Part Number: TM4C123GH6PM
Hello,
I would like to make my tm4c123 device, an i2c slave. I would like to read and write multiple bytes to different registers. Based on slave_receive_int.c I have devised the following:
void I2C0SlaveIntHandler(void) {
// clear data interrupt
HWREG(I2C0_BASE + I2C_O_SICR) = I2C_SICR_DATAIC;
uint8_t startDetected = 0;
uint8_t stopDetected = 0;
if(HWREG(I2C0_BASE + I2C_O_SRIS) & I2C_SLAVE_INT_START) {
startDetected = 1;
HWREG(I2C0_BASE + I2C_O_SICR) = I2C_SICR_STARTIC;
} else if(HWREG(I2C0_BASE + I2C_O_SRIS) & I2C_SLAVE_INT_STOP) {
stopDetected = 1;
HWREG(I2C0_BASE + I2C_O_SICR) = I2C_SICR_STOPIC;
}
switch(I2CSlaveStatus(I2C0_BASE) & (I2C_SCSR_TREQ | I2C_SCSR_RREQ)) {
// data received
case(I2C_SLAVE_ACT_RREQ):
if(startDetected) { rxBufferIdx = 0; }
if(I2CSlaveStatus(I2C0_BASE) & I2C_SCSR_FBR) {
//currentState = SLAVE_RX;
}
rxBuffer[rxBufferIdx] = I2CSlaveDataGet(I2C0_BASE);
rxBufferIdx++;
break;
// data requested
case(I2C_SLAVE_ACT_TREQ):
if(startDetected) { txBufferIdx = 0; }
I2CSlaveDataPut(I2C0_BASE, txBuffer[txBufferIdx]);
txBufferIdx++;
break;
default:
break;
}
if(stopDetected/* && currentState == SLAVE_RX*/) {
}
g_i2c_ready = true;
}
And it is somewhat working, but not as expected.
I have the following questions:
1. is there an example that contains the state machine for a i2c slave device implemented in tm4c. in other devices like msp430 series, the i2c slave examples contain a fsm based handler for received data, them tm4c123 lacks such example. I googled, but I was not able to find an example.
2. how can i get the first byte? when the state is I2C_SLAVE_ACT_RREQ_FBR? when i2c write starts from master device, i would like to use the first byte as address, and then use the rest of the data to do different things.
3. how and where do we the first byte for read?
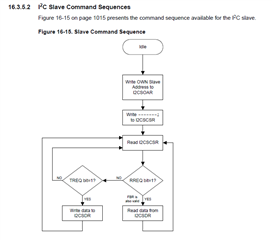
4. The interrupt handler is dealing with data, start, stop conditions/states. Are there any other states? On page 1015 of the datasheet, there is a "Figure 16-15. Slave Command Sequence" Is there a more detailed illustration of this?
Best Regards,
Can