Other Parts Discussed in Thread: AM3359, SYSBIOS, SYSCONFIG
Hi,
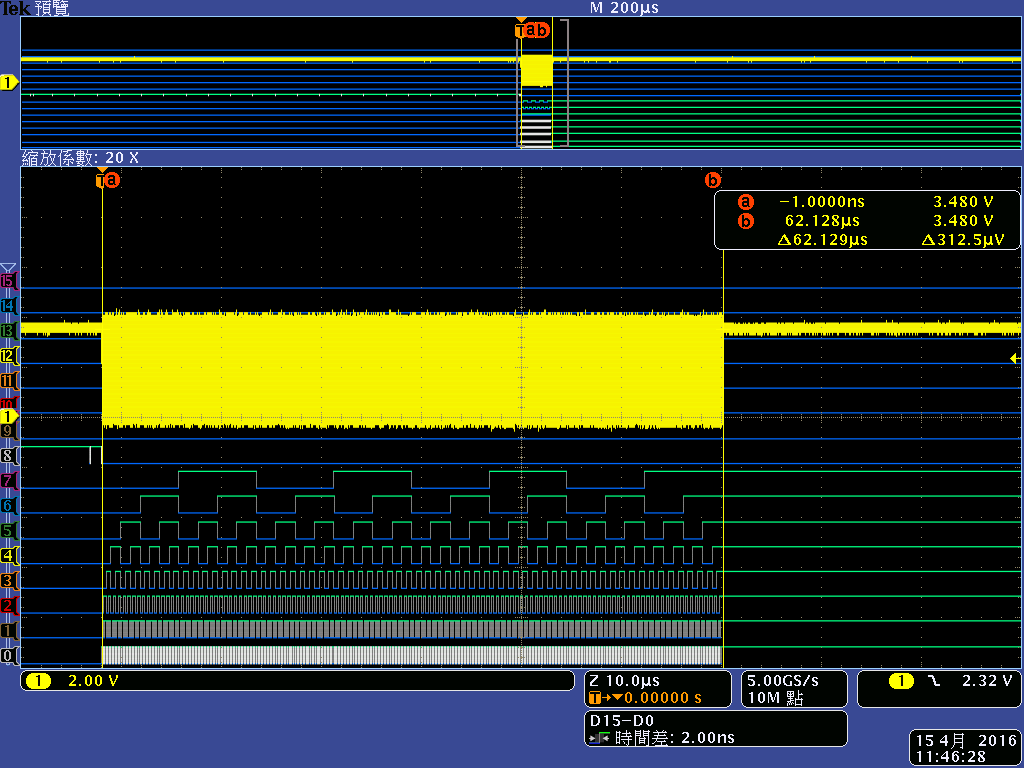
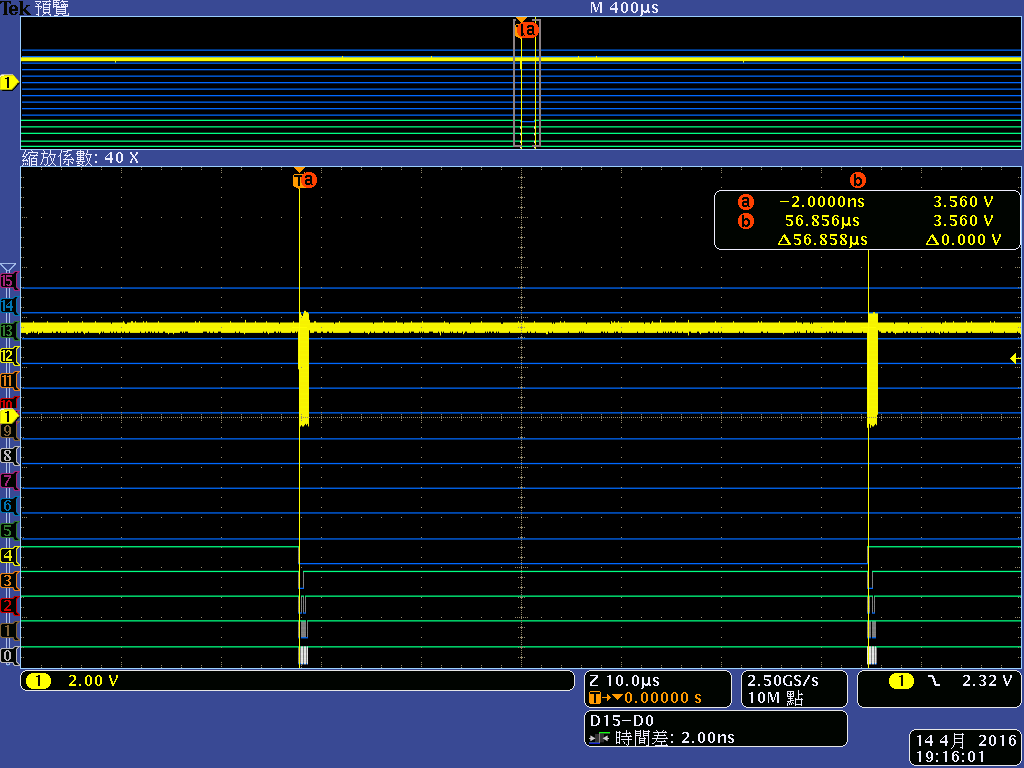
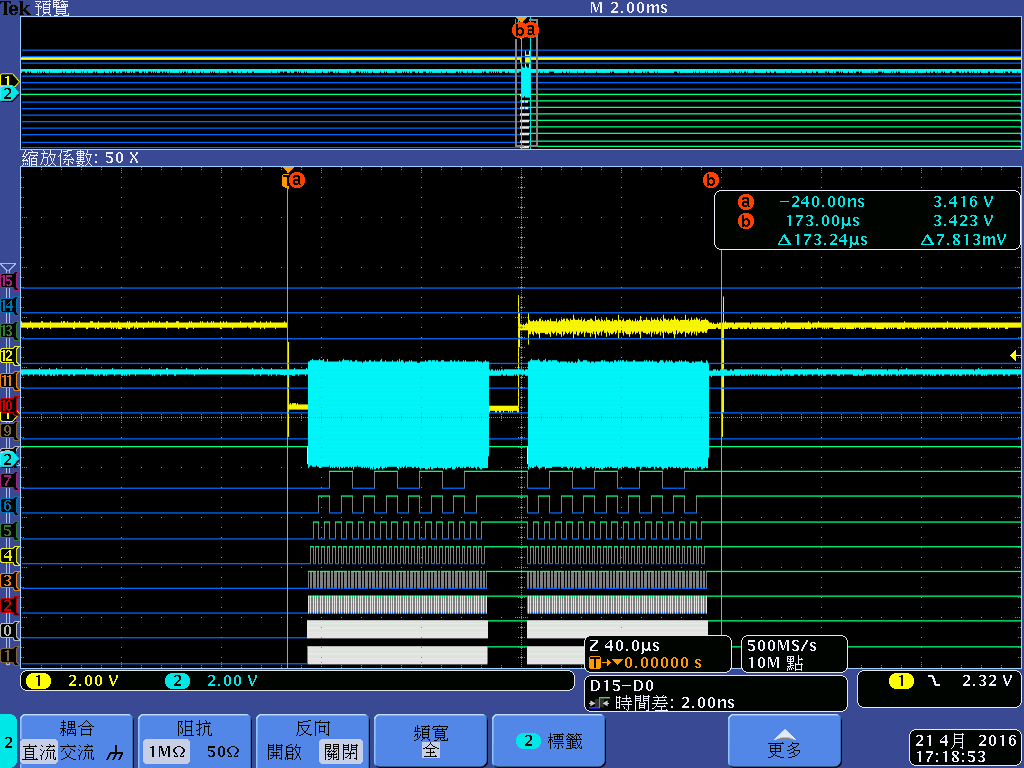
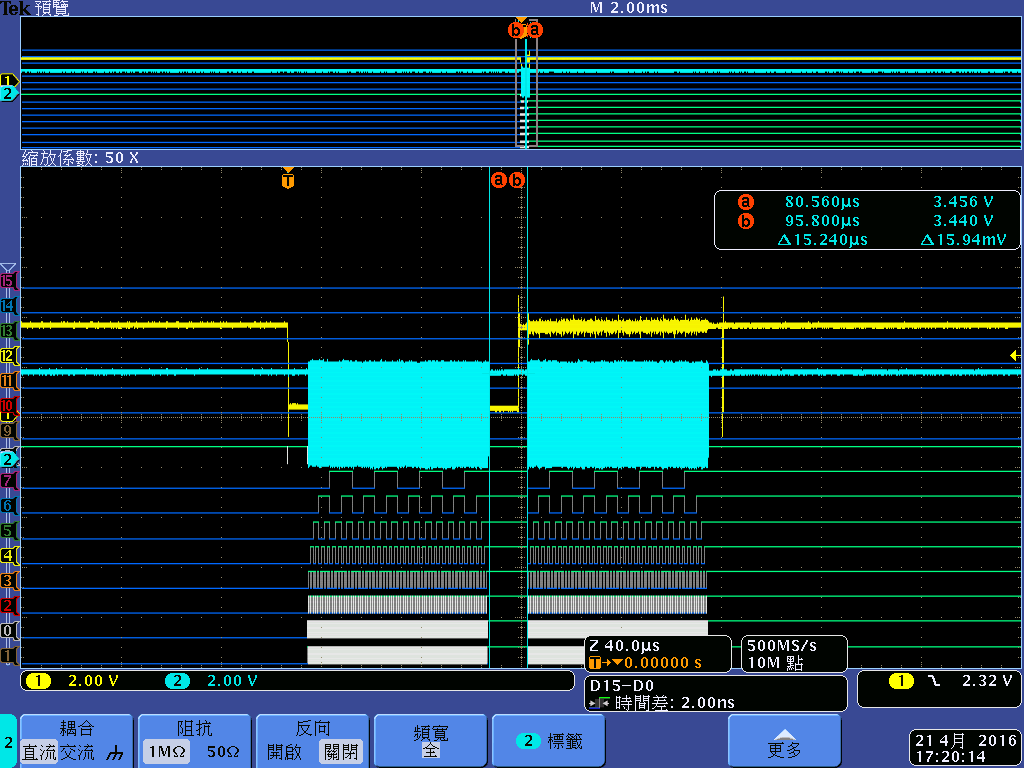
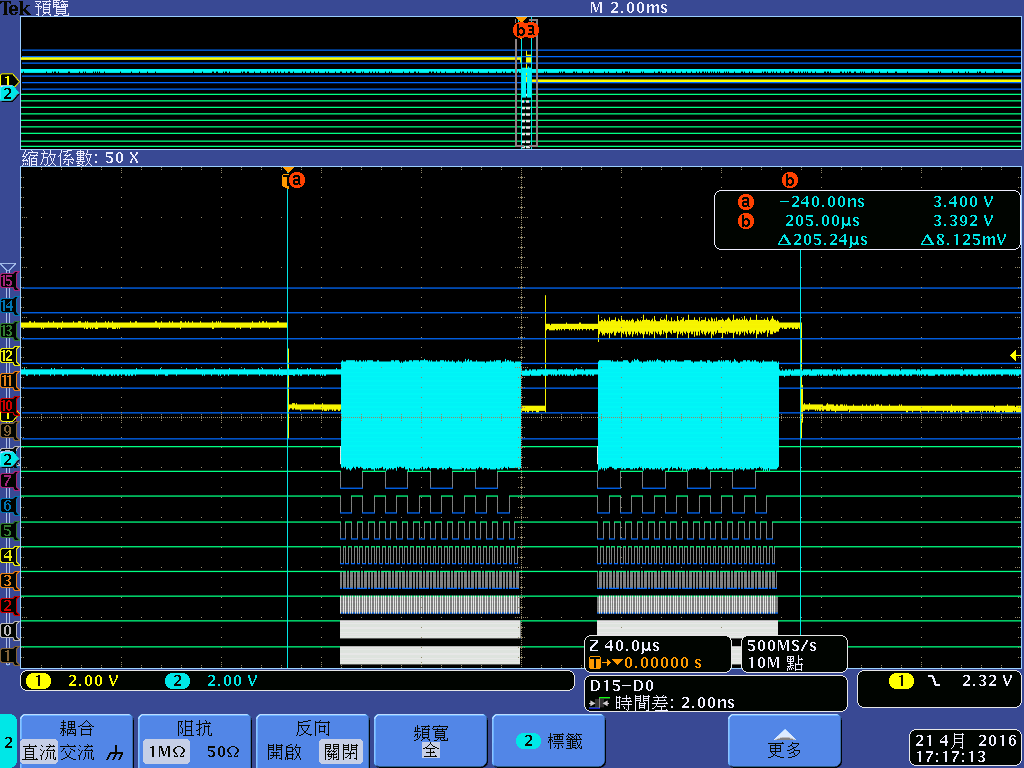
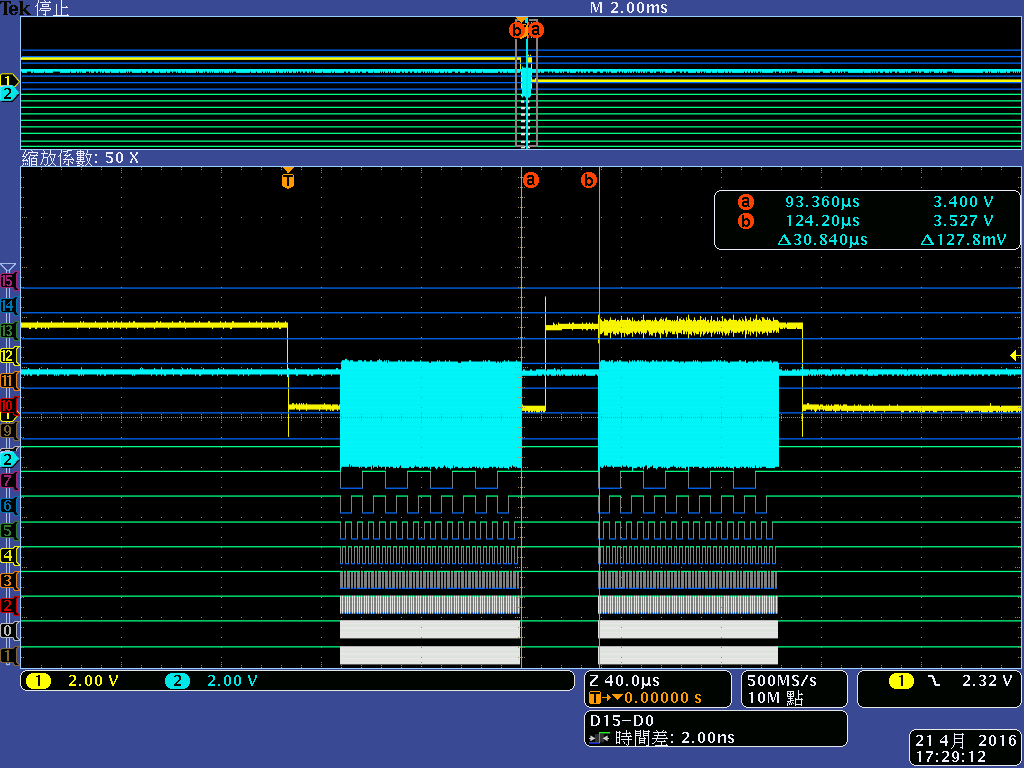
I have connected a CPLD to the AM3359 GPMC interface as an AD muxed device and found that single asynchronous read write access triggered by the CPU is much too slow for our application - we have to read/write about 32 registers within a few microseconds. This is mainly due to a 250 ns delay between the memory accesses, following Wolfgang Muees1 in
"the problem with the GPMC is the internal bus arbitration time. If you use single byte reads, you won't get any further."
As fas as I can see, I have the following options:
- reprogram the cpld making it understand burst accesses and/or
- use EDMA.
Following Thomas Renjith in
I have to use ASM statements to trigger burst lengths of 8 or 16 using the CPU.
My questions are:
- Will the 250 ns delay due to internal bus arbitration time vanish if I use DMA accesses in single asynchronous read/write mode?
- Can the EDMA do burst accesses if I use the right parameterization (maybe EDMA transfer controller default burst size (DBS) = GPMC ATTACHEDDEVICEPAGELENGTH ?
- My TI Code generation tools are not happy with the code examples given by Thomas Renjith for the GCC. Has anyone an example for TI CGTs? In a first quick seach into arm_assembly_language_tools_spnu118m.pdf, arm_c_compiler_spnu151j.pdf and ARM_TMS470R1xUsersGuide_spnu134b.pdf I did not find the right information how to do. The goal is to have (assembler or better C asm inline coded) functions interfacing to C that does the burst r/w accesses. Any tips where to read about?
Thanks,
Frank