Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TM4C123BH6PM, MSP430F135
Hi. I have trouble with Tiva(TM4C123BH6PM)'s SSI interface.
I'm using STmicro H3LIS331DL accelerometer.
I set SSI frame format to Freescale Mode (SPH=1, SPO=1) in order to match the accelerometer's frame format.
I used the Tivaware SSI example codes. However, I changed the SSI control register to match this frame format.
-Data frame size = 16bit
-SSInClk = 2MHz (SysClk = 16MHz, CPSDVSR= 2, SCR = 3)
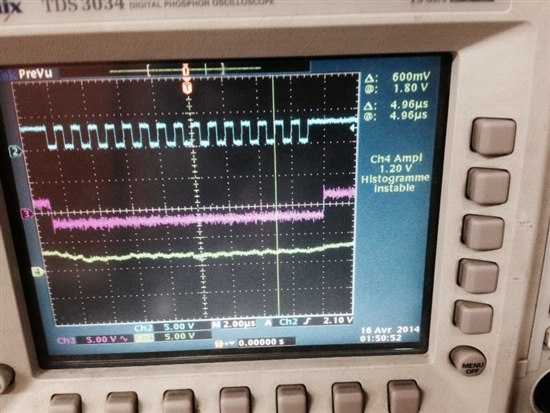
When the MCU communicates with this sensor, the RX value was only 0xFFFF
while changing the value of TX, The TX pin goes out correctly
with the wanted values(the sensor register addresses). Also the Fss and the Clock pulse was working fine.
What might be the problem?
Could it be soldering problems, difference of data order or SW problems?