Hello TI Team,
I'm currently trying to implement and use the Interconnect Firewalls in our project. During development a couple of questions arose which I want to address to you.
We want to use the Firewall as an additional safety measure with the MPU to separate cores from each other.
I am specifically interested in the exception handling of firewall faults.
SDK version in use 08.06.43
Documents referred to in this post:
[A] Technical Reference Manual AM64x/AM243x, literature number SPRUIM2F
[B] TISCI 08.06.04 software-dl.ti.com/.../index.html
[C] AM243x MCU+ SDK 08.06.00 User Guide dev.ti.com/.../node
For testing purposes I have configured the Firewall for DDR16SS0 (Firewall ID 1) from R5F_0_0 in main() running a freeRTOS.
I configured 7 regions tied to specific cores and purposes (private, dedicated shared memory for up to 2 cores) and 1 background region spanning the whole 2GB of DDR space.
When entering the initial freeRTOS task I provoke a fault by reading from firewalled memory.
1. Firewall configuration
[C] suggests using the firewall driver from <drivers/firewall.h>. Inspecting the implementation the driver configures firewall regions by directly writing to the registers.
As [B]-FirewallFAQ states that firewalls not owned by DMSC are only programmable through the TISCI interface only and "Firewall configuration registers are only writable by System Firmware".
Question: Don't these facts contradict each other? What is the preferred way of programming the firewalls?
2. Firewall exception registers
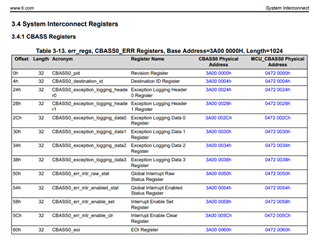
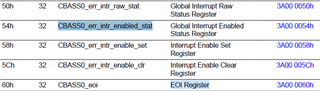
The chapter 3.3.2.1 in [A] mentions multiple bits in multiple registers:
- CBASS_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL[0]:DISABLE_F
- CBASS_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL[1] DISABLE_PEND
- CBASS_EXCEPTION_PEND_SET[0] PEND_SET
- CBASS_EXCEPTION_PEND_CLEAR[0] PEND_CLR
I could not find any reference in the subchapters under 3.4 System Interconnect Registers and the exact naming is never mentioned again in [A].
Question: Where can I find these registers? Are they under DMSC control?
3. CBASS Registers vs. CBASS_FW Registers
Chapter 3.4 System Interconnect Registers in document [A] contains subchapters called CBASS Registers and CBASS_FW Registers.
When reading the CBASS0_pid register from 0x3A000000 it returns plausible values. When reading CBASS_FW0_pid then 0 is returned
Question: To which of these collection of registers does the firewall functional description refer to? Which one shall be used for error handling?
Question: When provoking a Firewall exception by reading from firewalled memory - the CBASS_EXCEPTION_LOGGING registers all remain 0x0 when reading from DataAbort Handler. How can I retrieve the exception info?
4. CBASS_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0
The description in [A] for this register is "Lower 32 address bits (31:0) of the incoming transaction"
Question: What exactly is meant here as "incoming transaction"? Does this field correlate to the DFAR value when in DataAbort mode?
5. CBASS0_EXCEPTION_LOGGING registers contain data when halting on breakpoint entering main()
After power cycling the TMDS243EVM and running a debug session on R5F_0_0 I halt execution on entering main() for ~20 seconds.
I could observe from the Memory Browser that the exception logging registers starting at 0x3A000000 get updated with seemingly plausible data.
For example the CBASS_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 contains 0x39FFFFAC - an address which is observable concurrently in the Memory Browser.
Question: What could be causing this exception given that I am looking at the correct registers?
Greetings
Simon