Other Parts Discussed in Thread: ALP
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.

Hello,
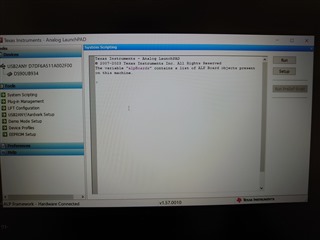
Thank you for reaching out. There are two ways to read and write registers within the scripting tab. The first option is to send commands individually in the command window pictured. At the ">" mark you can use the formats "board.WriteI2C(Address, Register, Data)" and "board.ReadI2C(Address, Register)" to write and read registers for a specific device. Alternatively, if you have many commands you'd like to run, you can write a configuration script using the same board.WriteI2C( ) or board.ReadI2C( ) format and save it as a .txt or .py file. To run the file select the "Run" button in ALP and select the script you'd like to run. When the script is run in ALP each command saved in the file will be issued sequentially as if it was written in the command window. I've listed some examples below.