Part Number: AM2612
Tool/software:
Hi,
My customer has some questions about VIM (Vectored Interrupt Manager). Could you help to answer their questions below ?
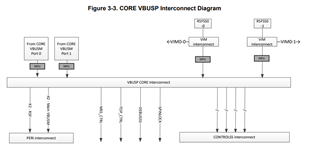
1. Could you tell them what is difference between VIM0 and VIM1 ?
2. Are these the same as VIM0-0 and VIM0-1 shown in the Figure 3-3 in the TRM ?

3. Could you tell them a use case how to use these two VIM0/1 differently ?
Thanks and regards,
Hideaki