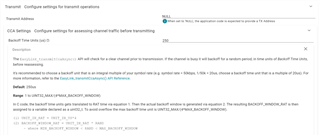
Other Parts Discussed in Thread: SYSCONFIG
…. So using the stock dmm for Sub1GHz + BLE project; I see it calling EasyLink_transmit and EasyLink_asyncReceive for the Sub 1GHz stuff. All good, but when I look in the .syscfg there’s this section in Easylink with the CCA parameters; that is, the Listen-Before-Talk parameters of the Sub 1GHz piece. I am unclear if the CCA parameters are actually used or not; it USED to be that you had to call EasyLink_transmitCcaAsync(); but the fact that those parameters are included coupled with what I think I see happening makes me think they are actually being observed.
So to the real question(s)-
- Are they in fact being used (if I am only calling EasyLink_transmit, not the EasyLink_transmitCcaAsync, and if so,
- Is there a way to turn them off (eg if I put 0’s in some/more of the backoffs or something in the .syscfg would it stop listening?
I am thinking I may need to get to a ‘shout’ mode; eg if I get back’d off too many times in a row then I decide to just talk regardless. Like anything RF, it’s a little hard to say I know exactly what’s happening; but I think I am seeing a case wherein my sensors aren’t talking like they should be in the presence of a ‘loud personality’ (that is, a really noisy environment)
-Dave