Hi Team,
I tried to install "TPS6598X Host Interface Utility Tool" from following link.
http://www.ti.com/tool/TPS65982-HIUTILITY?keyMatch=TPS65982&tisearch=Search-EN-Everything
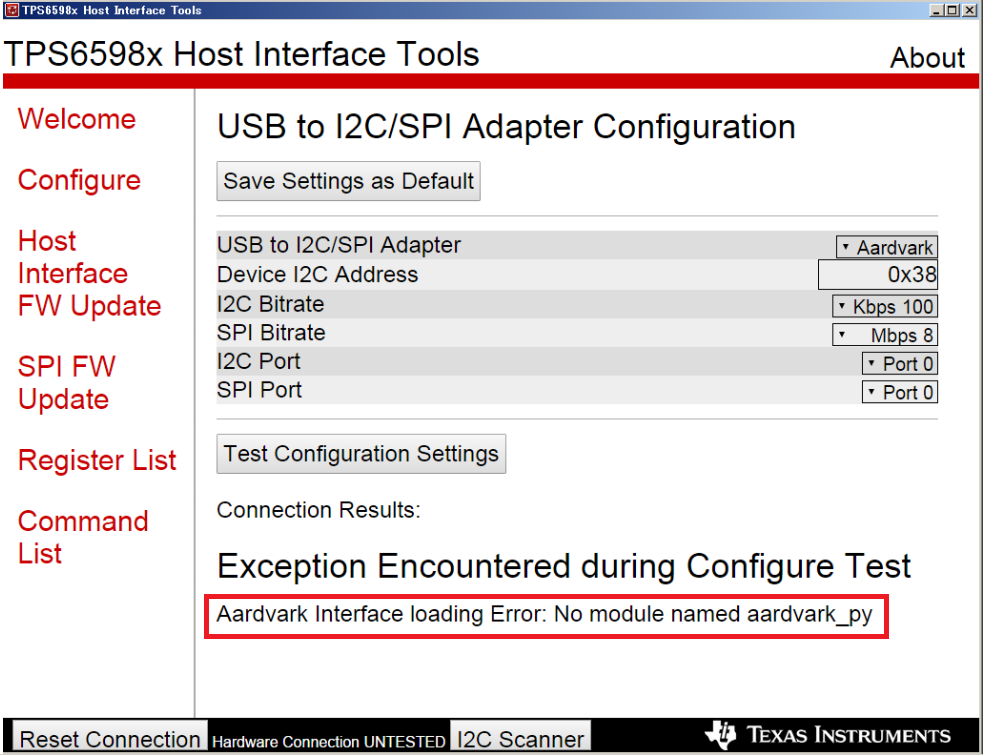
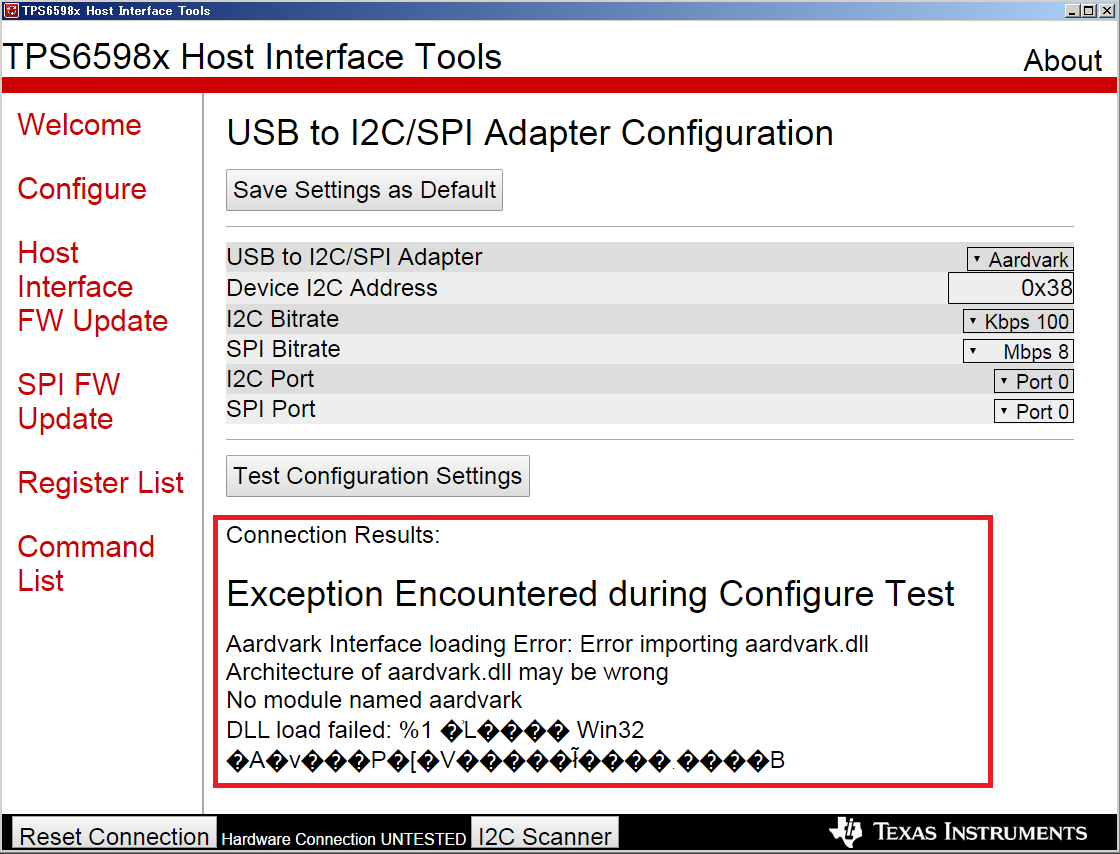
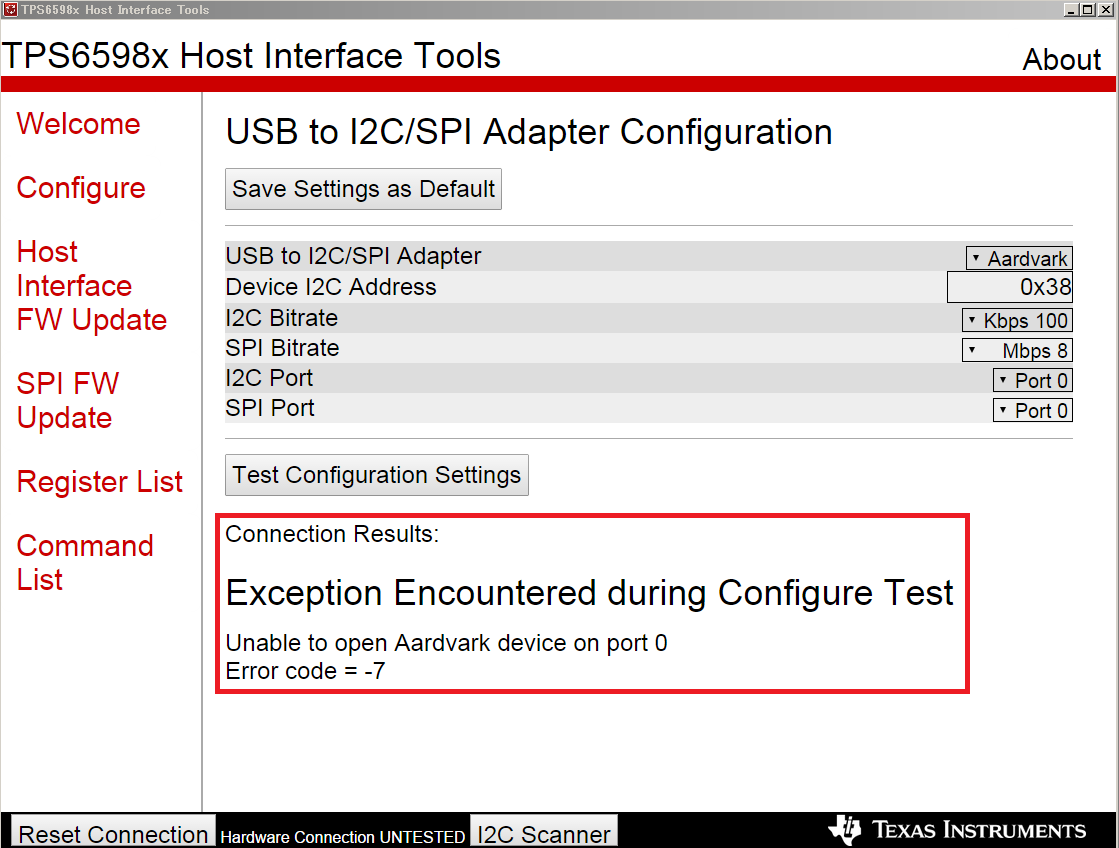
However I couldn't launch the tool because my PC is Windows 32bit.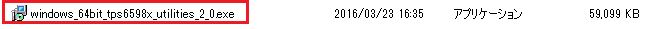
Could you give me the .exe file for Windows 32bit?
Best Regards,
Yaita / Japan disty
-
Ask a related question
What is a related question?A related question is a question created from another question. When the related question is created, it will be automatically linked to the original question.