Part Number: TMS570LS3137
Other Parts Discussed in Thread: HALCOGEN
Hello.
I've attached a SDRAM over EMIF.
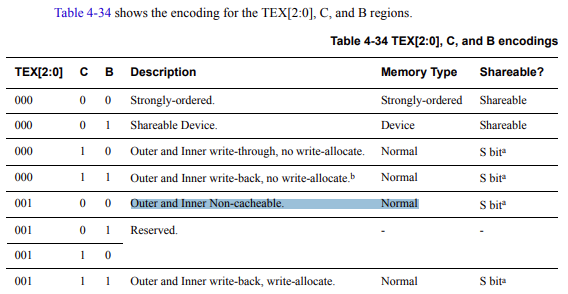
Now I've tried some memory configurations and if unaligned writes to the SDRAM are working (always with enabled MPU):
For "strongly order" and "device" configuration an unaligned write is not possible.
For "cacheable bufferable" an unaligend write is possible.
Also if MPU is disabled the unaligned write is not possible.
But which memory configuration is the right one?
Thanks and BR
Christian