Hi,
My example code for SPI (using SSI0) is working on TI Launchpad. See code below
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <inc/hw_types.h>
#include <inc/hw_ssi.h>
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include <driverlib/gpio.h>
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "driverlib/ssi.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/uart.h"
#include "utils/uartstdio.h"
#include <string.h>
//#include "main.h"
// Number of bytes to Send.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#define NUM_SSI_DATA 4
#define HB_ENABLE 0x0080
#define HB_CONFIG 0x0002
#ifdef DEBUG
void
__error__(char *pcFilename, uint32_t ui32Line)
{
}
#endif
uint32_t ui32SysClocks;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This function sets up UART0 to be used for a console to display information
// as the example is running.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void InitConsole(void)
{
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART0);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA0_U0RX);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA1_U0TX);
GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
UARTStdioConfig(0, 9600, ui32SysClocks);
}
void InitSPI0(void){
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_SSI0);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3|GPIO_PIN_2|GPIO_PIN_4);
GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOM);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOB);
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5);
GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_STRENGTH_12MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD_WPU );
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_PIN_5);//PULL UP
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4);
GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4, GPIO_STRENGTH_12MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD_WPU );
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4, GPIO_PIN_4);//PULL UP
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA2_SSI0CLK);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA3_SSI0FSS);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA4_SSI0XDAT0);//Tx
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA5_SSI0XDAT1);//Rx
GPIOPinTypeSSI(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5 | GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_3 | GPIO_PIN_2);
//SSIConfigSetExpClk(SSI0_BASE, ui32SysClocks, SSI_FRF_MOTO_MODE_2, SSI_MODE_MASTER, 40000000, 16);
//SSIConfigSetExpClk(SSI0_BASE, ui32SysClocks, SSI_FRF_MOTO_MODE_0, SSI_MODE_MASTER, 1500000, 16);
SSIConfigSetExpClk(SSI0_BASE, ui32SysClocks, SSI_FRF_MOTO_MODE_1, SSI_MODE_MASTER, 1500000, 16);//negative edge triggered
}
void SPI_write(const uint8_t* dataBuffer, uint8_t count){
while(count--){
SSIDataPut(SSI0_BASE, *dataBuffer++);
}
while(SSIBusy(SSI0_BASE));
}
//*****************************************************************************
//Main function Entry.
//
//*****************************************************************************
int
main(void)
{
bool pDO_Status[24];
uint8_t ui8Do_Source_Sink;
// spiConfigbus stSpiConfig;
// i2cConfigbus stI2cConfig;
uint16_t aui16SpiTxBuffer[2];
uint16_t aui16SpiRxBuffer[2][2];
uint8_t aui8I2cTxBuffer[3];
uint8_t aui8I2cRxBuffer[3];
uint8_t i;
uint8_t dataTX[4] = {0x40, 0x4F, 0x4F, 0x04};
//uint8_t dataTX = 0x40;
uint8_t count;
//ui32SysClocks = SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_USE_PLL | SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_240), 120000000);
ui32SysClocks = SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_USE_PLL | SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_480), 120000000);
InitConsole();
UARTprintf("SPI -> Master to Slave\n");
UARTprintf("SPI Bit_Rate: 16-bit\n\n");
InitSPI0();
SSIEnable(SSI0_BASE);
// GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_PIN_5); //enable
dataTX[0] = (HB_ENABLE << 0 )| (HB_CONFIG << 0);//output high
SysCtlDelay(100);
SPI_write(dataTX, 1);
SysCtlDelay(100);//delay of
}
UARTprintf("Done transferring the data\r\n");
UARTprintf("----------------------------------------------------------------------");
UARTprintf("\r\n\n");
while(1);
}But when I modify it for my requirement (using SSI3) ,it's not working on Launchpad. See the code modified for SSI3 below.
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <inc/hw_types.h>
#include <inc/hw_ssi.h>
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include <driverlib/gpio.h>
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "driverlib/ssi.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/uart.h"
#include "utils/uartstdio.h"
#include <string.h>
//#include "main.h"
// Number of bytes to Send.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#define NUM_SSI_DATA 4
#define HB_ENABLE 0x0080
#define HB_CONFIG 0x0002
#ifdef DEBUG
void
__error__(char *pcFilename, uint32_t ui32Line)
{
}
#endif
uint32_t ui32SysClocks;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This function sets up UART0 to be used for a console to display information
// as the example is running.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void InitConsole(void)
{
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART0);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA0_U0RX);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA1_U0TX);
GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
UARTStdioConfig(0, 9600, ui32SysClocks);
}
void InitSPI0(void){
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_SSI0);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3|GPIO_PIN_2|GPIO_PIN_4);
GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOM);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOB);
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5);
GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_STRENGTH_12MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD_WPU );
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_PIN_5);//PULL UP
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4);
GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4, GPIO_STRENGTH_12MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD_WPU );
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4, GPIO_PIN_4);//PULL UP
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA2_SSI0CLK);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA3_SSI0FSS);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA4_SSI0XDAT0);//Tx
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA5_SSI0XDAT1);//Rx
GPIOPinTypeSSI(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5 | GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_3 | GPIO_PIN_2);
//SSIConfigSetExpClk(SSI0_BASE, ui32SysClocks, SSI_FRF_MOTO_MODE_2, SSI_MODE_MASTER, 40000000, 16);
//SSIConfigSetExpClk(SSI0_BASE, ui32SysClocks, SSI_FRF_MOTO_MODE_0, SSI_MODE_MASTER, 1500000, 16);
SSIConfigSetExpClk(SSI0_BASE, ui32SysClocks, SSI_FRF_MOTO_MODE_1, SSI_MODE_MASTER, 1500000, 16);//negative edge triggered
}
void InitSPI3(void){
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_SSI3);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOQ);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOP);
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_0);
GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3);
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1);//cs
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5);
GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_STRENGTH_12MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD_WPU );
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_PIN_5);//PULL UP
// GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_STRENGTH_12MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD_WPU );
// GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_PIN_5);//PULL UP
// GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4);
GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_STRENGTH_12MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD_WPU );
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_1);//PULL UP
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PQ0_SSI3CLK);
//GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA3_SSI0FSS);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PQ2_SSI3XDAT0);//Tx
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PQ3_SSI3XDAT1);//Rx
GPIOPinTypeSSI(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_3 | GPIO_PIN_2);
//SSIConfigSetExpClk(SSI0_BASE, ui32SysClocks, SSI_FRF_MOTO_MODE_2, SSI_MODE_MASTER, 40000000, 16);
//SSIConfigSetExpClk(SSI0_BASE, ui32SysClocks, SSI_FRF_MOTO_MODE_0, SSI_MODE_MASTER, 1500000, 16);
SSIConfigSetExpClk(SSI3_BASE, ui32SysClocks, SSI_FRF_MOTO_MODE_1, SSI_MODE_MASTER, 1500000, 16);//negative edge triggered
}
/*void SPI_write(const uint8_t* dataBuffer, uint8_t count){
while(count--){
SSIDataPut(SSI0_BASE, *dataBuffer++);
}
while(SSIBusy(SSI0_BASE));
}*/
void SPI_write_SSI3(const uint8_t* dataBuffer, uint8_t count){
while(count--){
SSIDataPut(SSI3_BASE, *dataBuffer++);
}
while(SSIBusy(SSI3_BASE));
}
//*****************************************************************************
//Main function Entry.
//
//*****************************************************************************
int
main(void)
{
bool pDO_Status[24];
uint8_t ui8Do_Source_Sink;
volatile uint32_t ui32Loop;
uint16_t aui16SpiTxBuffer[2];
uint16_t aui16SpiRxBuffer[2][2];
uint8_t aui8I2cTxBuffer[3];
uint8_t aui8I2cRxBuffer[3];
uint8_t i;
uint8_t dataTX[4] = {0x40, 0x4F, 0x4F, 0x04};
//uint8_t dataTX = 0x40;
uint8_t count;
//ui32SysClocks = SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_USE_PLL | SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_240), 120000000);
ui32SysClocks = SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_USE_PLL | SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_480), 120000000);
InitConsole();
UARTprintf("SPI -> Master to Slave\n");
UARTprintf("SPI Bit_Rate: 16-bit\n\n");
InitSPI3();
SSIEnable(SSI3_BASE);
dataTX[0] = (HB_ENABLE << 0 )| (HB_CONFIG << 0);//output high
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1, 0);
SysCtlDelay(100);
SPI_write_SSI3(dataTX, 1);
SysCtlDelay(100);//delay of
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_1);
UARTprintf("Done transferring the data\r\n");
UARTprintf("----------------------------------------------------------------------");
UARTprintf("\r\n\n");
while(1);
}
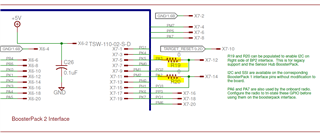
SSI3 is used in my schematic as below

Can you please guide if there's anything in the code that needs to be changed for SSI3 to run?
Thanks,
Kiran