Other Parts Discussed in Thread: HALCOGEN
Hi,
Can you illustrate how to use use NMPU module to detect stack underflow fault? Thanks a lot.
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
Do you mean MPU or NMPU?
MPU is for CPU, but NMPU is for other master such as DMA. The stack is used by CPU only.
A stack is a LIFO (last in first out) linear data structure. Push and Pop are the basic operations for stack.
The push operation adds a new item to the top of the stack. If the stack is full and does not contain enough space to accept the given item, the stack is then considered to be in an overflow state.
The pop operation removes an item from the top of the stack. If the stack is empty, then it goes into underflow state (It means no items are present in stack to be removed).
You can use MPU subregion or overlay region for stack protection, Please refer to ARM Cortex-R TRM.
Hi QJ,
I just find NMPU in TRM. Where is MPU and how to get the introduction about "MPU subregion or overlay region for stack protection"?
Hi QJ,
How to use MPU subregion or overlay region for stack protection?
Is there any avaliable API function?
Is there any avaliable API function?
We don't have API to configure MPU regions for stack protection. HALCOGen generates several APIs for MPU region operations (set, get, etc).
How to use MPU subregion or overlay region for stack protection?
Please refer to 7.1.2 of the ARM Cortex-R TRM
Hi QJ,
I don't find MPU related operation in HALCOGen program, but just NMPU.
Can you tell me directly whether or not we can detect stack underflow for RM57 CPU in our diagnostic program?
If yes, how to do it? Thanks a lot.
You can use sub-region or overlap region for stack overflow or stack underflow protection:
1. overflow
• allocate to region 1 the appropriate size for all stacks
• allocate to region 2 the minimum region size, 32 bytes, and position it at the end of the stack for the current process
• set the region 2 access permissions to No Access.
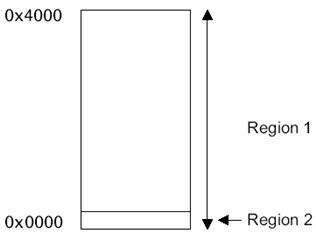 Stack region: 0x20 ~ 0x4000
Stack region: 0x20 ~ 0x4000
2. underflow
• allocate to region 1 the appropriate size for all stacks
• allocate to region 2 the minimum region size, 32 bytes, and position just above the stack region (0x3FE0~0x4000) for the current process
• set the region 2 access permissions to No Access.
Hi QJ,
In my understanding, it must cause permission fault if we just set the region 2 access permissions to No Access.
What's the purpose of the first two steps before the step "set the region 2 access permissions to No Access" for this test?
In my understanding, it must cause permission fault if we just set the region 2 access permissions to No Access.
You are correct. The permission fault will be generated when stack is overflowed or underflowed.
What's the purpose of the first two steps before the step "set the region 2 access permissions to No Access" for this test?
When stack is full, the push operation will push data to region #2 and generate permission fault.
When stack is empty, the pop operation from region #2 will generate permission fault too.
Hi QJ,
Got it. Thanks.
The problem is how we get the access permission fault in application program. By interrupt or CPU abort?