Tool/software:
When implementing a signal conditioning device in a system, one design consideration is the device power consumption. In order to address this design consideration, it's valuable to understand how to calculate the estimated device power.
Power Consumption Calculation:
For many signal conditioning devices, device power is composed of a "idle" power consumption and "per channel" power consumption. The "idle" power consumption is the power associated with just having the device powered on. The "per channel" power consumption is power associated with having an active channel on the device.
For devices that have similar power decomposition in the datasheet, device power can be estimated by Ptotal = Pidle + N * Pchannel, where N is the number of active channels.
Example Power Consumption Calculation:
As an example, let's review a power calculation for DS280DF810. In this example, let's assume we are using 3 channels of the device in straight mode (crosspoint disabled) with CTLE, full DFE, and TX FIR. Reviewing our power calculation formula and data sheet, there are two key power specifications from the data sheet that we will use.
- Power consumption per active channel
- Idle/Static device power consumption
Based on our use case, we can select the power consumption per active channel that is closest to the device application use case.
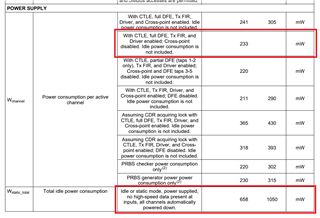
When selecting power values, it is also important to consider whether a typical or maximum value will be more suitable for your power calculation use case.
Pchannel = 233 mW
Pidle = 658 mW
N = 3
Ptotal = Pidle + N * Pchannel
Ptotal = 658 mW + 3 * 233 mW
Ptotal = 1357 mW

