Dear all
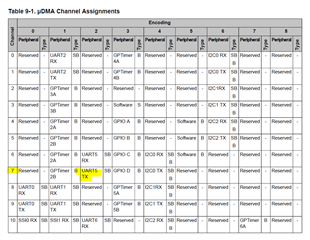
I am new to DMA and just had a basic understanding of the example in udma_demo, it uses UART1 and channel number is defined as
#define UDMA_CHANNEL_UART1TX 23
While I am going to use UART5 for Tx with DMA, and cannot find the definition for that, help please!
Regards!
Ping