Other Parts Discussed in Thread: HALCOGEN
Hi TI,
I'm trying to write and read the sector 7 (0xF0200000) of the the flash. I'm able to do it. but the issue is, the flash is not erasing properly even when loading the code for debug and executing erase function. after erasing it leaves behind some random junk values in the flash as shown in the below ss.
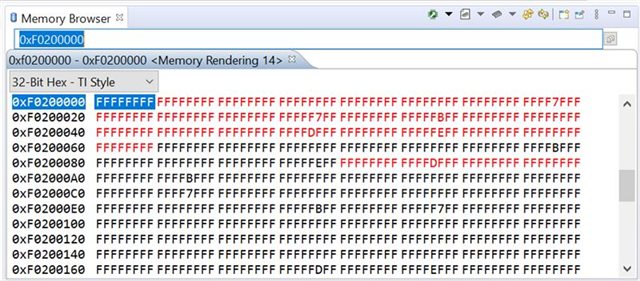
and sometimes the flash will not erase fully as shown in the below ss.
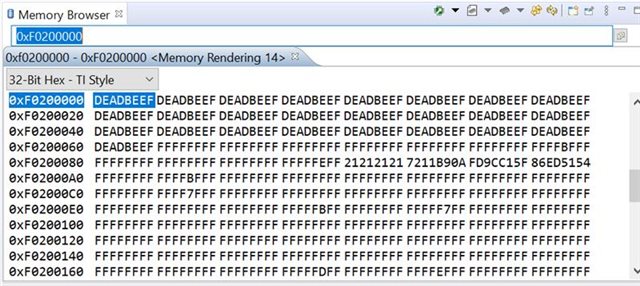
because of this issue, my data is corrupting sometimes while writing to the flash. what is the reason for this and how i can solve the error. can you please help me on this.
with regards,
Nagaraju M