Hi,
I am trying to build spi slave driver that will receive and process incoming SPI frame (1 byte) and prepare new data to reply in the next SPI frame (when SPI master generate next clk).
For the current implementation I use a RTOS thread and spi in SPI_MODE_CALLBACK. Enclosed you can find a source code.
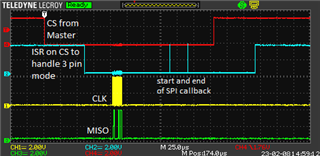
I notice quite a delay in hwi and swi. Total time of reaction and processing is some 150us. But the reaction to hardware event is some multiple of 30us delayed.
I assume that it comes from RTOS.
So the question is quite broad...
* Is there any example of SPI receiving a direct ISR from DMA after transfer is done (and avoid delay of RTOS)?
* How to best minimize a reaction time on spi slave and combine it with another thread doing Radio communication.
Thanks, Ivan