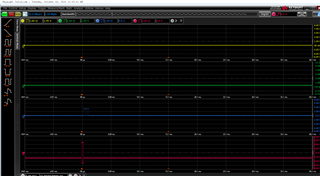
Tool/software:
I am having trouble figuring out why there is a long uart delay between receiving a packet of data and transmitting a packet of data.

The delay between receiving a packet and transmitting a packet is about 25ms.
Below is the code that is running in main.c.
int main()
{
//Vars
//Modbus
eMBErrorCode eStatus;
//1. Enable lazy stacking for interrupt handlers.
FPUEnable();
FPULazyStackingEnable();
//2. Run from the internal oscillator.
//SysCtlClockSet(SYSCTL_OSC_INT | SYSCTL_USE_OSC | SYSCTL_SYSDIV_1);
SysCtlClockSet(SYSCTL_OSC_INT | SYSCTL_USE_PLL | SYSCTL_SYSDIV_2_5);
//16MHz -> 400MHz PLL -> /5 -> 80MHz!
//3. Setup I2C for adc.
i2c_init();
//4. Get the User settings from EEPROM.
//a. Initialize the EEPROM
uint32_t ui32_eeprom_status = eeprom_init();
if (ui32_eeprom_status != 0)
{
while(1)
{
//EEPROM Failure
}
}
//b. Get the Modbus Settings.
//i. MB Mode
//uint32_t wr_stat_mode = eeprom_mb_mode_write(MB_RTU);
eMBMode _mode = eeprom_mb_mode_read();
if (_mode != MB_RTU)
{
if (_mode != MB_ASCII)
{
if (_mode != MB_TCP)
{
_mode = MB_RTU;
}
}
}
//ii. Slave Address
//uint32_t wr_stat_sl_addr = eeprom_mb_slave_addr_write(0x0A);
UCHAR _slave_addr = eeprom_mb_slave_addr_read(); //Set to 0x0A.
//iii. BaudRate
//uint32_t wr_stat_BR = eeprom_mb_baudrate_write(256000UL);
ULONG _baudrate = eeprom_mb_baudrate_read(); //Set to 256000;
if (_baudrate != 9600)
{
if (_baudrate != 14400)
{
if (_baudrate != 19200)
{
if (_baudrate != 38400)
{
if (_baudrate != 57600)
{
if (_baudrate != 115200)
{
if (_baudrate != 128000)
{
if (_baudrate != 256000)
{
_baudrate = 115200;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
//iv. Parity
//uint32_t wr_stat_parity = eeprom_mb_parity_write(MB_PAR_NONE);
eMBParity _parity = eeprom_mb_parity_read(); //Set to None
if (_parity != MB_PAR_NONE)
{
if (_parity != MB_PAR_ODD)
{
if (_parity != MB_PAR_EVEN)
{
_parity = MB_PAR_NONE;
}
}
}
//c. Get the ADC Settings.
//i. Data Rate.
uint32_t _wr_stat_dr = eeprom_adc_dr_write(20);
uint32_t _dr = eeprom_adc_dr_read();
//ii. Gain.
uint32_t _wr_stat_gain = eeprom_adc_gain_write(1);
uint32_t _gain = eeprom_adc_gain_read();
//5. Setup the ADC.
//a. Continuous conversions.
set_adc_cm(true);
//b. Samples Per Second.
set_adc_sps(_dr);
//c. Gain
set_adc_gain(_gain);
//d. Send the start sync command.
tx_adc_start_sync();
//e. Send the config to the adc.
tx_adc_wreg();
//6. Setup Modbus
if ((eStatus = eMBInit(_mode,
_slave_addr,
0,
_baudrate,
_parity)) != MB_ENOERR)
{
}
else if( (eStatus = eMBEnable()) != MB_ENOERR)
{
IntMasterEnable();
}
else
{
for(;;)
{
eStatus = eMBPoll();
}
}
for (;;);
}
I am using a third party library called FreeModbus to handle the communication.
Before you say IT doesn't support third party libraries, I am looking for some general guidance on how to profile or determine where my application it is taking so long to run.
I have found some guidance here,

/****************************************************************************/
/* EXIT.C */
/* */
/* Copyright (c) 1995 Texas Instruments Incorporated */
/* http://www.ti.com/ */
/* */
/* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without */
/* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions */
/* are met: */
/* */
/* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright */
/* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. */
/* */
/* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright */
/* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in */
/* the documentation and/or other materials provided with the */
/* distribution. */
/* */
/* Neither the name of Texas Instruments Incorporated nor the names */
/* of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products */
/* derived from this software without specific prior written */
/* permission. */
/* */
/* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS */
/* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT */
/* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR */
/* A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT */
/* OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, */
/* SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT */
/* LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, */
/* DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY */
/* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT */
/* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE */
/* OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. */
/* */
/****************************************************************************/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <_lock.h>
#include <pprof.h>
#ifdef __TI_RTS_BUILD
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* __TI_default_exit indicates that the default TI exit routine is being */
/* used. The linker makes assumptions about what exit does when this symbol */
/* is seen. This symbols should NOT be defined if a customized exit routine */
/* is used. */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
__asm("__TI_default_exit .set 1");
#endif
void (*__TI_cleanup_ptr)(void) = NULL;
void _DATA_ACCESS (*__TI_dtors_ptr)(int) = NULL;
typedef void (*PTRFUNC)();
int __TI_enable_exit_profile_output = 1;
extern void abort(void);
/****************************************************************************/
/* EXIT() - NORMAL PROGRAM TERMINATION. */
/****************************************************************************/
extern void exit(int status)
{
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Output profile info if we have a valid path profile output handler */
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
if (__TI_enable_exit_profile_output &&
_symval(&__TI_pprof_out_hndl) != (unsigned)-1)
{
PTRFUNC ppfunc = (PTRFUNC)(_symval(&__TI_pprof_out_hndl));
(ppfunc)();
}
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* MUST LOCK WHEN ACCESSING GLOBALS, like __TI_dtors_ptr, */
/* __TI_cleanup_ptr */
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------*/
_lock();
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* BOTH ATEXIT FUNCTIONS AND STATIC OBJECT DESTRUCTORS ARE */
/* REGISTERED IN A LINK LIST TO BE PROCESSED BY THE FUNCTION POINTED */
/* TO BY __TI_dtors_ptr. PROCESS THEM NOW. */
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------*/
if (__TI_dtors_ptr) (*__TI_dtors_ptr)(status);
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* IF FILES ARE POSSIBLY OPEN, __TI_cleanup_ptr() WILL BE SETUP TO */
/* CLOSE THEM. */
/*-------------------------------------------------------------------*/
if (__TI_cleanup_ptr) (*__TI_cleanup_ptr)();
_unlock();
abort();
}
/****************************************************************************/
/* ABORT - ABNORMAL PROGRAM TERMINATION. CURRENTLY JUST HALTS EXECUTION. */
/****************************************************************************/
__attribute__((section(".text:abort")))
void abort(void)
{
#if defined(EMBED_CIO_BP)
__asm(" .global C$$EXITE");
#if defined(__32bis__)
__asm("C$$EXITE:.word 0xDEFED0FE");
#else
__asm(" .align 4");
#if defined(__big_endian__)
__asm("C$$EXITE:.half 0xDEFE");
#else
__asm("C$$EXITE:.half 0xD0FE");
#endif /* __big_endian__ */
#endif /* __32bis__ */
#else /* !EMBED_CIO_BP */
__asm(" .global C$$EXIT");
__asm("C$$EXIT: nop");
#endif
for (;;); /* SPINS FOREVER */
}
/*
* FreeModbus Libary: BARE Port
* Copyright (C) 2006 Christian Walter <wolti@sil.at>
*
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
*
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
*
* File: $Id$
*/
#include "port.h"
/* ----------------------- Modbus includes ----------------------------------*/
#include "mb.h"
#include "mbport.h"
//TI Tiva Includes
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "inc/hw_ints.h"
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "inc/hw_gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/debug.h"
#include "driverlib/fpu.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/interrupt.h"
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/uart.h"
/* ----------------------- static functions ---------------------------------*/
void prvvUARTTxReadyISR( void );
void prvvUARTRxISR( void );
/* ----------------------- Start implementation -----------------------------*/
void
vMBPortSerialEnable( BOOL xRxEnable, BOOL xTxEnable )
{
/* If xRXEnable enable serial receive interrupts. If xTxENable enable
* transmitter empty interrupts.
*/
if( xRxEnable )
{
UARTIntEnable(UART0_BASE, UART_INT_RX|UART_INT_RT);
UARTIntRegister(UART0_BASE,&prvvUARTRxISR);
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2, 0); //UART_TX_EN (Active High) -> TX OFF
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3, 0); //UART_RX_EN (Active Low) -> RX ON
}
else
{
UARTIntDisable(UART0_BASE,UART_INT_RX);
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2, 0); //UART_TX_EN (Active High) -> TX OFF
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3, 0); //UART_RX_EN (Active Low) -> RX ON
}
if( xTxEnable )
{
UARTIntEnable(UART0_BASE, UART_INT_TX);
UARTIntRegister(UART0_BASE,&prvvUARTTxReadyISR);
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2, GPIO_PIN_2); //UART_TX_EN (Active High) -> TX ON
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3, GPIO_PIN_3); //UART_RX_EN (Active Low) -> RX OFF
}
else
{
UARTIntDisable(UART0_BASE,UART_INT_TX);
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2, 0); //UART_TX_EN (Active High) -> TX OFF
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3, 0); //UART_RX_EN (Active Low) -> RX ON
}
}
BOOL
xMBPortSerialInit( UCHAR ucPORT, ULONG ulBaudRate, UCHAR ucDataBits, eMBParity eParity )
{
//Vars
(void)ucPORT;
uint32_t Parity,Bits,StopBits;
//Enable the GPIO Peripheral used by the UART.
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
// Enable UART0
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART0);
while(!SysCtlPeripheralReady(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA))
{
}
while(!SysCtlPeripheralReady(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART0))
{
}
// Configure GPIO Pins for UART mode.
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA0_U0RX);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA1_U0TX);
GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
// Select the length and Parity of UART
switch( eParity )
{
case MB_PAR_EVEN:
Parity = UART_CONFIG_PAR_EVEN;
StopBits = UART_CONFIG_STOP_ONE;
break;
case MB_PAR_ODD:
Parity = UART_CONFIG_PAR_ODD;
StopBits = UART_CONFIG_STOP_ONE;
break;
case MB_PAR_NONE:
Parity = UART_CONFIG_PAR_NONE;
StopBits = UART_CONFIG_STOP_ONE;
break;
}
switch( ucDataBits )
{
case 8:
Bits = UART_CONFIG_WLEN_8;
break;
case 7:
Bits = UART_CONFIG_WLEN_7;
break;
}
// Initialize the UART for console I/O.
UARTConfigSetExpClk(UART0_BASE,
SysCtlClockGet(),
ulBaudRate,
(Bits | StopBits | Parity));
//Disable the fifo in order to ensure the interrupt is only for a change in RX
UARTFIFODisable(UART0_BASE);
// Enable UART & Interrupts
UARTIntEnable(UART0_BASE, UART_INT_RX | UART_INT_RT);
UARTIntRegister(UART0_BASE,&prvvUARTRxISR);
UARTEnable(UART0_BASE);
//Enable the GPIO Pins.
GPIOPinUnlockGPIO(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2);
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2); //TX EN
GPIOPinUnlockGPIO(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3);
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3); //RX EN
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2, 0); //UART_TX_EN (Active High)
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3, 0); //UART_RX_EN (Active Low)
return TRUE;
}
BOOL
xMBPortSerialPutByte( CHAR ucByte )
{
/* Put a byte in the UARTs transmit buffer. This function is called
* by the protocol stack if pxMBFrameCBTransmitterEmpty( ) has been
* called. */
UARTCharPut(UART0_BASE, ucByte);
while (UARTBusy(UART0_BASE))
{
}
return TRUE;
}
BOOL
xMBPortSerialGetByte( CHAR * pucByte )
{
/* Return the byte in the UARTs receive buffer. This function is called
* by the protocol stack after pxMBFrameCBByteReceived( ) has been called.
*/
uint32_t ui32Status;
ui32Status = UARTIntStatus(UART0_BASE, true);
UARTIntClear(UART0_BASE,ui32Status);
*pucByte = UARTCharGet(UART0_BASE);
return TRUE;
}
/* Create an interrupt handler for the transmit buffer empty interrupt
* (or an equivalent) for your target processor. This function should then
* call pxMBFrameCBTransmitterEmpty( ) which tells the protocol stack that
* a new character can be sent. The protocol stack will then call
* xMBPortSerialPutByte( ) to send the character.
*/
void prvvUARTTxReadyISR( void )
{
pxMBFrameCBTransmitterEmpty( );
}
/* Create an interrupt handler for the receive interrupt for your target
* processor. This function should then call pxMBFrameCBByteReceived( ). The
* protocol stack will then call xMBPortSerialGetByte( ) to retrieve the
* character.
*/
void prvvUARTRxISR(void)
{
pxMBFrameCBByteReceived( );
}
void vMBPPortEnterCritical()
{
//GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2, GPIO_PIN_2); //UART_TX_EN (Active High) -> TX OFF
//GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3, GPIO_PIN_3); //UART_RX_EN (Active Low) -> RX OFF
}
void vMBPPortExitCritical()
{
//GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2, 0); //UART_TX_EN (Active High) -> TX OFF
//GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3, 0); //UART_RX_EN (Active Low) -> RX ON
}
These microcontrollers are going to be connected with multiple other slaves, so having a 25ms delay is unacceptable.
Any advice on how to debug this further would be appreciated.
Thanks,
Allan