Part Number: OPA657
Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TINA-TI, LMH6629, OPA847
Hi ,
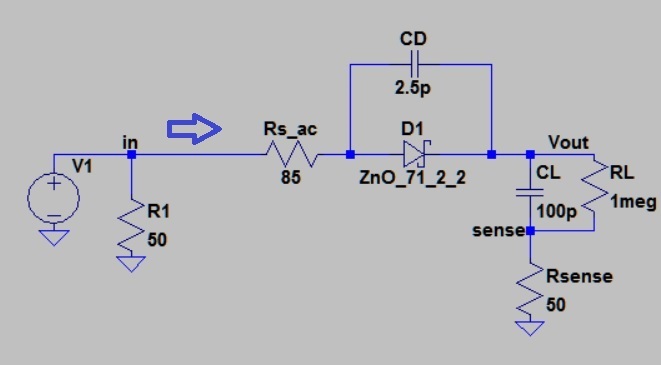
I am trying to measure the input power to my half wave rectifier (HWR) (shown below). R1(50 ohm) is just placed to match impedance and get the desired Vin and I don't care the power spent on it. What I am trying to do is measuring power consumed by the HWR. So I need to measure V_in and I_in without losing the phase information and multiply them in time domain, take average power on MATLAB. My Vin is (4Vp-p 100kHz to 10MHz, sine wave, testing one frequency at a time)
I placed Rsense (50ohm) just to measure the current and got the following V_sense and V_in from my simulations.
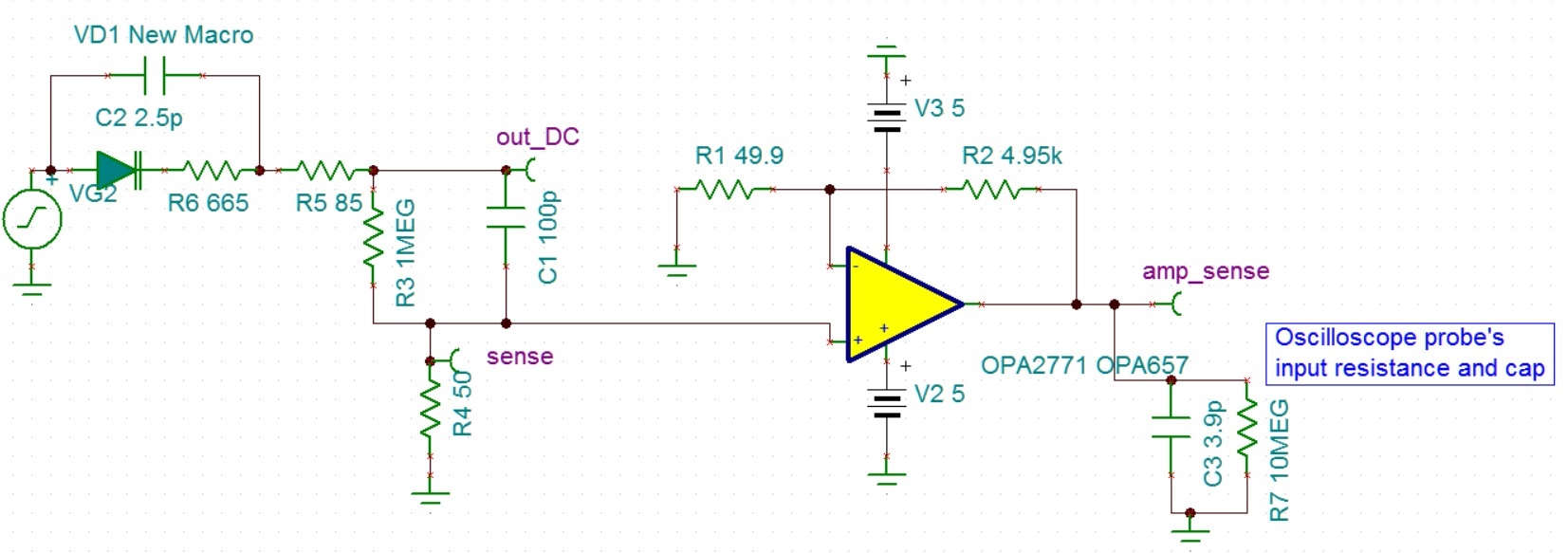
After searching for a high frequency, low input bias current opamp, I found OPA657 as a potential solution and designed the following amplifier.
When I run the simulation on TINA-TI, it works ok at 1 MHz with 100 V/V gain but when I run it with 10 MHz at 100 V/V, I am getting a phase shift. If I reduce my gain to 10 V/V, it works ok even at 10 MHz but I don't want to reduce the input signal to the oscilloscope.
My questions:
- Would you recommend using an opamp other than OPA657?
- Is there a better way to measure the input power ? I am open for suggestions.
Thanks a lot,
Levent