Part Number: LAUNCHCC3220MODASF
Tool/software: TI-RTOS
Hello,
On CC3220MODASF Launch Pad "LAUNCHCC3220MODASF",
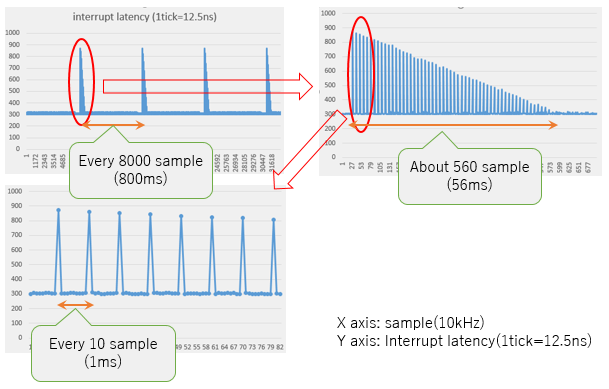
interrupt latency looks like periodically get longer.
Usually, it's approx 3us, but periodically get 10us.
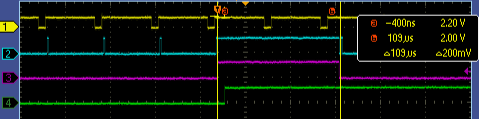
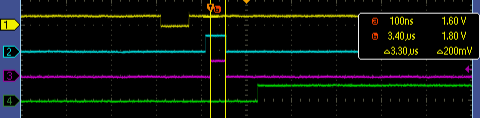
For more details, show the graph below.
This is the result of my sample program.
In my project, CPU must respond within several microseconds.
Therefore this latency is a issue to be solved.
How can I make the latency at around 3us constantly?
Sample program is attached.
#include <stddef.h>
#include <ti/drivers/GPIO.h>
#include <ti/drivers/Timer.h>
#include <ti/sysbios/BIOS.h>
#include "Board.h"
Timer_Handle timerHandle = 0;
Timer_Params timerParams;
unsigned long interruptLatency;
#define RECORD_LENGTH 32768
unsigned long interruptLatencyHistory[RECORD_LENGTH] = {};
unsigned long recordIndex = 0;
void timerCallback(Timer_Handle myHandle)
{
if (timerHandle != 0) { // avoid exception
interruptLatency = Timer_getCount(timerHandle);
if (recordIndex >= RECORD_LENGTH) {
GPIO_write(Board_GPIO_LED0, Board_GPIO_LED_OFF);
while(1); // fin.
}
interruptLatencyHistory[recordIndex++] = interruptLatency;
}
}
void *mainThread(void *arg0)
{
GPIO_init();
GPIO_setConfig(Board_GPIO_LED0, GPIO_CFG_OUT_STD | GPIO_CFG_OUT_LOW);
GPIO_write(Board_GPIO_LED0, Board_GPIO_LED_ON);
Timer_init();
Timer_Params_init(&timerParams);
timerParams.period = 100; // 100us
timerParams.periodUnits = Timer_PERIOD_US;
timerParams.timerMode = Timer_CONTINUOUS_CALLBACK;
timerParams.timerCallback = timerCallback;
timerHandle = Timer_open(Board_TIMER0, &timerParams);
Timer_start(timerHandle);
return (NULL);
}
Sample program usage
1) Import timerled_CC3220SF_LAUNCHXL_tirtos_ccs from SDK 2.10.
2) Replace serial_wifi.c in the project with attached file.
3) Build, load, and run.
4) Then Save Memory array interruptLatencyHistory in order to get latency data.
Tools
CCS8.0.0.00016_win32
simplelink_cc32xx_sdk_2_10_00_04
ti-cgt-arm_18.1.1.LTS (within SDK)
TI-RTOS 6.55.00.07 (within SDK)
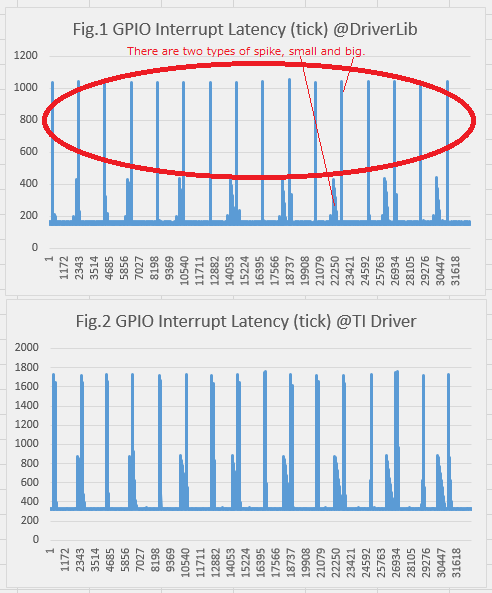
I've tried below on the sample program,
- Change Board_TIMER0 to Board_TIMER1
- Change configuration Debug to Release
- Change base program timerled_CC3220SF_LAUNCHXL_tirtos_ccs to timerled_CC3220SF_LAUNCHXL_tirtos_gcc
- Change base program timerled_CC3220SF_LAUNCHXL_tirtos_ccs to serial_wifi_CC3220SF_LAUNCHXL_tirtos_ccs
- Change tools CCS8.0+SDK2.10+CGT18.1 to CCS7.4+SDK1.60+CGT16.9
The results did not change.
Unfortunately, I'm not familiar with FreeRTOS, so I've not tried yet...
Regards,
Nobuhiro