Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TM4C123BH6PM
Hi, I'm using QEI in order to count a rotation of a remote car's wheel.
I connected a digital hall sensor output to QEI module 1's input A(PHA1/PC5, capture mode : Only PhA).
The hall sensor is WSH131-XPAN3.
(Datasheet link : http://pdf1.alldatasheet.co.kr/datasheet-pdf/view/227165/WINSON/WSH131-XPAN3.html )
Attaching a magnet to the wheel, the pulse comes out well.
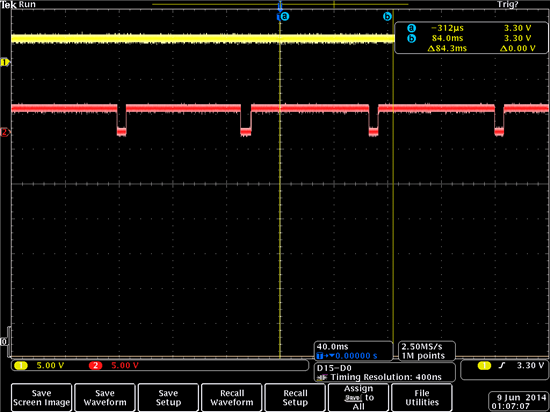
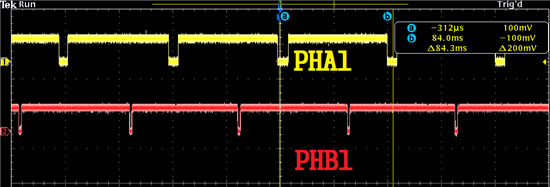
The yellow pulse is the IDX1. It is constantly digital '1'.
The red pulse is PHA1. The hall sensor's output is 0 when there is a manget in front.
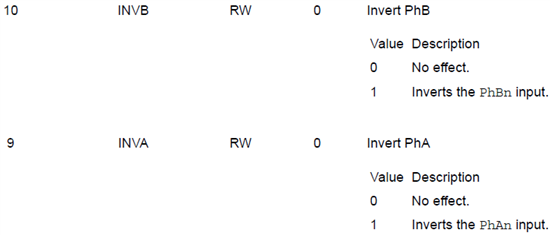
Due to the hall sensor's output, I used the invert mode.
(reference : TM4C123BH6PM datasheet, 1186pg)
However, when I read the QEI position register, it doesn't increase as i expected.
For some reason, it looked like it was reset.
The IDX1 and PHB1 pin is not connected to anything. What might be the problem..?
This is the source code I made. It is a code about printing the qei position to the terminal.
Always thanks to your help.
-Regards, Min-Ku