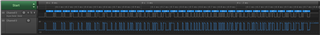
I used Mr. Tsai's sample program to continue to work on UART uDMA (I modified it to use K0/1 instead, and baud rate). It works "fine", I can see data streaming out of TiVa1294 continuously.
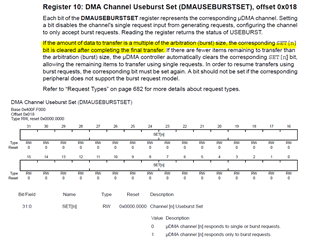
Now, I want to just send out ONE burst of DMA, so I remove the codes to restart another DMA transfer inside UART4IntHandler. but UART4IntHandler is kept being called, it is like the interrupt flag could not be clear. So I add ROM_UARTDMADisable(UART4_BASE, UART_DMA_TX); to UART4IntHandler. This time the ISR is called twice before it stops. Is this the correct order work with uDMA on UART?
The final codes is attached below
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "inc/hw_ints.h"
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "inc/hw_uart.h"
#include "driverlib/fpu.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/interrupt.h"
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "driverlib/rom.h"
#include "driverlib/rom_map.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/systick.h"
#include "driverlib/uart.h"
#include "driverlib/udma.h"
#include "utils/cpu_usage.h"
#include "utils/uartstdio.h"
#include "utils/ustdlib.h"
//*****************************************************************************
//
//! \addtogroup example_list
//! <h1>uDMA (udma_demo)</h1>
//!
//! This example application demonstrates the use of the uDMA controller to
//! transfer data between memory buffers, and to transfer data to and from a
//! UART. The test runs for 10 seconds before exiting.
//!
//! UART0, connected to the ICDI virtual COM port and running at 115,200,
//! 8-N-1, is used to display messages from this application.
//
//*****************************************************************************
//****************************************************************************
//
// System clock rate in Hz.
//
//****************************************************************************
uint32_t g_ui32SysClock;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The number of SysTick ticks per second used for the SysTick interrupt.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#define SYSTICKS_PER_SECOND 100
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The size of the memory transfer source and destination buffers (in words).
//
//*****************************************************************************
#define MEM_BUFFER_SIZE 1024
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The size of the UART transmit and receive buffers. They do not need to be
// the same size.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#define UART_TXBUF_SIZE 65536
#define UART_RXBUF_SIZE 256
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The source and destination buffers used for memory transfers.
//
//*****************************************************************************
static uint32_t g_ui32SrcBuf[MEM_BUFFER_SIZE];
static uint32_t g_ui32DstBuf[MEM_BUFFER_SIZE];
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The transmit buffers used for the UART transfers.
//
//*****************************************************************************
static uint8_t g_ui8TxBuf[UART_TXBUF_SIZE];
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The count of uDMA errors. This value is incremented by the uDMA error
// handler.
//
//*****************************************************************************
static uint32_t g_ui32uDMAErrCount = 0;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The count of times the uDMA interrupt occurred but the uDMA transfer was not
// complete. This should remain 0.
//
//*****************************************************************************
static uint32_t g_ui32BadISR = 0;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The count of memory uDMA transfer blocks. This value is incremented by the
// uDMA interrupt handler whenever a memory block transfer is completed.
//
//*****************************************************************************
static uint32_t g_ui32MemXferCount = 0;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The number of seconds elapsed since the start of the program. This value is
// maintained by the SysTick interrupt handler.
//
//*****************************************************************************
static uint32_t g_ui32Seconds = 0;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The control table used by the uDMA controller. This table must be aligned
// to a 1024 byte boundary.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#if defined(ewarm)
#pragma data_alignment=1024
uint8_t pui8ControlTable[1024];
#elif defined(ccs)
#pragma DATA_ALIGN(pui8ControlTable, 1024)
uint8_t pui8ControlTable[1024];
#else
uint8_t pui8ControlTable[1024] __attribute__ ((aligned(1024)));
#endif
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The error routine that is called if the driver library encounters an error.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#ifdef DEBUG
void
__error__(char *pcFilename, uint32_t ui32Line)
{
}
#endif
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The interrupt handler for the SysTick timer. This handler will increment a
// seconds counter whenever the appropriate number of ticks has occurred. It
// will also call the CPU usage tick function to find the CPU usage percent.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
SysTickHandler(void)
{
static uint32_t ui32TickCount = 0;
//
// Increment the tick counter.
//
ui32TickCount++;
//
// If the number of ticks per second has occurred, then increment the
// seconds counter.
//
if(!(ui32TickCount % SYSTICKS_PER_SECOND))
{
g_ui32Seconds++;
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The interrupt handler for uDMA errors. This interrupt will occur if the
// uDMA encounters a bus error while trying to perform a transfer. This
// handler just increments a counter if an error occurs.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
uDMAErrorHandler(void)
{
uint32_t ui32Status;
//
// Check for uDMA error bit
//
ui32Status = ROM_uDMAErrorStatusGet();
//
// If there is a uDMA error, then clear the error and increment
// the error counter.
//
if(ui32Status)
{
ROM_uDMAErrorStatusClear();
g_ui32uDMAErrCount++;
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The interrupt handler for uDMA interrupts from the memory channel. This
// interrupt will increment a counter, and then restart another memory
// transfer.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
uDMAIntHandler(void)
{
uint32_t ui32Mode;
//
// Check for the primary control structure to indicate complete.
//
ui32Mode = ROM_uDMAChannelModeGet(UDMA_CH19_UART4TX);
if(ui32Mode == UDMA_MODE_STOP)
{
//
// Increment the count of completed transfers.
//
g_ui32MemXferCount++;
//
// Configure it for another transfer.
//
ROM_uDMAChannelTransferSet(UDMA_CH19_UART4TX, UDMA_MODE_AUTO,
g_ui32SrcBuf, g_ui32DstBuf,
MEM_BUFFER_SIZE);
//
// Initiate another transfer.
//
ROM_uDMAChannelEnable(UDMA_CH19_UART4TX);
ROM_uDMAChannelRequest(UDMA_CH19_UART4TX);
}
//
// If the channel is not stopped, then something is wrong.
//
else
{
g_ui32BadISR++;
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The interrupt handler for UART4. This interrupt will occur when a DMA
// transfer is complete using the UART4 uDMA channel. It will also be
// triggered if the peripheral signals an error. This interrupt handler will
// switch between receive ping-pong buffers A and B. It will also restart a TX
// uDMA transfer if the prior transfer is complete. This will keep the UART
// running continuously (looping TX data back to RX).
//
//*****************************************************************************
uint32_t uart_interrupt_enterred = 0;
uint32_t uart_dma_done = 0;
void
UART4IntHandler(void)
{
uint32_t ui32Status;
uint32_t ui32Mode;
uart_interrupt_enterred++;
//
// Read the interrupt status of the UART.
//
ui32Status = ROM_UARTIntStatus(UART4_BASE, 1);
//
// Clear any pending status, even though there should be none since no UART
// interrupts were enabled. If UART error interrupts were enabled, then
// those interrupts could occur here and should be handled. Since uDMA is
// used for both the RX and TX, then neither of those interrupts should be
// enabled.
//
ROM_UARTIntClear(UART4_BASE, ui32Status);
//
// Check the DMA control table to see if the ping-pong "A" transfer is
// complete. The "A" transfer uses receive buffer "A", and the primary
// control structure.
//
//
ui32Mode = ROM_uDMAChannelModeGet(UDMA_CH19_UART4TX | UDMA_PRI_SELECT);
//
// If the UART4 DMA TX channel is disabled, that means the TX DMA transfer
// is done.
//
if(!ROM_uDMAChannelIsEnabled(UDMA_CH19_UART4TX))
{
uart_dma_done++;
ROM_UARTDMADisable(UART4_BASE, UART_DMA_TX);
//
// Start another DMA transfer to UART4 TX.
//
/*ROM_uDMAChannelTransferSet(UDMA_CH19_UART4TX | UDMA_PRI_SELECT,
UDMA_MODE_BASIC, g_ui8TxBuf,
(void *)(UART4_BASE + UART_O_DR),
sizeof(g_ui8TxBuf));
//
// The uDMA TX channel must be re-enabled.
//
ROM_uDMAChannelEnable(UDMA_CH19_UART4TX);*/
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Initializes the UART4 peripheral and sets up the TX and RX uDMA channels.
// The UART is configured for loopback mode so that any data sent on TX will be
// received on RX. The uDMA channels are configured so that the TX channel
// will copy data from a buffer to the UART TX output. And the uDMA RX channel
// will receive any incoming data into a pair of buffers in ping-pong mode.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
InitUART4Transfer(void)
{
uint_fast16_t ui16Idx;
//
// Enable the peripherals used by this example.
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOK);
//
// Set GPIO A0 and A1 as UART pins.
//
//GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA3_U4TX);
//ROM_GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PK0_U4RX);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PK1_U4TX);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
//
// Fill the TX buffer with a simple data pattern.
//
for(ui16Idx = 0; ui16Idx < UART_TXBUF_SIZE; ui16Idx++)
{
g_ui8TxBuf[ui16Idx] = 'c';
}
//
// Enable the UART peripheral, and configure it to operate even if the CPU
// is in sleep.
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART4);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralSleepEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART4);
//
// Configure the UART communication parameters.
//
ROM_UARTConfigSetExpClk(UART4_BASE, g_ui32SysClock, 3000000,
UART_CONFIG_WLEN_8 | UART_CONFIG_STOP_ONE |
UART_CONFIG_PAR_NONE);
//
// Set both the TX and RX trigger thresholds to 4. This will be used by
// the uDMA controller to signal when more data should be transferred. The
// uDMA TX and RX channels will be configured so that it can transfer 4
// bytes in a burst when the UART is ready to transfer more data.
//
ROM_UARTFIFOLevelSet(UART4_BASE, UART_FIFO_TX4_8, UART_FIFO_RX4_8);
//
// Enable the UART for operation, and enable the uDMA interface for both TX
// and RX channels.
//
ROM_UARTEnable(UART4_BASE);
ROM_UARTDMAEnable(UART4_BASE, UART_DMA_TX);
//
// Put the attributes in a known state for the uDMA UART4TX channel. These
// should already be disabled by default.
//
uDMAChannelAssign(UDMA_CH19_UART4TX);
ROM_uDMAChannelAttributeDisable(UDMA_CH19_UART4TX,
UDMA_ATTR_ALTSELECT |
UDMA_ATTR_HIGH_PRIORITY |
UDMA_ATTR_REQMASK);
//
// Set the USEBURST attribute for the uDMA UART TX channel. This will
// force the controller to always use a burst when transferring data from
// the TX buffer to the UART. This is somewhat more efficient bus usage
// than the default which allows single or burst transfers.
//
ROM_uDMAChannelAttributeEnable(UDMA_CH19_UART4TX, UDMA_ATTR_USEBURST);
//
// Configure the control parameters for the UART TX. The uDMA UART TX
// channel is used to transfer a block of data from a buffer to the UART.
// The data size is 8 bits. The source address increment is 8-bit bytes
// since the data is coming from a buffer. The destination increment is
// none since the data is to be written to the UART data register. The
// arbitration size is set to 4, which matches the UART TX FIFO trigger
// threshold.
//
ROM_uDMAChannelControlSet(UDMA_CH19_UART4TX | UDMA_PRI_SELECT,
UDMA_SIZE_8 | UDMA_SRC_INC_8 |
UDMA_DST_INC_NONE |
UDMA_ARB_4);
//
// Set up the transfer parameters for the uDMA UART TX channel. This will
// configure the transfer source and destination and the transfer size.
// Basic mode is used because the peripheral is making the uDMA transfer
// request. The source is the TX buffer and the destination is the UART
// data register.
//
//
ROM_uDMAChannelTransferSet(UDMA_CH19_UART4TX | UDMA_PRI_SELECT,
UDMA_MODE_BASIC, g_ui8TxBuf,
(void *)(UART4_BASE + UART_O_DR),
sizeof(g_ui8TxBuf));
//
// Now both the uDMA UART TX and RX channels are primed to start a
// transfer. As soon as the channels are enabled, the peripheral will
// issue a transfer request and the data transfers will begin.
//
ROM_uDMAChannelEnable(UDMA_CH19_UART4TX);
//
// Enable the UART DMA TX/RX interrupts.
//
ROM_UARTIntEnable(UART4_BASE, UART_INT_DMATX);
//
// Enable the UART peripheral interrupts.
//
ROM_IntEnable(INT_UART4);
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Configure the UART and its pins. This must be called before UARTprintf().
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
ConfigureUART(void)
{
//
// Enable the GPIO Peripheral used by the UART.
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
//
// Enable UART0
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART0);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralSleepEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART0);
//
// Configure GPIO Pins for UART mode.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA0_U0RX);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA1_U0TX);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
//
// Initialize the UART for console I/O.
//
UARTStdioConfig(0, 115200, g_ui32SysClock);
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This example demonstrates how to use the uDMA controller to transfer data
// between memory buffers and to and from a peripheral, in this case a UART.
// The uDMA controller is configured to repeatedly transfer a block of data
// from one memory buffer to another. It is also set up to repeatedly copy a
// block of data from a buffer to the UART output. The UART data is looped
// back so the same data is received, and the uDMA controlled is configured to
// continuously receive the UART data using ping-pong buffers.
//
// The processor is put to sleep when it is not doing anything, and this allows
// collection of CPU usage data to see how much CPU is being used while the
// data transfers are ongoing.
//
//*****************************************************************************
int
main(void)
{
//
// Set the clocking to run directly from the crystal at 120MHz.
//
g_ui32SysClock = MAP_SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ |
SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN |
SYSCTL_USE_PLL |
SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_480), 120000000);
//
// Enable peripherals to operate when CPU is in sleep.
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralClockGating(true);
//
// Enable the GPIO port that is used for the on-board LED.
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPION);
//
// Enable the GPIO pins for the LED (PN0).
//
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTN_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0);
//
// Initialize the UART.
//
//ConfigureUART();
//UARTprintf("\033[2J\033[H");
//UARTprintf("uDMA for UART4TX Example \n");
//
// Enable the uDMA controller at the system level. Enable it to continue
// to run while the processor is in sleep.
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UDMA);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralSleepEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UDMA);
//
// Enable the uDMA controller error interrupt. This interrupt will occur
// if there is a bus error during a transfer.
//
ROM_IntEnable(INT_UDMAERR);
//
// Enable the uDMA controller.
//
ROM_uDMAEnable();
//
// Point at the control table to use for channel control structures.
//
ROM_uDMAControlBaseSet(pui8ControlTable);
//
// Initialize the uDMA UART transfers.
//
InitUART4Transfer();
//
// Loop forever with the CPU not sleeping, so the debugger can connect.
//
while(1)
{
//
// Turn on the LED.
//
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTN_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0, GPIO_PIN_0);
//
// Delay for a bit.
//
SysCtlDelay(g_ui32SysClock / 20 / 3);
//
// Turn off the LED.
//
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTN_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0, 0);
//
// Delay for a bit.
//
SysCtlDelay(g_ui32SysClock / 20 / 3);
}
}