Other Parts Discussed in Thread: DS90UB954-Q1
Hi Expert,
What is the max back channel frequency of 92x, 93x, 94x, 95x and 96x?
Thanks
Best regards,
David
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
Hi Expert,
What is the max back channel frequency of 92x, 93x, 94x, 95x and 96x?
Thanks
Best regards,
David
Hello David,
Max BC speeds are listed below:
92x = 5Mbps
934/933 = 2.5Mbps
936/935 = 50Mbps
94x = 20Mbps
95x = 50Mbps
96x = 50Mbps
Best Regards,
Casey
Hi Casey,
Thanks for your feedback, want to confirm with you this BC speed can support
Could you help talk about the BC speed from these two use?
Thanks
Best regards,
David
Hello David,
Yes, both of those are common applications for the back channel communication in these devices. Automatic exposure triggers are usually frame rate based so are extremely low frequency signals. Touch IC communication is very common with these devices, typically with I2C, bus also SPI in some cases. Both can be supported
Best Regards,
Casey
Hi Casey,
Thanks for feedback. Could you have a detail calculation process to make sure the BC speed is enough for the Automatic exposure and touch IC?
Best regards,
David
Hello David,
I suggest to take a look at the supported back channel GPIO rates from the datasheets based on which device you are looking at. For example, in the 954 datasheet there is this table:
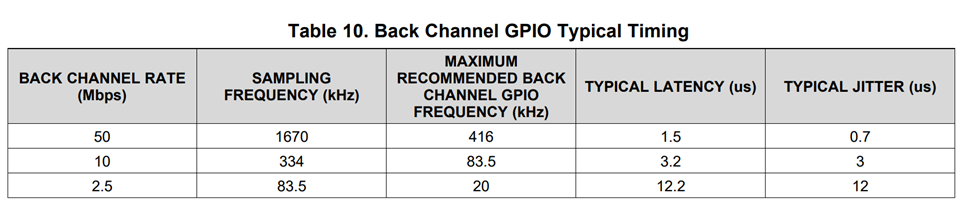
All devices have information like this in the datasheet documentation. Please reach out if you are having trouble finding it.
Here are a couple of useful docs for I2C throughput:
https://www.ti.com/lit/pdf/snla131
https://www.ti.com/lit/pdf/snla222
Best Regards,
Casey
Hi Casey,
Thanks for your sharing. Just went through the two docs:
1.
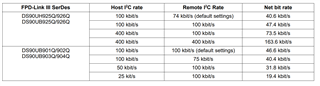
Why the host I2C 100k and remote I2C 100K, and the net bit rate is only 47.4k?
How does the lost colomn result be calculated?
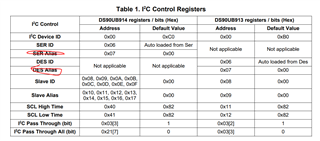
2. What is the difference between pass through and pass through all?
3. For this table, why need to use SER alias and DES alias, because there are already SER ID and DES ID, if use SER Alias and DES Alias, they are repeated, could you help use a example to illustrate?
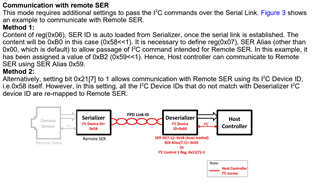
4. For Method 1, if the SER side have only one camera with one sensor and one SER, still need to configure the SER Alias to communicate with SER?
It doesn't work if use the SER ID 0x58?
Also for the I2C command , use 7-bit address 0x59 or 8-bit address 0xB2?
Best regards,
David
David,
1.
Why the host I2C 100k and remote I2C 100K, and the net bit rate is only 47.4k?
How does the lost colomn result be calculated?
This is explained in section 5 of the app note. The I2C communication takes place across the BCC which add forward channel and back channel delays between different points of the transaction (clock stretching). The added delay means there is an effective throughput decrease. Section 5 shows how to estimate it
2. What is the difference between pass through and pass through all?
Pass through mode enables I2C transactions to go through the FPD-Link when the address of the transaction matches an address that has been configured in the I2C slave ID/alias registers of the SER/DES. Pass through all mode enables passthrough of all transactions through the FPD-Link even if the address of the transaction does not match the any address configured in the slave ID/alias registers.
3. For this table, why need to use SER alias and DES alias, because there are already SER ID and DES ID, if use SER Alias and DES Alias, they are repeated, could you help use a example to illustrate?
The aliasing allows communication with multiple remote slave devices which have the same physical I2C address. For example let's say you have a dual deserializer hub like DS90UB954-Q1 connected to two identical imager modules which use the same addresses for the serializer and the imager. In order to communicate with each slave device independently you need to create an alias map so that transactions intended for each individual component can be addressed independently and re-mapped through the FPD-Link chain.
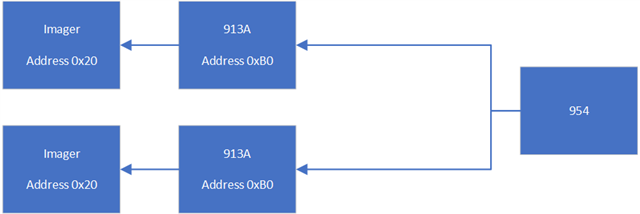
For example you could set
FPD RX Port 0 Slave ID0 = 0xB0
FPD RX Port 1 Slave ID0 = 0xB0
FPD RX Port 0 Slave ID1 = 0x20
FPD RX Port 1 Slave ID1 = 0x20
FPD RX Port 0 Slave Alias0= 0xB2
FPD RX Port 1 Slave Alias0= 0xB4
FPD RX Port 0 Slave Alias1= 0x22
FPD RX Port 1 Slave Alias1 = 0x24
Now when the host attached to 954 tries to access address 0xB2, the transaction will be automatically remapped to target 0xB0 on port 0. When the host tries to access address 0xB4, the transaction will be automatically remapped to address 0xB0 on port 1 and so on.
4. For Method 1, if the SER side have only one camera with one sensor and one SER, still need to configure the SER Alias to communicate with SER?
It doesn't work if use the SER ID 0x58?
Also for the I2C command , use 7-bit address 0x59 or 8-bit address 0xB2?
If there is only one SER in the system it is not necessary to create an alias or the alias can just match the physical address of the part since there are no conflicts. I2C command 8 bit format or 7 bit format depends on how the host processor processes I2C transactions. Some processors/programming languages use 8 bit addressing while others use 7 bit. They are functionally equivalent
Best Regards,
Casey
Hi Casey,
Thanks for your feedback. Clear about 1 3 4.
For 2, under what kind of condition need to use Pass through and under what kind of condition need to use Pass through?
Better to use example to illustrate. Thanks
Best regards,
David
Hello David,
Typically we recommend using regular I2C passthrough "not all" for most use cases, especially when there are multiple deserializers connected to the hub so that transactions can get routed accordingly.
The main reason why we would recommend passthrough all would be in a case where there are more than 8 I2C devices on the remote side which need to be accessed. There are only 8 address/alias registers to configure passthrough so if you need to access more addresses than that, you can set passthrough all. But this is best to use only for setups where there is one serializer connected so that you can avoid the same transaction going out blindly to both SER even if there is no device there to respond.
Best Regards,
Casey