
* Pick one:
* - System.exitStd (default)
* Call the ANSI C Standard 'exit()' to terminate the application.
* - System.exitSpin
* A lightweight exit function that loops indefinitely in a while(1) trap
* function.
* - A custom exit function
* A user-defined function. See the System module documentation for
* details.
*/
//System.exitFxn = System.exitStd;
System.exitFxn = System.exitSpin;
//System.exitFxn = "&myExitSystem";
/*
* Minimize exit handler array in the System module. The System module includes
* an array of functions that are registered with System_atexit() which is
* called by System_exit(). The default value is 8.
*/
System.maxAtexitHandlers = 2;
/*
* The System.SupportProxy defines a low-level implementation of System
* functions such as System_printf(), System_flush(), etc.
*
* Pick one pair:
* - SysMin
* This module maintains an internal configurable circular buffer that
* stores the output until System_flush() is called.
* The size of the circular buffer is set via SysMin.bufSize.
* - SysCallback
* SysCallback allows for user-defined implementations for System APIs.
* The SysCallback support proxy has a smaller code footprint and can be
* used to supply custom System_printf services.
* The default SysCallback functions point to stub functions. See the
* SysCallback module's documentation.
*/
var SysMin = xdc.useModule('xdc.runtime.SysMin');
SysMin.bufSize = 512;
System.SupportProxy = SysMin;
//var SysCallback = xdc.useModule('xdc.runtime.SysCallback');
//System.SupportProxy = SysCallback;
//SysCallback.abortFxn = "&myUserAbort";
//SysCallback.exitFxn = "&myUserExit";
//SysCallback.flushFxn = "&myUserFlush";
//SysCallback.putchFxn = "&myUserPutch";
//SysCallback.readyFxn = "&myUserReady";
/* ================ Task configuration ================ */
var Task = xdc.useModule('ti.sysbios.knl.Task');
/*
* Check task stacks for overflow conditions.
*
* Pick one:
* - true (default)
* Enables runtime checks for task stack overflow conditions during
* context switching ("from" and "to")
* - false
* Disables runtime checks for task stack overflow conditions.
*
* When using BIOS in ROM:
* This option must be set to false.
*/
//Task.checkStackFlag = true;
Task.checkStackFlag = false;
/*
* Set the default task stack size when creating tasks.
*
* The default is dependent on the device being used. Reducing the default stack
* size yields greater memory savings.
*/
Task.defaultStackSize = 512;
/*
* Enables the idle task.
*
* Pick one:
* - true (default)
* Creates a task with priority of 0 which calls idle hook functions. This
* option must be set to true to gain power savings provided by the Power
* module.
* - false
* No idle task is created. This option consumes less memory as no
* additional default task stack is needed.
* To gain power savings by the Power module without having the idle task,
* add Idle.run as the Task.allBlockedFunc.
*/
Task.enableIdleTask = true;
//Task.enableIdleTask = false;
//Task.allBlockedFunc = Idle.run;
/*
* If Task.enableIdleTask is set to true, this option sets the idle task's
* stack size.
*
* Reducing the idle stack size yields greater memory savings.
*/
Task.idleTaskStackSize = 512;
/*
* Reduce the number of task priorities.
* The default is 16.
* Decreasing the number of task priorities yield memory savings.
*/
Task.numPriorities = 4;
/* ================ Text configuration ================ */
var Text = xdc.useModule('xdc.runtime.Text');
/*
* These strings are placed in the .const section. Setting this parameter to
* false will save space in the .const section. Error, Assert and Log messages
* will print raw ids and args instead of a formatted message.
*
* Pick one:
* - true (default)
* This option loads test string into the .const for easier debugging.
* - false
* This option reduces the .const footprint.
*/
//Text.isLoaded = true;
Text.isLoaded = false;
/* ================ Types configuration ================ */
var Types = xdc.useModule('xdc.runtime.Types');
/*
* This module defines basic constants and types used throughout the
* xdc.runtime package.
*/
/* ================ Application Specific Instances ================ */
var LoggingSetup = xdc.useModule('ti.uia.sysbios.LoggingSetup');
LoggingSetup.sysbiosLoggerSize = 1024;
LoggingSetup.loadLogging = false;
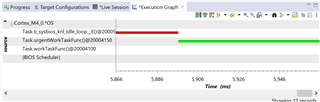
When I run the code and try to start the Execution Analysis Tool, nothing happens. I have to start the tool by clicking on the Task Profile Tool, and then select the Execution Graph instead. But it still only produces a blank/empty graph. I can't see the core in the tool, but it does show up in the Live Session. Hope you can help me with this