Other Parts Discussed in Thread: EK-TM4C1294XL,
I have a custom PCB with a TM4C129ENCZADT3 MCU that I am trying to get the enet_uip example for the EK-TM4C1294XL launchpad board to work with the TM4C129ENCZADT3 MCU.
I start by testing the enet_uip example project on the EK-TM4C1294XL to check that it is working correctly. In order to get this project working on the custom board I had to uncomment,
#define USE_STATIC_IP
To set a static ip address on the launchpad and the custom board.
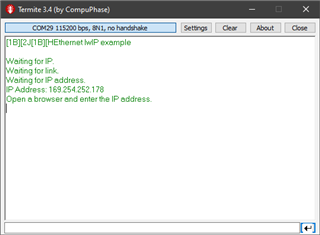
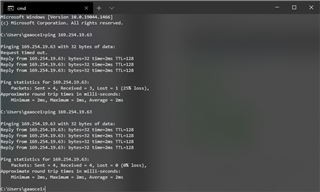
My PC has a static ip of 169.254.19.62, and the EK-TM4C1294XL has a static ip of 169.254.19.63. After programming the EK-TM4C1294XL I can send ping requests to the launchpad and can see packets being sent back to the PC.
Below is debug output from the launchpad. Packets are being sent in response to a ping request.
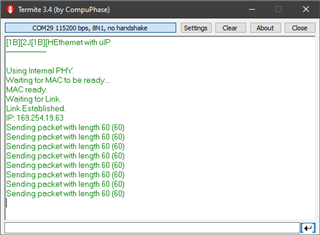
Below is the PC sending packets to the launchpad,
I attempt the change the example enet_uip project to work with the custom PCB that has a TM4C129ENCZADT3 MCU.
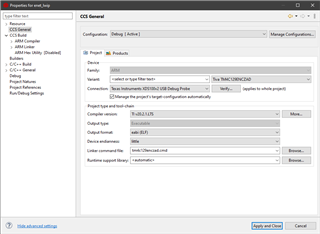
I first go to the project properties and change the Device and Connection:
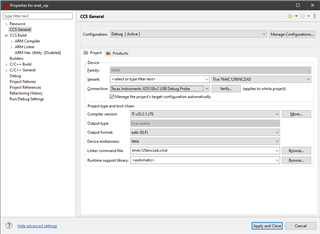
After clicking apply and close CCS seems to add a new linker command file, and startup source file.
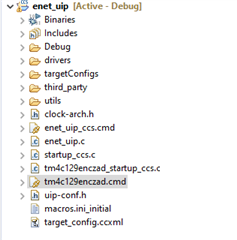
I modified tm4c129enczad_startup_ccs.c so that it matches startup_ccs.c and modified tm4c129enczad.cmd so that it matches enet_uip_ccs.cmd. After changing these files, the old files from the example project are removed.
A MAC address is programmed into the custom PCB successfully.
CORTEX_M4_0: GEL Output: Memory Map Initialization Complete CORTEX_M4_0: User Register operation... CORTEX_M4_0: Writing the following value to Register0 (9a9413) and Register1 (2af7e2) translated from the given MAC address CORTEX_M4_0: Programmed value committing to User Register 0 CORTEX_M4_0: Programmed value was committed to User Register 0 CORTEX_M4_0: Programmed value committing to User Register 1 CORTEX_M4_0: Programmed value was committed to User Register 1 CORTEX_M4_0: Operation completed successfully. CORTEX_M4_0: User Register operation... CORTEX_M4_0: MAC address value: 13-94-9a-e2-f7-2a CORTEX_M4_0: Operation completed successfully.
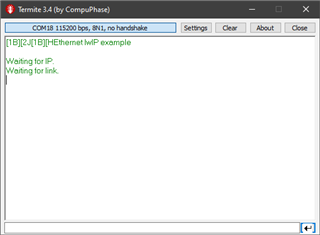
After programming the custom pcb I can not get a link to be established. The program sits at Waiting for Link.
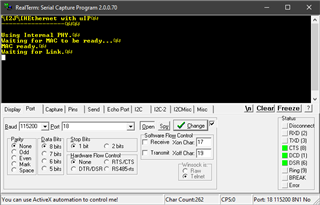
I am not sure if this is a software or hardware problem. I have tried multiple ethernet switches and CAT5e cables with no success. Schematics and gerber files are attached for the custom PCB. Does anyone have any suggestions?
Thanks,
Allan