Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TCAN4550, MSP430FR6989,
Greetings, I want to connect TCAN4550 with CC1352R1. Is there any driver available.
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
Greetings, I want to connect TCAN4550 with CC1352R1. Is there any driver available.
Hi Joju,
I'm not aware of any dedicated software for this MCU to work with TCAN4550. The drivers in the demo code written for MSP430FR6989 (available on TCAN4550's store page) can be modified to work with this MCU. Once the SPI and external pinout configurations are changed to use corresponding CC1352R1 values, the rest of the functions are general C methods and can be used as shown in the demo.
Let me know if this works and if you have any questions on the demo software.
Regards,
Eric Schott
Sir,
Thank you for the response.
Today we were able to get TCAN4550 into normal mode. (Reason for being in Standby was: the supply to CAN module was under 5V)
Now we cannot see the data in our CAN Bus analyser, which is limited to 1Mbps speed.
In demo code data speed is set for 2Mbps .
Can you guide us to set the NBTP, DBTP and TDCR to set entire communication to 1Mbps. The TCAN4550EVM module has 40Mhz crystal.
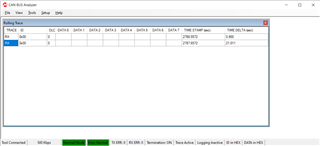
Thanks
Joju John
Hi Joju,
CAN FD can be disabled by setting the cccrConfig.FDOE and cccrConfig.BRSE variables to 0 in the Init_CAN() function in main.c. This will set the device only to use the nominal bit rate (default configured for 500kbps with 40MHz crystal) for all portions of the CAN frame. You may also choose to comment out the TCANDataTiming section as this will not be used with CANFD disabled.
Regards,
Eric Schott
Dear Sir,
Thank you for the support.
We are trying to connect in Normal CAN bus with 500Kbps. The initialization code is shown below:
/*
* Configure the TCAN4550
*/
void Init_CAN(void)
{
uint32_t readValue;
CAN_SPI_Init();
TCAN4x5x_Device_ClearSPIERR(); // Clear any SPI ERR flags that might be set as a result of our pin mux changing during MCU startup
/* Step one attempt to clear all interrupts */
TCAN4x5x_Device_Interrupt_Enable dev_ie = {0}; // Initialize to 0 to all bits are set to 0.
TCAN4x5x_Device_ConfigureInterruptEnable(&dev_ie); // Disable all non-MCAN related interrupts for simplicity
TCAN4x5x_Device_Interrupts dev_ir = {0}; // Setup a new MCAN IR object for easy interrupt checking
TCAN4x5x_Device_ReadInterrupts(&dev_ir); // Request that the struct be updated with current DEVICE (not MCAN) interrupt values
if (dev_ir.PWRON) // If the Power On interrupt flag is set
TCAN4x5x_Device_ClearInterrupts(&dev_ir); // Clear it because if it's not cleared within ~4 minutes, it goes to sleep
/* Configure the CAN bus speeds NBTP & DBTP*/
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_Nominal_Timing_Simple TCANNomTiming = {0}; // 500k arbitration with a 40 MHz crystal ((40E6 / 2) / (32 + 8) = 500E3)
TCANNomTiming.NominalBitRatePrescaler = 2; //2, 1Mk arbitration with a 40 MHz crystal ((40E6 / 1) / (32 + 8) = 1E6)
TCANNomTiming.NominalTqBeforeSamplePoint = 32; //32
TCANNomTiming.NominalTqAfterSamplePoint = 8; //8
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_Data_Timing_Simple TCANDataTiming = {0}; // 2 Mbps CAN FD with a 40 MHz crystal (40E6 / (15 + 5) = 2E6)
TCANDataTiming.DataBitRatePrescaler = 2; // previous data 1, Now 1 Mbps CAN FD with a 40 MHz crystal ((40E6 / 2) / (15 + 5) = 1E6)
TCANDataTiming.DataTqBeforeSamplePoint = 15;
TCANDataTiming.DataTqAfterSamplePoint = 5;
/* Configure the MCAN core settings */
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_CCCR_Config cccrConfig = {0}; // Remember to initialize to 0, or you'll get random garbage!
cccrConfig.FDOE = 0; //1, CAN FD mode enable
cccrConfig.BRSE = 0; //1, CAN FD Bit rate switch enable
/* Configure the default CAN packet filtering settings */
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_Global_Filter_Configuration gfc = {0};
gfc.RRFE = 1; // Reject remote frames (TCAN4x5x doesn't support this)
gfc.RRFS = 1; // Reject remote frames (TCAN4x5x doesn't support this)
gfc.ANFE = TCAN4x5x_GFC_ACCEPT_INTO_RXFIFO0; // Default behavior if incoming message doesn't match a filter is to accept into RXFIO0 for extended ID messages (29 bit IDs)
gfc.ANFS = TCAN4x5x_GFC_ACCEPT_INTO_RXFIFO0; // Default behavior if incoming message doesn't match a filter is to accept into RXFIO0 for standard ID messages (11 bit IDs)
/* ************************************************************************
* In the next configuration block, we will set the MCAN core up to have:
* - 1 SID filter element
* - 1 XID Filter element
* - 5 RX FIFO 0 elements
* - RX FIFO 0 supports data payloads up to 64 bytes
* - RX FIFO 1 and RX Buffer will not have any elements, but we still set their data payload sizes, even though it's not required
* - No TX Event FIFOs
* - 2 Transmit buffers supporting up to 64 bytes of data payload
*/
TCAN4x5x_MRAM_Config MRAMConfiguration = {0};
MRAMConfiguration.SIDNumElements = 1; // Standard ID number of elements, you MUST have a filter written to MRAM for each element defined
MRAMConfiguration.XIDNumElements = 1; // Extended ID number of elements, you MUST have a filter written to MRAM for each element defined
MRAMConfiguration.Rx0NumElements = 5; // RX0 Number of elements
MRAMConfiguration.Rx0ElementSize = MRAM_64_Byte_Data; // RX0 data payload size
MRAMConfiguration.Rx1NumElements = 0; // RX1 number of elements
MRAMConfiguration.Rx1ElementSize = MRAM_64_Byte_Data; // RX1 data payload size
MRAMConfiguration.RxBufNumElements = 0; // RX buffer number of elements
MRAMConfiguration.RxBufElementSize = MRAM_64_Byte_Data; // RX buffer data payload size
MRAMConfiguration.TxEventFIFONumElements = 0; // TX Event FIFO number of elements
MRAMConfiguration.TxBufferNumElements = 2; // TX buffer number of elements
MRAMConfiguration.TxBufferElementSize = MRAM_64_Byte_Data; // TX buffer data payload size
/* Configure the MCAN core with the settings above, the changes in this block are write protected registers, *
* so it makes the most sense to do them all at once, so we only unlock and lock once */
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_EnableProtectedRegisters(); // Start by making protected registers accessible
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ConfigureCCCRRegister(&cccrConfig); // Enable FD mode and Bit rate switching
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ConfigureGlobalFilter(&gfc); // Configure the global filter configuration (Default CAN message behavior)
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ConfigureNominalTiming_Simple(&TCANNomTiming);// Setup nominal/arbitration bit timing
// TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ConfigureDataTiming_Simple(&TCANDataTiming); // Setup CAN FD timing
TCAN4x5x_MRAM_Clear(); // Clear all of MRAM (Writes 0's to all of it)
TCAN4x5x_MRAM_Configure(&MRAMConfiguration); // Set up the applicable registers related to MRAM configuration
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_DisableProtectedRegisters(); // Disable protected write and take device out of INIT mode
/* Set the interrupts we want to enable for MCAN */
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_Interrupt_Enable mcan_ie = {0}; // Remember to initialize to 0, or you'll get random garbage!
mcan_ie.RF0NE = 1; // RX FIFO 0 new message interrupt enable
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ConfigureInterruptEnable(&mcan_ie); // Enable the appropriate registers
/* Setup filters, this filter will mark any message with ID 0x055 as a priority message */
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_SID_Filter SID_ID = {0};
SID_ID.SFT = TCAN4x5x_SID_SFT_CLASSIC; // SFT: Standard filter type. Configured as a classic filter
SID_ID.SFEC = TCAN4x5x_SID_SFEC_PRIORITYSTORERX0; // Standard filter element configuration, store it in RX fifo 0 as a priority message
SID_ID.SFID1 = 0x055; // SFID1 (Classic mode Filter)
SID_ID.SFID2 = 0x7FF; // SFID2 (Classic mode Mask)
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_WriteSIDFilter(0, &SID_ID); // Write to the MRAM
/* Store ID 0x12345678 as a priority message */
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_XID_Filter XID_ID = {0};
XID_ID.EFT = TCAN4x5x_XID_EFT_CLASSIC; // EFT
XID_ID.EFEC = TCAN4x5x_XID_EFEC_PRIORITYSTORERX0; // EFEC
XID_ID.EFID1 = 0x12345678; // EFID1 (Classic mode filter)
XID_ID.EFID2 = 0x1FFFFFFF; // EFID2 (Classic mode mask)
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_WriteXIDFilter(0, &XID_ID); // Write to the MRAM
/* Configure the TCAN4550 Non-CAN-related functions */
TCAN4x5x_DEV_CONFIG devConfig = {0}; // Remember to initialize to 0, or you'll get random garbage!
devConfig.SWE_DIS = 0; // 0, Keep Sleep Wake Error Enabled (it's a disable bit, not an enable)
devConfig.DEVICE_RESET = 0; // Not requesting a software reset
devConfig.WD_EN = 0; // Watchdog disabled
devConfig.nWKRQ_CONFIG = 0; // Mirror INH function (default)
devConfig.INH_DIS = 0; // INH enabled (default)
devConfig.GPIO1_GPO_CONFIG = TCAN4x5x_DEV_CONFIG_GPO1_MCAN_INT1; // MCAN nINT 1 (default)
devConfig.FAIL_SAFE_EN = 0; // 0, Failsafe disabled (default)
devConfig.GPIO1_CONFIG = TCAN4x5x_DEV_CONFIG_GPIO1_CONFIG_GPO; // GPIO set as GPO (Default)
devConfig.WD_ACTION = TCAN4x5x_DEV_CONFIG_WDT_ACTION_nINT; // Watchdog set an interrupt (default)
devConfig.WD_BIT_RESET = 0; // Don't reset the watchdog
devConfig.nWKRQ_VOLTAGE = 0; // Set nWKRQ to internal voltage rail (default)
devConfig.GPO2_CONFIG = TCAN4x5x_DEV_CONFIG_GPO2_NO_ACTION; // GPO2 has no behavior (default)
devConfig.CLK_REF = 1; // Input crystal is a 40 MHz crystal (default)
devConfig.WAKE_CONFIG = TCAN4x5x_DEV_CONFIG_WAKE_BOTH_EDGES;// Wake pin can be triggered by either edge (default)
TCAN4x5x_Device_Configure(&devConfig); // Configure the device with the above configuration
// while(!TCAN4x5x_Device_SetMode(TCAN4x5x_DEVICE_MODE_NORMAL));
TCAN4x5x_Device_SetMode(TCAN4x5x_DEVICE_MODE_NORMAL); // Set to normal mode, since configuration is done. This line turns on the transceiver
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ClearInterruptsAll(); // Resets all MCAN interrupts (does NOT include any SPIERR interrupts)
/* Define the CAN message we want to send*/
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_TX_Header header = {0}; // Remember to initialize to 0, or you'll get random garbage!
uint8_t data[4] = {0x55, 0x66, 0x77, 0x88}; // Define the data payload
header.DLC = MCAN_DLC_4B; // Set the DLC to be equal to or less than the data payload (it is ok to pass a 64 byte data array into the WriteTXFIFO function if your DLC is 8 bytes, only the first 8 bytes will be read)
header.ID = 0x144; // Set the ID
header.FDF = 0; // CAN FD frame enabled
header.BRS = 0; // Bit rate switch enabled
header.EFC = 0;
header.MM = 0;
header.RTR = 0;
header.XTD = 0; // We are not using an extended ID in this example
header.ESI = 0; // Error state indicator
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_WriteTXBuffer(0, &header, data); // This function actually writes the header and data payload to the TCAN's MRAM in the specified TX queue number. It returns the bit necessary to write to TXBAR,
// but does not necessarily require you to use it. In this example, we won't, so that we can send the data queued up at a later point.
/* Let's make a different CAN message */
data[0] = 0x11;
data[1] = 0x22;
data[2] = 0x33;
data[3] = 0x44; // Define the data payload
header.DLC = MCAN_DLC_4B; // Set the DLC to be equal to or less than the data payload (it is ok to pass a 64 byte data array into the WriteTXFIFO function if your DLC is 8 bytes, only the first 8 bytes will be read)
header.ID = 0x123; // Set the ID
header.FDF = 0; // CAN FD frame enabled
header.BRS = 0; // Bit rate switch enabled
header.EFC = 0;
header.MM = 0;
header.RTR = 0;
header.XTD = 0; // We are not using an extended ID in this example
header.ESI = 0; // Error state indicator
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_WriteTXBuffer(1, &header, data); // This line writes the data and header to TX FIFO 1
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_TransmitBufferContents(1); // Request that TX Buffer 1 be transmitted
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_TransmitBufferContents(0); // Now we can send the TX FIFO element 0 data that we had queued up earlier but didn't send.
}
The CAN analyser is still behaving the same way.
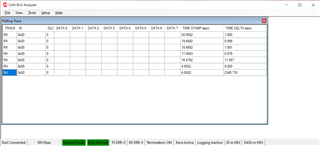
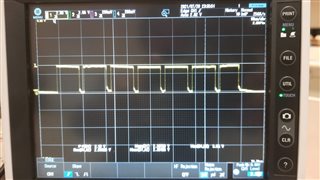
The signal from CAN analyser is also shown above.
Thanks
Joju John
Hi Joju,
The changes to the code look good here. I haven't reviewed beyond the changes we discussed, so if there's something particular you have concerns about, please point it out and I can take a look.
It appears that TCAN4550 is transmitting a series of error frames. This can occur when the device does not recognize any acknowledgement from other nodes on the bus. I commonly see this in my own testing before I have connected the node to the bus with another active node. Please ensure that the CAN analyser or other node is configured to acknowledge the information sent by TCAN4550.
Regards,
Eric Schott
/*
* main.c
* Author: Texas Instruments
* Date: 4/25/2019
*
* Description: A basic version of code to set up and receive a packet.
* - This is designed to work with the EVM the BOOSTXL-CANFD-LIN Rev 1.0 Boosterpack
* - It assumes TCAN4550 Oscillator of 40 MHz
* - Sets CAN arbitration rate at 500 kBaud
* - Sets CAN FD data phase for 2 MBaud
* - The interrupt pin is used for signal a received message, rather than polling
*
* Pressing S1 will transmit a CAN message. S1 is on the MSP430FR6989 launchpad to the left.
*
* Pinout
* - P1.4 SPI Clock / SCLK
* - P1.6 MOSI / SDI
* - P1.7 MISO / SDO
* - P2.5 SPI Chip Select / nCS
*
* - P2.3 MCAN Interrupt 1 / nINT
* - Ground wire is important
*
*
*
* Copyright (c) 2019 Texas Instruments Incorporated. All rights reserved.
* Software License Agreement
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
* are met:
*
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
*
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
* documentation and/or other materials provided with the
* distribution.
*
* Neither the name of Texas Instruments Incorporated nor the names of
* its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
* A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
* OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
* SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
* LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
* DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
* OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*/
#include <driverlib.h>
#include <msp430.h>
#include "tcan4x5x/TCAN4550.h"
void Init_GPIO(void);
void Init_Clock(void);
void Init_SPI(void);
void Init_CAN(void);
volatile uint8_t TCAN_Int_Cnt = 0; // A variable used to keep track of interrupts the MCAN Interrupt pin
int
main(void)
{
/***********************************
* MSP430 Specific Initializations *
***********************************/
WDT_A_hold(__MSP430_BASEADDRESS_WDT_A__);
Init_GPIO(); // Set up GPIOs for SPI and TCAN4550 connections
Init_Clock(); // Set up the system clocks for 16 MHz (on the MSP430)
Init_SPI(); // Initialize the SPI hardware module for 2 MHz SPI
GPIO_clearInterrupt(GPIO_PORT_P1, GPIO_PIN1); // Clear any interrupts on pin 1.1 before we enable global interrupts
GPIO_clearInterrupt(GPIO_PORT_P2, GPIO_PIN3); // Clear any interrupts on pin 2.3 before we enable global interrupts
__enable_interrupt();
/*********************************************
* Everything at this point is for TCAN4550 *
*********************************************/
Init_CAN(); // Run the main MCAN configuration sequence. The bulk of the configuration is in this!
/* Define the CAN message we want to send*/
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_TX_Header header = {0}; // Remember to initialize to 0, or you'll get random garbage!
uint8_t data[4] = {0x55, 0x66, 0x77, 0x88}; // Define the data payload
header.DLC = MCAN_DLC_4B; // Set the DLC to be equal to or less than the data payload (it is ok to pass a 64 byte data array into the WriteTXFIFO function if your DLC is 8 bytes, only the first 8 bytes will be read)
header.ID = 0x144; // Set the ID
header.FDF = 0; // CAN FD frame enabled
header.BRS = 0; // Bit rate switch enabled
header.EFC = 0;
header.MM = 0;
header.RTR = 0;
header.XTD = 0; // We are not using an extended ID in this example
header.ESI = 0; // Error state indicator
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_WriteTXBuffer(0, &header, data); // This function actually writes the header and data payload to the TCAN's MRAM in the specified TX queue number. It returns the bit necessary to write to TXBAR,
// but does not necessarily require you to use it. In this example, we won't, so that we can send the data queued up at a later point.
/* Let's make a different CAN message */
data[0] = 0x11;
data[1] = 0x22;
data[2] = 0x33;
data[3] = 0x44; // Define the data payload
header.DLC = MCAN_DLC_4B; // Set the DLC to be equal to or less than the data payload (it is ok to pass a 64 byte data array into the WriteTXFIFO function if your DLC is 8 bytes, only the first 8 bytes will be read)
header.ID = 0x123; // Set the ID
header.FDF = 0; // CAN FD frame enabled
header.BRS = 0; // Bit rate switch enabled
header.EFC = 0;
header.MM = 0;
header.RTR = 0;
header.XTD = 0; // We are not using an extended ID in this example
header.ESI = 0; // Error state indicator
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_WriteTXBuffer(1, &header, data); // This line writes the data and header to TX FIFO 1
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_TransmitBufferContents(1); // Request that TX Buffer 1 be transmitted
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_TransmitBufferContents(0); // Now we can send the TX FIFO element 0 data that we had queued up earlier but didn't send.
while (1)
{
if (TCAN_Int_Cnt > 0 )
{
TCAN_Int_Cnt--;
TCAN4x5x_Device_Interrupts dev_ir = {0}; // Define a new Device IR object for device (non-CAN) interrupt checking
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_Interrupts mcan_ir = {0}; // Setup a new MCAN IR object for easy interrupt checking
TCAN4x5x_Device_ReadInterrupts(&dev_ir); // Read the device interrupt register
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ReadInterrupts(&mcan_ir); // Read the interrupt register
if (dev_ir.SPIERR) // If the SPIERR flag is set
TCAN4x5x_Device_ClearSPIERR(); // Clear the SPIERR flag
if (mcan_ir.RF0N) // If a new message in RX FIFO 0
{
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_RX_Header MsgHeader = {0}; // Initialize to 0 or you'll get garbage
uint8_t numBytes = 0; // Used since the ReadNextFIFO function will return how many bytes of data were read
uint8_t dataPayload[64] = {0}; // Used to store the received data
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ClearInterrupts(&mcan_ir); // Clear any of the interrupt bits that are set.
numBytes = TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ReadNextFIFO( RXFIFO0, &MsgHeader, dataPayload); // This will read the next element in the RX FIFO 0
// numBytes will have the number of bytes it transfered in it. Or you can decode the DLC value in MsgHeader.DLC
// The data is now in dataPayload[], and message specific information is in the MsgHeader struct.
if (MsgHeader.ID == 0x0AA) // Example of how you can do an action based off a received address
{
// Do something
}
}
}
}
}
/*
* Configure the TCAN4550
*/
void
Init_CAN(void)
{
TCAN4x5x_Device_ClearSPIERR(); // Clear any SPI ERR flags that might be set as a result of our pin mux changing during MCU startup
/* Step one attempt to clear all interrupts */
TCAN4x5x_Device_Interrupt_Enable dev_ie = {0}; // Initialize to 0 to all bits are set to 0.
TCAN4x5x_Device_ConfigureInterruptEnable(&dev_ie); // Disable all non-MCAN related interrupts for simplicity
TCAN4x5x_Device_Interrupts dev_ir = {0}; // Setup a new MCAN IR object for easy interrupt checking
TCAN4x5x_Device_ReadInterrupts(&dev_ir); // Request that the struct be updated with current DEVICE (not MCAN) interrupt values
if (dev_ir.PWRON) // If the Power On interrupt flag is set
TCAN4x5x_Device_ClearInterrupts(&dev_ir); // Clear it because if it's not cleared within ~4 minutes, it goes to sleep
/* Configure the CAN bus speeds */
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_Nominal_Timing_Simple TCANNomTiming = {0}; // 500k arbitration with a 40 MHz crystal ((40E6 / 2) / (32 + 8) = 500E3)
TCANNomTiming.NominalBitRatePrescaler = 2;
TCANNomTiming.NominalTqBeforeSamplePoint = 32;
TCANNomTiming.NominalTqAfterSamplePoint = 8;
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_Data_Timing_Simple TCANDataTiming = {0}; // 2 Mbps CAN FD with a 40 MHz crystal (40E6 / (15 + 5) = 2E6)
TCANDataTiming.DataBitRatePrescaler = 1;
TCANDataTiming.DataTqBeforeSamplePoint = 15;
TCANDataTiming.DataTqAfterSamplePoint = 5;
/* Configure the MCAN core settings */
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_CCCR_Config cccrConfig = {0}; // Remember to initialize to 0, or you'll get random garbage!
cccrConfig.FDOE = 0; // CAN FD mode enable
cccrConfig.BRSE = 0; // CAN FD Bit rate switch enable
/* Configure the default CAN packet filtering settings */
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_Global_Filter_Configuration gfc = {0};
gfc.RRFE = 1; // Reject remote frames (TCAN4x5x doesn't support this)
gfc.RRFS = 1; // Reject remote frames (TCAN4x5x doesn't support this)
gfc.ANFE = TCAN4x5x_GFC_ACCEPT_INTO_RXFIFO0; // Default behavior if incoming message doesn't match a filter is to accept into RXFIO0 for extended ID messages (29 bit IDs)
gfc.ANFS = TCAN4x5x_GFC_ACCEPT_INTO_RXFIFO0; // Default behavior if incoming message doesn't match a filter is to accept into RXFIO0 for standard ID messages (11 bit IDs)
/* ************************************************************************
* In the next configuration block, we will set the MCAN core up to have:
* - 1 SID filter element
* - 1 XID Filter element
* - 5 RX FIFO 0 elements
* - RX FIFO 0 supports data payloads up to 64 bytes
* - RX FIFO 1 and RX Buffer will not have any elements, but we still set their data payload sizes, even though it's not required
* - No TX Event FIFOs
* - 2 Transmit buffers supporting up to 64 bytes of data payload
*/
TCAN4x5x_MRAM_Config MRAMConfiguration = {0};
MRAMConfiguration.SIDNumElements = 1; // Standard ID number of elements, you MUST have a filter written to MRAM for each element defined
MRAMConfiguration.XIDNumElements = 1; // Extended ID number of elements, you MUST have a filter written to MRAM for each element defined
MRAMConfiguration.Rx0NumElements = 5; // RX0 Number of elements
MRAMConfiguration.Rx0ElementSize = MRAM_64_Byte_Data; // RX0 data payload size
MRAMConfiguration.Rx1NumElements = 0; // RX1 number of elements
MRAMConfiguration.Rx1ElementSize = MRAM_64_Byte_Data; // RX1 data payload size
MRAMConfiguration.RxBufNumElements = 0; // RX buffer number of elements
MRAMConfiguration.RxBufElementSize = MRAM_64_Byte_Data; // RX buffer data payload size
MRAMConfiguration.TxEventFIFONumElements = 0; // TX Event FIFO number of elements
MRAMConfiguration.TxBufferNumElements = 2; // TX buffer number of elements
MRAMConfiguration.TxBufferElementSize = MRAM_64_Byte_Data; // TX buffer data payload size
/* Configure the MCAN core with the settings above, the changes in this block are write protected registers, *
* so it makes the most sense to do them all at once, so we only unlock and lock once */
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_EnableProtectedRegisters(); // Start by making protected registers accessible
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ConfigureCCCRRegister(&cccrConfig); // Enable FD mode and Bit rate switching
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ConfigureGlobalFilter(&gfc); // Configure the global filter configuration (Default CAN message behavior)
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ConfigureNominalTiming_Simple(&TCANNomTiming);// Setup nominal/arbitration bit timing
// TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ConfigureDataTiming_Simple(&TCANDataTiming); // Setup CAN FD timing
TCAN4x5x_MRAM_Clear(); // Clear all of MRAM (Writes 0's to all of it)
TCAN4x5x_MRAM_Configure(&MRAMConfiguration); // Set up the applicable registers related to MRAM configuration
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_DisableProtectedRegisters(); // Disable protected write and take device out of INIT mode
/* Set the interrupts we want to enable for MCAN */
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_Interrupt_Enable mcan_ie = {0}; // Remember to initialize to 0, or you'll get random garbage!
mcan_ie.RF0NE = 1; // RX FIFO 0 new message interrupt enable
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ConfigureInterruptEnable(&mcan_ie); // Enable the appropriate registers
/* Setup filters, this filter will mark any message with ID 0x055 as a priority message */
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_SID_Filter SID_ID = {0};
SID_ID.SFT = TCAN4x5x_SID_SFT_CLASSIC; // SFT: Standard filter type. Configured as a classic filter
SID_ID.SFEC = TCAN4x5x_SID_SFEC_PRIORITYSTORERX0; // Standard filter element configuration, store it in RX fifo 0 as a priority message
SID_ID.SFID1 = 0x055; // SFID1 (Classic mode Filter)
SID_ID.SFID2 = 0x7FF; // SFID2 (Classic mode Mask)
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_WriteSIDFilter(0, &SID_ID); // Write to the MRAM
/* Store ID 0x12345678 as a priority message */
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_XID_Filter XID_ID = {0};
XID_ID.EFT = TCAN4x5x_XID_EFT_CLASSIC; // EFT
XID_ID.EFEC = TCAN4x5x_XID_EFEC_PRIORITYSTORERX0; // EFEC
XID_ID.EFID1 = 0x12345678; // EFID1 (Classic mode filter)
XID_ID.EFID2 = 0x1FFFFFFF; // EFID2 (Classic mode mask)
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_WriteXIDFilter(0, &XID_ID); // Write to the MRAM
/* Configure the TCAN4550 Non-CAN-related functions */
TCAN4x5x_DEV_CONFIG devConfig = {0}; // Remember to initialize to 0, or you'll get random garbage!
devConfig.SWE_DIS = 0; // Keep Sleep Wake Error Enabled (it's a disable bit, not an enable)
devConfig.DEVICE_RESET = 0; // Not requesting a software reset
devConfig.WD_EN = 0; // Watchdog disabled
devConfig.nWKRQ_CONFIG = 0; // Mirror INH function (default)
devConfig.INH_DIS = 0; // INH enabled (default)
devConfig.GPIO1_GPO_CONFIG = TCAN4x5x_DEV_CONFIG_GPO1_MCAN_INT1; // MCAN nINT 1 (default)
devConfig.FAIL_SAFE_EN = 0; // Failsafe disabled (default)
devConfig.GPIO1_CONFIG = TCAN4x5x_DEV_CONFIG_GPIO1_CONFIG_GPO; // GPIO set as GPO (Default)
devConfig.WD_ACTION = TCAN4x5x_DEV_CONFIG_WDT_ACTION_nINT; // Watchdog set an interrupt (default)
devConfig.WD_BIT_RESET = 0; // Don't reset the watchdog
devConfig.nWKRQ_VOLTAGE = 0; // Set nWKRQ to internal voltage rail (default)
devConfig.GPO2_CONFIG = TCAN4x5x_DEV_CONFIG_GPO2_NO_ACTION; // GPO2 has no behavior (default)
devConfig.CLK_REF = 1; // Input crystal is a 40 MHz crystal (default)
devConfig.WAKE_CONFIG = TCAN4x5x_DEV_CONFIG_WAKE_BOTH_EDGES;// Wake pin can be triggered by either edge (default)
TCAN4x5x_Device_Configure(&devConfig); // Configure the device with the above configuration
TCAN4x5x_Device_SetMode(TCAN4x5x_DEVICE_MODE_NORMAL); // Set to normal mode, since configuration is done. This line turns on the transceiver
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_ClearInterruptsAll(); // Resets all MCAN interrupts (does NOT include any SPIERR interrupts)
}
/*
* GPIO Initialization
*/
void
Init_GPIO()
{
// Set all GPIO pins to output low to prevent floating input and reduce power consumption
GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(GPIO_PORT_P1, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(GPIO_PORT_P2, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(GPIO_PORT_P3, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(GPIO_PORT_P4, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(GPIO_PORT_P5, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(GPIO_PORT_P6, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(GPIO_PORT_P7, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(GPIO_PORT_P8, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(GPIO_PORT_P9, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(GPIO_PORT_P1, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(GPIO_PORT_P2, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(GPIO_PORT_P3, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(GPIO_PORT_P4, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(GPIO_PORT_P5, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(GPIO_PORT_P6, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(GPIO_PORT_P7, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(GPIO_PORT_P8, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
GPIO_setAsOutputPin(GPIO_PORT_P9, GPIO_PIN0|GPIO_PIN1|GPIO_PIN2|GPIO_PIN3|GPIO_PIN4|GPIO_PIN5|GPIO_PIN6|GPIO_PIN7);
// Set P3.2 as input with weak pull up since this is GPIO1
GPIO_setAsInputPinWithPullUpResistor(GPIO_PORT_P3, GPIO_PIN2);
// Set P3.1 as input for GPO2
GPIO_setAsInputPinWithPullUpResistor(GPIO_PORT_P3, GPIO_PIN1);
// Set P2.1 as input with weak pull up since this is GPO2
GPIO_setAsInputPinWithPullUpResistor(GPIO_PORT_P2, GPIO_PIN1);
// Configure P1.1 interrupt for S1 (left button on launchpad)
GPIO_setAsInputPinWithPullUpResistor(GPIO_PORT_P1, GPIO_PIN1);
GPIO_selectInterruptEdge(GPIO_PORT_P1, GPIO_PIN1, GPIO_HIGH_TO_LOW_TRANSITION);
GPIO_clearInterrupt(GPIO_PORT_P1, GPIO_PIN1);
GPIO_enableInterrupt(GPIO_PORT_P1, GPIO_PIN1);
// Configure P2.3 interrupt for MCAN Interrupt 1
GPIO_setAsInputPinWithPullUpResistor(GPIO_PORT_P2, GPIO_PIN3);
GPIO_selectInterruptEdge(GPIO_PORT_P2, GPIO_PIN3, GPIO_HIGH_TO_LOW_TRANSITION);
GPIO_clearInterrupt(GPIO_PORT_P2, GPIO_PIN3);
GPIO_enableInterrupt(GPIO_PORT_P2, GPIO_PIN3);
// Set P4.1 and P4.2 as Secondary Module Function Input, LFXT.
GPIO_setAsPeripheralModuleFunctionInputPin(
GPIO_PORT_PJ,
GPIO_PIN4 + GPIO_PIN5,
GPIO_PRIMARY_MODULE_FUNCTION
);
/*********************************************************
* SPI Interface Pins
*********************************************************/
//P1.4(SPI CLK on UCB0CLK)
GPIO_setAsPeripheralModuleFunctionOutputPin(
GPIO_PORT_P1,
GPIO_PIN4,
GPIO_PRIMARY_MODULE_FUNCTION
);
//P1.6(MOSI on UCB0SIMO)
GPIO_setAsPeripheralModuleFunctionOutputPin(
GPIO_PORT_P1,
GPIO_PIN6,
GPIO_PRIMARY_MODULE_FUNCTION
);
//P1.7(MISO on UCB0SOMI)
GPIO_setAsPeripheralModuleFunctionInputPin(
GPIO_PORT_P1,
GPIO_PIN7,
GPIO_PRIMARY_MODULE_FUNCTION
);
//set P2.5 as SPI CS, already set to output above
GPIO_setOutputLowOnPin(GPIO_PORT_P2, GPIO_PIN5);
GPIO_setOutputHighOnPin(GPIO_PORT_P2, GPIO_PIN5);
// Disable the GPIO power-on default high-impedance mode
// to activate previously configured port settings
PMM_unlockLPM5();
}
/*
* Clock System Initialization
*/
void Init_Clock()
{
// Set DCO frequency to default 8MHz
CS_setDCOFreq(CS_DCORSEL_0, CS_DCOFSEL_6);
// Configure MCLK and SMCLK to 8MHz
CS_initClockSignal(CS_MCLK, CS_DCOCLK_SELECT, CS_CLOCK_DIVIDER_1);
CS_initClockSignal(CS_SMCLK, CS_DCOCLK_SELECT, CS_CLOCK_DIVIDER_1);
// Initializes the XT1 crystal oscillator
CS_turnOnLFXT(CS_LFXT_DRIVE_3);
}
/*
* Initialize the EUSCI B SPI
*/
void Init_SPI()
{
struct EUSCI_B_SPI_initMasterParam SPIParam = {0};
SPIParam.selectClockSource=EUSCI_B_SPI_CLOCKSOURCE_SMCLK;
SPIParam.clockSourceFrequency=8000000;
SPIParam.desiredSpiClock=2000000;
SPIParam.msbFirst=EUSCI_B_SPI_MSB_FIRST;
SPIParam.clockPhase=EUSCI_B_SPI_PHASE_DATA_CAPTURED_ONFIRST_CHANGED_ON_NEXT;
SPIParam.clockPolarity=EUSCI_B_SPI_CLOCKPOLARITY_INACTIVITY_LOW;
SPIParam.spiMode=EUSCI_B_SPI_4PIN_UCxSTE_ACTIVE_HIGH;
EUSCI_B_SPI_initMaster(EUSCI_B0_BASE, &SPIParam);
EUSCI_B_SPI_select4PinFunctionality(EUSCI_B0_BASE,0x00);
EUSCI_B_SPI_enable(EUSCI_B0_BASE);
}
/*
* PORT1 Interrupt Service Routine
* Handles Interrupt from the TCAN4550 on P2.3
*/
#pragma vector = PORT1_VECTOR
__interrupt void PORT1_ISR(void)
{
switch(__even_in_range(P1IV, P1IV_P1IFG7))
{
case P1IV_NONE : break;
case P1IV_P1IFG0 : break;
case P1IV_P1IFG1 :
TCAN4x5x_MCAN_TransmitBufferContents(0); // Transmits the contents of TX queue index 0 when S1 (P1.1) is pressed
break;
case P1IV_P1IFG2 : break;
case P1IV_P1IFG3 : break;
case P1IV_P1IFG4 : break;
case P1IV_P1IFG5 : break;
case P1IV_P1IFG6 : break;
case P1IV_P1IFG7 : break;
}
}
/*
* PORT2 Interrupt Service Routine
* Handles Interrupt from the TCAN4550 on P2.3
*/
#pragma vector = PORT2_VECTOR
__interrupt void PORT2_ISR(void)
{
switch(__even_in_range(P2IV, P2IV_P2IFG7))
{
case P2IV_NONE : break;
case P2IV_P2IFG0 : break;
case P2IV_P2IFG1 : break;
case P2IV_P2IFG2 : break;
case P2IV_P2IFG3 : TCAN_Int_Cnt++; break;
case P2IV_P2IFG4 : break;
case P2IV_P2IFG5 : break;
case P2IV_P2IFG6 : break;
case P2IV_P2IFG7 : break;
}
}
Dear Sir,
Thank you for the support.
We are now using TCAN4550 with MSP430FR6989. The demo code from TI is used here.
Our CAN analyzer supports till 1Mbps and normal CAN. We implemented the following changes
cccrConfig.FDOE = 0;
cccrConfig.BRSE = 0;
apart from that, FDF and BRS bits were also set to 0 for both the ID's
header.FDF = 0;
header.BRS = 0;
Now we are able to receive the data in 500kbps

However, we are not able to receive any data. The nINH pin never gets high and the RFON bit also never gets to 1.
Is there any changes we need to do in code while receiving the normal CAN data?
Following are the data that we send at an interval of 500ms.
ID=0x0AA,Type=D,Length=4,Data=01020304,CycleTime=500,IDFormat=hex
ID=0x055,Type=D,Length=4,Data=01020304,CycleTime=500,IDFormat=hex
Thanks
Joju John
Hi Joju,
I'm glad to hear that the transition tests have gone well.
Your logic for receiving looks good here. There should not be any changes required in order to receive generic CAN data (FD or non-FD) as long as it is at the configured data rate.
You say that INH does not go high. This would mean that the device is in sleep mode. To receive data, TCAN4550 should be in normal mode - similar to if the device was transmitting. Can you confirm the device is in normal mode for this test?
Or perhaps you are referring to the nINT pin. If this is the case and nINT is continuously low, there is some other interrupt set that needs to be handled. The demo code will only check the state of the received message interrupt when there is a transition from high to low on the nINT pin (see interrupt vector PORT2_ISR). Do you find that nINT is stuck low? If so, what is the value of the interrupt register at this time?
Regards,
Eric Schott