Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TM4C129EKCPDT,
I am working with a PCB that needs pin 62 of the TM4C129 MCU to be driven using PWM. That is straightforward enough if the MCU part number is known at compile time. But I would like to make it possible to use any of the TQFP-packaged TM4C129 variants without having to change the software. About half of the parts (e.g. TM4C1290NCPDT) assign different functions to some pins (51-63) than other parts do (e.g. TM4C129EKCPDT). Pin 62 is PK4/PWM6 on the former and PK5/PWM7 on the latter. I would like to be able to detect at runtime which port/PWM needs to be configured to drive pin 62.
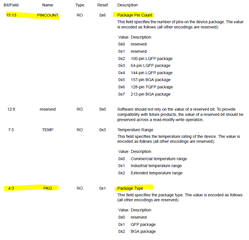
I figured out how to do this by directly reading the MCU's Device Identification register and comparing with a list of PARTNO values from the datasheets, but I wondered if there was a better way. Ideally, I would like to use something like SysCtlPeripheralPresent() that would indicate which pinout the current MCU uses, so I wouldn't have to maintain a list of PARTNO values (actually the maintenance isn't so bad, but actually testing that I got it right would require loading PCBs with each of the eight different MCU parts).
This is what I am doing now:
#define DeviceIdentification1 (*( (volatile uint32_t*) ( 0x400FE000 + 0x004 ) ) )
const uint32_t ReadOfDID1 = DeviceIdentification1; // Read the MCU's DID1 register.
const uint32_t ReadOfPARTNO = ( ReadOfDID1 >> 16 ) & 0x000000FF; // Extract the PARTNO field.
tracepointLogWithCommentAndValueMacro("Device Identification 1 register: 0x%08X", ReadOfDID1 );
tracepointLogWithCommentAndValueMacro("PARTNO field: 0x%08X", ReadOfPARTNO );
// Parts with PK4/PWM6 on pin 62.
#define PARTNO_TM4C1290NCPDT (0x19)
// Parts with PK5/PWM7 on pin 62.
#define PARTNO_TM4C129EKCPDT (0x35)
#warning "Expand this to test more CPU variants."
if( ReadOfPARTNO == PARTNO_TM4C1290NCPDT )
{
Thanks,
Steve
P.S. FWIW, this wouldn't be an issue if the functions which are on MCU pins 59-62 on some parts weren't shifted over by one (to pins 60-63) on the other half of the parts, but of course it is too late to change that now.