Hi Teams
Customer is using TCAN1043-Q1 in their new project and have few questions about SLEEP mode control.
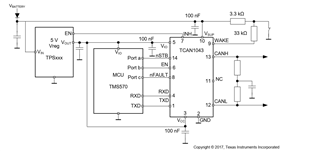
The power supply connection is the same like below diagram in datasheet.
When we enter the SLEEP mode through MCU output high level in EN pin exceed go-to-sleep time.
The power supply for MCU or VIO pin power off as IHN transient to floating output.
Base on my understanding, the only way to exist SLEEP MODE is wake up from CAN bus (wakeup from external system)?
Wakeup through WAKE pin is vaild or not when VIO is power off?