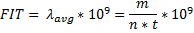Part Number: DS26C31MQML
Other Parts Discussed in Thread: AM26C31
Hi, I'm daejin
As seen in the related question, I configured the redundancy structure using 2ea DS26C31MQML.
When the primary channel driver is working, VCC power is not applied to the secondary channel.
Usually, the 422 communication is operated using the primary channel, and when there is a problem with 422 communication, are changed to the secondary channel. This means that the VCC of the primary channel is cut off and VCC is supplied to the secondary channel.
My question is:
If part failure occurs in the primary channel, how does it affect communication using the secondary channel?
I am curious about the typical part failure mode. Could you tell me the type of failure mode for this part?
I am concerned that the output pin is shorted to GND, internally.
If the part's output of the channel in use is shorted to GND internally, I think that both the primary and secondary channels cannot be operated for 422 communication even if it be changed to other channel.
Regards,
Daejin