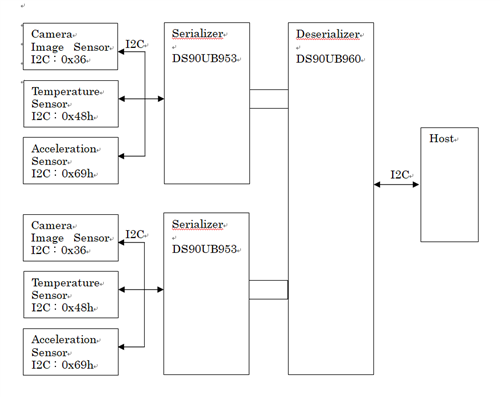
In this case of the I2C connection block diagram below, please tell me the register settings for us.
In particular, A lot of I2C devices are connected to one serializer. And, a device with the same I2C register address is connected to each serializer.
Q)Please tell me the register settings.
Especially below.
- SER_ID
- SER_ALIAS_ID
- SER_ID
- SER_ALIAS_ID