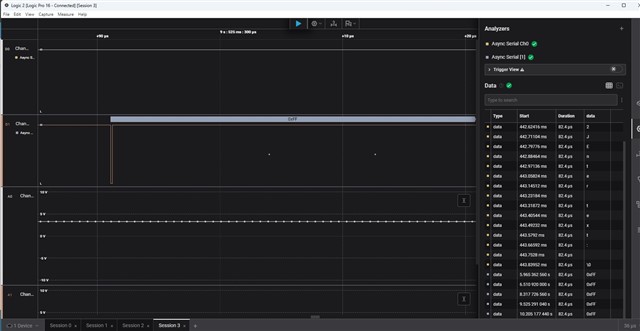
Tool/software:
I modified demo project uart_echo a little bit to use UART7. I connected the eval board to my laptop through USB to TTL cable then started the debugger and Putty. The main function sent a prompt string to UART and I could see it in Putty. But if I typed something in Putty, it didn't echoed back. What I typed were supposed to be received by UARTIntHandler(my UART ISR) then wrote back to the UART. But that didn't happen. I set a breakpoint in the ISR at line after line: char c = MAP_UARTCharGetNonBlocking(UART7_BASE); The breakpoint was just hit once. It was after the program was launched. When I typed anything in Putty, the break was not hit. I don't know what was wrong.
Here is main()
void
UARTSend(const uint8_t *pui8Buffer, uint32_t ui32Count)
{
//
// Loop while there are more characters to send.
//
while(ui32Count--)
{
//
// Write the next character to the UART.
//
MAP_UARTCharPutNonBlocking(UART7_BASE, *pui8Buffer++);
// MAP_UARTCharPutNonBlocking(UART0_BASE, *pui8Buffer++);
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This example demonstrates how to send a string of data to the UART.
//
//*****************************************************************************
int
main(void)
{
//
// Run from the PLL at 120 MHz.
// Note: SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_240 is a new setting provided in TivaWare 2.2.x and
// later to better reflect the actual VCO speed due to SYSCTL#22.
//
g_ui32SysClock = MAP_SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ |
SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN |
SYSCTL_USE_PLL |
SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_240), 120000000);
//
// Enable the GPIO port that is used for the on-board LED.
//
MAP_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPION);
//
// Enable the GPIO pins for the LED (PN0).
//
MAP_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTN_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0);
//
// Enable the peripherals used by this example.
//
MAP_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART7);
MAP_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOC);
//
// Enable processor interrupts.
//
MAP_IntMasterEnable();
//
// Set GPIO C4 and C5 as UART pins.
//
MAP_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PC4_U7RX);
MAP_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PC5_U7TX);
MAP_GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTC_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5);
//
// Configure the UART for 115,200, 8-N-1 operation.
//
MAP_UARTConfigSetExpClk(UART7_BASE, g_ui32SysClock, 115200,
(UART_CONFIG_WLEN_8 | UART_CONFIG_STOP_ONE |
UART_CONFIG_PAR_NONE));
//
// Enable the UART interrupt.
//
MAP_IntEnable(INT_UART7);
MAP_UARTIntEnable(UART7_BASE, UART_INT_RX | UART_INT_RT);
//
// Prompt for text to be entered.
//
UARTSend((uint8_t *)"\033[2JEnter text: ", 16);
//
// Loop forever echoing data through the UART.
//
while(1)
{
}
}
ISR:
void
UARTIntHandler(void)
{
uint32_t ui32Status;
//
// Get the interrrupt status.
//
ui32Status = MAP_UARTIntStatus(UART7_BASE, true);
//
// Clear the asserted interrupts.
//
MAP_UARTIntClear(UART7_BASE, ui32Status);
//
// Loop while there are characters in the receive FIFO.
//
while(MAP_UARTCharsAvail(UART7_BASE))
{
//
// Read the next character from the UART and write it back to the UART.
//
/*
MAP_UARTCharPutNonBlocking(UART7_BASE,
MAP_UARTCharGetNonBlocking(UART7_BASE));
*/
char c = MAP_UARTCharGetNonBlocking(UART7_BASE);
MAP_UARTCharPutNonBlocking(UART7_BASE, c);
//
// Blink the LED to show a character transfer is occuring.
//
MAP_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTN_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0, GPIO_PIN_0);
//
// Delay for 1 millisecond. Each SysCtlDelay is about 3 clocks.
//
SysCtlDelay(g_ui32SysClock / (1000 * 3));
//
// Turn off the LED
//
MAP_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTN_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0, 0);
}
}
startup file to set ISR on UART7
//*****************************************************************************
//
// startup_ccs.c - Startup code for use with TI's Code Composer Studio.
//
// Copyright (c) 2013-2020 Texas Instruments Incorporated. All rights reserved.
// Software License Agreement
//
// Texas Instruments (TI) is supplying this software for use solely and
// exclusively on TI's microcontroller products. The software is owned by
// TI and/or its suppliers, and is protected under applicable copyright
// laws. You may not combine this software with "viral" open-source
// software in order to form a larger program.
//
// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND WITH ALL FAULTS.
// NO WARRANTIES, WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING, BUT
// NOT LIMITED TO, IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE APPLY TO THIS SOFTWARE. TI SHALL NOT, UNDER ANY
// CIRCUMSTANCES, BE LIABLE FOR SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
// DAMAGES, FOR ANY REASON WHATSOEVER.
//
// This is part of revision 2.2.0.295 of the EK-TM4C129EXL Firmware Package.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#include <stdint.h>
#include "inc/hw_nvic.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Forward declaration of the default fault handlers.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void ResetISR(void);
static void NmiSR(void);
static void FaultISR(void);
static void IntDefaultHandler(void);
//*****************************************************************************
//
// External declaration for the reset handler that is to be called when the
// processor is started
//
//*****************************************************************************
extern void _c_int00(void);
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Linker variable that marks the top of the stack.
//
//*****************************************************************************
extern uint32_t __STACK_TOP;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// External declaration for the interrupt handler used by the application.
//
//*****************************************************************************
extern void UARTIntHandler(void);
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The vector table. Note that the proper constructs must be placed on this to
// ensure that it ends up at physical address 0x0000.0000 or at the start of
// the program if located at a start address other than 0.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#pragma DATA_SECTION(g_pfnVectors, ".intvecs")
void (* const g_pfnVectors[])(void) =
{
(void (*)(void))((uint32_t)&__STACK_TOP),
// The initial stack pointer
ResetISR, // The reset handler
NmiSR, // The NMI handler
FaultISR, // The hard fault handler
IntDefaultHandler, // The MPU fault handler
IntDefaultHandler, // The bus fault handler
IntDefaultHandler, // The usage fault handler
0, // Reserved
0, // Reserved
0, // Reserved
0, // Reserved
IntDefaultHandler, // SVCall handler
IntDefaultHandler, // Debug monitor handler
0, // Reserved
IntDefaultHandler, // The PendSV handler
IntDefaultHandler, // The SysTick handler
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port A
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port B
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port C
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port D
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port E
IntDefaultHandler, // UART0 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // UART1 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // SSI0 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C0 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // PWM Fault
IntDefaultHandler, // PWM Generator 0
IntDefaultHandler, // PWM Generator 1
IntDefaultHandler, // PWM Generator 2
IntDefaultHandler, // Quadrature Encoder 0
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC Sequence 0
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC Sequence 1
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC Sequence 2
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC Sequence 3
IntDefaultHandler, // Watchdog timer
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 0 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 0 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 1 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 1 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 2 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 2 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // Analog Comparator 0
IntDefaultHandler, // Analog Comparator 1
IntDefaultHandler, // Analog Comparator 2
IntDefaultHandler, // System Control (PLL, OSC, BO)
IntDefaultHandler, // FLASH Control
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port F
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port G
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port H
IntDefaultHandler, // UART2 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // SSI1 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 3 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 3 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C1 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // CAN0
IntDefaultHandler, // CAN1
IntDefaultHandler, // Ethernet
IntDefaultHandler, // Hibernate
IntDefaultHandler, // USB0
IntDefaultHandler, // PWM Generator 3
IntDefaultHandler, // uDMA Software Transfer
IntDefaultHandler, // uDMA Error
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC1 Sequence 0
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC1 Sequence 1
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC1 Sequence 2
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC1 Sequence 3
IntDefaultHandler, // External Bus Interface 0
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port J
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port K
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port L
IntDefaultHandler, // SSI2 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // SSI3 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // UART3 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // UART4 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // UART5 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // UART6 Rx and Tx
UARTIntHandler, // UART7 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C2 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C3 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 4 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 4 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 5 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 5 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // FPU
0, // Reserved
0, // Reserved
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C4 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C5 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port M
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port N
0, // Reserved
IntDefaultHandler, // Tamper
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P (Summary or P0)
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P1
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P2
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P3
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P4
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P5
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P6
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P7
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q (Summary or Q0)
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q1
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q2
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q3
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q4
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q5
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q6
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q7
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port R
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port S
IntDefaultHandler, // SHA/MD5 0
IntDefaultHandler, // AES 0
IntDefaultHandler, // DES3DES 0
IntDefaultHandler, // LCD Controller 0
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 6 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 6 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 7 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 7 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C6 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C7 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // HIM Scan Matrix Keyboard 0
IntDefaultHandler, // One Wire 0
IntDefaultHandler, // HIM PS/2 0
IntDefaultHandler, // HIM LED Sequencer 0
IntDefaultHandler, // HIM Consumer IR 0
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C8 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C9 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler // GPIO Port T
};
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This is the code that gets called when the processor first starts execution
// following a reset event. Only the absolutely necessary set is performed,
// after which the application supplied entry() routine is called. Any fancy
// actions (such as making decisions based on the reset cause register, and
// resetting the bits in that register) are left solely in the hands of the
// application.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
ResetISR(void)
{
//
// Jump to the CCS C initialization routine. This will enable the
// floating-point unit as well, so that does not need to be done here.
//
__asm(" .global _c_int00\n"
" b.w _c_int00");
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This is the code that gets called when the processor receives a NMI. This
// simply enters an infinite loop, preserving the system state for examination
// by a debugger.
//
//*****************************************************************************
static void
NmiSR(void)
{
//
// Enter an infinite loop.
//
while(1)
{
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This is the code that gets called when the processor receives a fault
// interrupt. This simply enters an infinite loop, preserving the system state
// for examination by a debugger.
//
//*****************************************************************************
static void
FaultISR(void)
{
//
// Enter an infinite loop.
//
while(1)
{
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This is the code that gets called when the processor receives an unexpected
// interrupt. This simply enters an infinite loop, preserving the system state
// for examination by a debugger.
//
//*****************************************************************************
static void
IntDefaultHandler(void)
{
//
// Go into an infinite loop.
//
while(1)
{
}
}