Hello,
I want to connect my PC to my TM4C1294NCZAD over a direct ethernet connection using lwIP, and have been porting the lwIP project "enet_tcpecho_client_lwip" to do so (see SPNA 248: TM4C129x Ethernet Applications for Lightweight IP).
I am able to communicate with the MCU using DHCP over my company's network, but have not been able to connect using static addressing. Below is an image of my defined IP address variables. I defined the server (PC) address statically on my PC ethernet port. The last three lines are arbitrary addresses for the client (MCU) that match the server address.
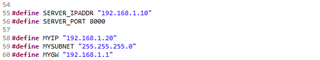
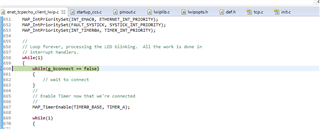
When I use the IPADDR_USE_STATIC in lwIPInit and call tcp_connect (see two images below), the ConnectCallback function never gets called and the g_bconnect variable never gets toggled (see next two images).
lwIPInit

calling tcp_connect after lwIPInit

Connect callback function (never gets called)

above function never gets called, g_bconnect never gets toggled.
I have changed LWIP_DHCP and LWIP_AUTOIP to 0 in lwipopts.h (as per SPNA 248: TM4C129x Ethernet Applications for Lightweight IP).
Any suggestions or comments about why I am not receiving a connection signal from my PC and why my ConnectCallback function isn't getting called would be appreciated!
Below is the full main c file.
//*****************************************************************************
//
// enet_tcpecho_client_lwip.c - Sample Echo Client Application using lwIP.
//
//
//
//*****************************************************************************
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "inc/hw_ints.h"
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_emac.h"
#include "driverlib/flash.h"
#include "driverlib/interrupt.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/rom_map.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/systick.h"
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "driverlib/timer.h"
#include "drivers/pinout.h"
#include "utils/lwiplib.h"
#include "utils/ustdlib.h"
#include "utils/uartstdio.h"
#include "lwip/debug.h"
#include "lwip/stats.h"
#include "lwip/tcp.h"
#include "lwip/inet.h"
//*****************************************************************************
//
//! This code is a modification of enet_tcpecho_client_lwip for the purposes of
//! sending messages perpetually so that an oscilloscope can see the data and
//! form an eye diagram.
//!
//! For additional details on lwIP, refer to the lwIP web page at:
//! http://savannah.nongnu.org/projects/lwip/
//
//*****************************************************************************
#define PART_TM4C1294NCZAD 1
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Defines for the server IP address and PORT numbers.
//
// TODO: User must change these settings per their application.
//
//*****************************************************************************
//#define SERVER_IPADDR "10.33.10.12"
#define SERVER_IPADDR "192.168.1.10"
#define SERVER_PORT 8000
#define MYIP "192.168.1.20"
#define MYSUBNET "255.255.255.0"
#define MYGW "192.168.1.1"
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Defines for setting up the system clock.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#define SYSTICKHZ 8
#define SYSTICKMS (1000 / SYSTICKHZ)
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Interrupt priority definitions. The top 3 bits of these values are
// significant with lower values indicating higher priority interrupts.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#define SYSTICK_INT_PRIORITY 0x80
#define ETHERNET_INT_PRIORITY 0xC0
#define TIMER_INT_PRIORITY 0
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The variable g_ui32SysClock contains the system clock frequency in Hz.
//
//*****************************************************************************
uint32_t g_ui32SysClock;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The current IP address.
//
//*****************************************************************************
uint32_t g_ui32IPAddress;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Global counter to keep track the duration the connection has been idle.
//
//*****************************************************************************
uint32_t g_ui32tcpPollTick = 0;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Volatile global flag to manage LED blinking, since it is used in interrupt
// and main application. The LED blinks at the rate of SYSTICKHZ.
//
//*****************************************************************************
//volatile bool g_bLED;
volatile bool g_bsend;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Global flag indicating when the IP address is acquired
//
//*****************************************************************************
bool g_bIPAddrValid = 0;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Global flag indicating when the client connects to the server
//
//*****************************************************************************
bool g_bconnect = 0;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Global LwIP PCB structure and error variables.
//
//*****************************************************************************
err_t err;
static struct tcp_pcb *tpcb;
static char *g_string = "Hello World! \n\r ";
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The error routine that is called if the driver library encounters an error.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#ifdef DEBUG
void
__error__(char *pcFilename, uint32_t ui32Line)
{
}
#endif
//#define UART_DEBUG_OUT 1
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Display an lwIP type IP Address.
//
//*****************************************************************************
//void
//DisplayIPAddress(uint32_t ui32Addr)
//{
// char pcBuf[16];
// // Convert the IP Address into a string.
// usprintf(pcBuf, "%d.%d.%d.%d", ui32Addr & 0xff, (ui32Addr >> 8) & 0xff,
// (ui32Addr >> 16) & 0xff, (ui32Addr >> 24) & 0xff);
// UARTprintf(pcBuf);
//}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Required by lwIP library to support any host-related timer functions.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
lwIPHostTimerHandler(void)
{
uint32_t ui32NewIPAddress;
//
// Get the current IP address.
//
ui32NewIPAddress = lwIPLocalIPAddrGet();
//
// See if the IP address has changed.
//
if(ui32NewIPAddress != g_ui32IPAddress)
{
//
// See if there is an IP address assigned.
//
if(ui32NewIPAddress == 0xffffffff)
{
//
// Indicate that there is no link.
//
// UARTprintf("Waiting for link.\n");
}
else if(ui32NewIPAddress == 0)
{
//
// There is no IP address, so indicate that the DHCP process is
// running.
//
// UARTprintf("Waiting for IP address.\n");
}
else
{
g_bIPAddrValid = 1;
//
// Display the new IP address.
//
// UARTprintf("IP Address: ");
// DisplayIPAddress(ui32NewIPAddress);
}
//
// Save the new IP address.
//
g_ui32IPAddress = ui32NewIPAddress;
}
//
// If there is not an IP address.
//
if((ui32NewIPAddress == 0) || (ui32NewIPAddress == 0xffffffff))
{
//
// Do nothing and keep waiting.
//
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The interrupt handler for the SysTick interrupt.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
SysTickIntHandler(void)
{
//
// Call the lwIP timer handler.
//
lwIPTimer(SYSTICKMS);
//
// Tell the application to change the state of the LED (in other words
// blink).
//
// g_bLED = true;
// if(g_bconnect)
// {
// g_bsend = true;
// }
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The interrupt handler for the first timer interrupt.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
Timer0IntHandler(void)
{
//
// Clear the timer interrupt.
//
MAP_TimerIntClear(TIMER0_BASE, TIMER_TIMA_TIMEOUT);
g_bsend = true;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The EchoReceive is a callback function when payload is received from the
// remote host
//
//*****************************************************************************
//err_t
//EchoReceive(void *arg, struct tcp_pcb *tpcb, struct pbuf *p, err_t err)
//{
// int len;
// char *header = "Client: ";
// int header_len = strlen(header);
// char mydata[1024];
//
// //
// // Check for null pointer.
// //
// if (p == NULL)
// {
// //
// // If null pointer has been passed in, close the connection.
// //
//// UARTprintf("The remote host closed the connection.\n");
// tcp_close(tpcb);
// return ERR_ABRT;
// }
// else
// {
// tcp_recved(tpcb, p->tot_len);
//
////#if UART_DEBUG_OUT
//// UARTprintf("Receive %d bytes from the remote host.\n", p->tot_len);
////#endif
//
// //
// // Determine the size of the payload.
// //
// len = p->tot_len + header_len;
//
// strcpy(mydata, header);
// strcat(mydata, (char *)p->payload);
//
// //
// // Free the packet buffer.
// //
// pbuf_free(p);
//
// //
// // Check output buffer capacity.
// //
// if (len > tcp_sndbuf(tpcb))
// len= tcp_sndbuf(tpcb);
//
// //
// // Queue the data to transmit.
// //
// err = tcp_write(tpcb, mydata, len, 0);
// if (err == ERR_OK)
// {
////#if UART_DEBUG_OUT
//// UARTprintf("Echo the data out\n");
////#endif
// }
// else if(err == ERR_MEM)
// {
// //
// // We are low on memory, try later, defer to poll.
// //
//// UARTprintf("Low on memory.\n");
//
// }
// else
// {
// //
// // Other problems to take care of.
// //
//// UARTprintf("Other problems.\n");
// }
//
// //
// // No need for a callback when transmitting.
// //
// tcp_sent(tpcb, NULL);
// }
//
// return ERR_OK;
//}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Function to send TCP packets to the server
//
//*****************************************************************************
uint32_t
TcpSendPacket(char *string)
{
//
// Queues the data pointed to by string.
//
err = tcp_write(tpcb, string, strlen(string), TCP_WRITE_FLAG_COPY);
if (err)
{
// UARTprintf("ERROR: Code: %d (TcpSendPacket :: tcp_write)\n", err);
return 1;
}
//
// Transmit the data.
//
err = tcp_output(tpcb);
//
// Report any error that occurs.
//
if (err)
{
// UARTprintf("ERROR: Code: %d (TcpSendPacket :: tcp_output)\n", err);
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Callback function when the client establishes a successful connection to
// the remote host.
//
//*****************************************************************************
err_t
ConnectCallback(void *arg, struct tcp_pcb *tpcb, err_t err)
{
// char *string = "Hello World! \n\r ";
if (err == ERR_OK){
//#if UART_DEBUG_OUT
// UARTprintf("Connection Established.\n");
//#endif
g_bconnect = true;
//
// Register the callback function EchoReceive when
// receiving data
//
tcp_recv(tpcb, NULL);
tcp_sent(tpcb, NULL);
//#if UART_DEBUG_OUT
// UARTprintf("Sending a greeting message to the Server\n");
//#endif
TcpSendPacket(g_string);
return 0;
}
else
{
// UARTprintf("No Connection Established.\n");
return 1;
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Function to create a LwIP client.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
EchoClientInit(void)
{
//
// Create IP address structure.
//
struct ip_addr server_addr;
//
// Create a new TCP control block.
//
tpcb = tcp_new();
if (tpcb != NULL)
{
//
// Assign destination server IP address.
//
server_addr.addr = inet_addr(SERVER_IPADDR);
//
// Configure destination IP address and port.
//
err = tcp_connect(tpcb, &server_addr, SERVER_PORT, ConnectCallback);
// if (err)
// {
// UARTprintf("ERROR: Code: %d (tcp_connect)\n", err);
// }
//
// UARTprintf("\nPCB CREATED\n");
}
else
{
memp_free(MEMP_TCP_PCB, tpcb);
// UARTprintf("PCB NOT CREATED\n");
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This example demonstrates the use of the Ethernet Controller.
//
//*****************************************************************************
int
main(void)
{
uint32_t ui32User0, ui32User1;
uint8_t pui8MACArray[8];
//
// Make sure the main oscillator is enabled because this is required by
// the PHY. The system must have a 25MHz crystal attached to the OSC
// pins. The SYSCTL_MOSC_HIGHFREQ parameter is used when the crystal
// frequency is 10MHz or higher.
//
SysCtlMOSCConfigSet(SYSCTL_MOSC_HIGHFREQ);
//
// Run from the PLL at 120 MHz.
// Note: SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_240 is a new setting provided in TivaWare 2.2.x and
// later to better reflect the actual VCO speed due to SYSCTL#22.
//
g_ui32SysClock = MAP_SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ |
SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN |
SYSCTL_USE_PLL |
SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_240), 120000000);
//
// Configure the device pins.
//
// PinoutSet(true, false);
//
// Configure UART.
//
// UARTStdioConfig(0, 115200, g_ui32SysClock);
//
// Clear the terminal and print banner.
//
// UARTprintf("\033[2J\033[H");
// UARTprintf("Ethernet lwIP TCP echo client example\n\n");
// //
// // Configure Port N1 for as an output for the animation LED.
// //
// MAP_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTN_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1);
//
// Configure Ethernet LEDs instead
// EN0LED1: PK6
// EN0LED2: PK5
//
// Step 1: MAP_GPIOPinConfigure()
// Step 2: MAP_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput()
// Step 3: MAP_GPIOPadConfigSet()
// Step 3: MAP_GPIOPinWrite()
//
MAP_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOK);
while(!MAP_SysCtlPeripheralReady(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOK))
{
}
MAP_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PK6_EN0LED1);
MAP_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PK5_EN0LED2);
MAP_GPIOPinTypeEthernetLED(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5 | GPIO_PIN_6);
// //
// // Step 1: Configure Ethernet GPIO Pins PK6 and PK5
// // (Potential Alternative: Use MAP_GPIOPinTypeEthernetLED())
// //
//
// //
// // Step 2: Configure pins as output
// //
// MAP_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6);
// MAP_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5);
//
//
// //
// // Step 3: Configure pins at 4mA or 8mA
// //
// MAP_GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6, GPIO_STRENGTH_4MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD);
// MAP_GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_STRENGTH_4MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD);
//
// //
// // Step 4: Initialize LEDs to OFF (0)
// //
// MAP_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6, GPIO_PIN_6);
// MAP_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_PIN_5);
//
// Configure SysTick for a periodic interrupt.
//
MAP_SysTickPeriodSet(g_ui32SysClock / SYSTICKHZ);
MAP_SysTickEnable();
MAP_SysTickIntEnable();
//
// Configure the hardware MAC address for Ethernet Controller filtering of
// incoming packets. The MAC address will be stored in the non-volatile
// USER0 and USER1 registers.
//
MAP_FlashUserGet(&ui32User0, &ui32User1);
if((ui32User0 == 0xffffffff) || (ui32User1 == 0xffffffff))
{
//
// We should never get here. This is an error if the MAC address has
// not been programmed into the device. Exit the program.
// Let the user know there is no MAC address
//
// UARTprintf("No MAC programmed!\n");
while(1)
{
}
}
//
// Tell the user what we are doing just now.
//
// UARTprintf("Waiting for IP.\n");
//
// Convert the 24/24 split MAC address from NV ram into a 32/16 split MAC
// address needed to program the hardware registers, then program the MAC
// address into the Ethernet Controller registers.
//
pui8MACArray[0] = ((ui32User0 >> 0) & 0xff);
pui8MACArray[1] = ((ui32User0 >> 8) & 0xff);
pui8MACArray[2] = ((ui32User0 >> 16) & 0xff);
pui8MACArray[3] = ((ui32User1 >> 0) & 0xff);
pui8MACArray[4] = ((ui32User1 >> 8) & 0xff);
pui8MACArray[5] = ((ui32User1 >> 16) & 0xff);
//
// Set up timer interrupt
//
MAP_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_TIMER0);
while(!MAP_SysCtlPeripheralReady(SYSCTL_PERIPH_TIMER0))
{
}
MAP_TimerConfigure(TIMER0_BASE, TIMER_CFG_PERIODIC);
MAP_TimerLoadSet(TIMER0_BASE, TIMER_A, 3*g_ui32SysClock);
MAP_TimerIntEnable(TIMER0_BASE, TIMER_TIMA_TIMEOUT);
MAP_IntEnable(INT_TIMER0A);
//
// Initialize the lwIP library, using DHCP (now static).
//
lwIPInit(g_ui32SysClock, pui8MACArray, inet_addr(MYIP), inet_addr(MYSUBNET), inet_addr(MYGW), IPADDR_USE_STATIC);
// lwIPInit(g_ui32SysClock, pui8MACArray, ntohl(inet_addr(MYIP)), ntohl(inet_addr(MYSUBNET)), ntohl(inet_addr(MYGW)), IPADDR_USE_STATIC);
// lwIPInit(g_ui32SysClock, pui8MACArray, 0, 0, 0, IPADDR_USE_DHCP);
//
// Wait here until a valid IP address is obtained before
// starting the client connection to the server.
//
while (g_bIPAddrValid == 0);
//
// Initialize the client.
//
EchoClientInit();
//
// Set the interrupt priorities. We set the SysTick interrupt to a higher
// priority than the Ethernet interrupt to ensure that the file system
// tick is processed if SysTick occurs while the Ethernet handler is being
// processed. This is very likely since all the TCP/IP and HTTP work is
// done in the context of the Ethernet interrupt.
//
MAP_IntPrioritySet(INT_EMAC0, ETHERNET_INT_PRIORITY);
MAP_IntPrioritySet(FAULT_SYSTICK, SYSTICK_INT_PRIORITY);
MAP_IntPrioritySet(INT_TIMER0A, TIMER_INT_PRIORITY);
//
// Loop forever, processing the LED blinking. All the work is done in
// interrupt handlers.
while(1)
{
while(g_bconnect == false)
{
// wait to connect
}
//
// Enable Timer now that we're connected
//
MAP_TimerEnable(TIMER0_BASE, TIMER_A);
while(1)
{
while(g_bsend == false)
{
}
//
// Clear the flag.
//
// g_bLED = false;
g_bsend = false;
//
// Toggle the LEDs.
//
// MAP_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6,
// (MAP_GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6) ^
// GPIO_PIN_6));
// MAP_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5,
// (MAP_GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5) ^
// GPIO_PIN_5));
//
// Send string packet to server
//
TcpSendPacket(g_string);
}
}
}

