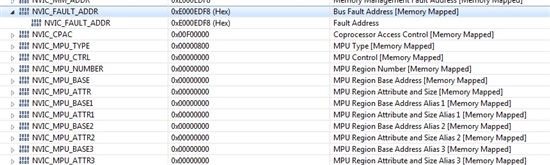
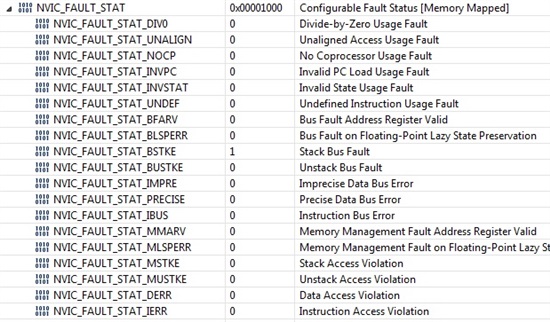
Hiii all
please suggest mistakes in program lines given below. my code is going in fault ISR. but after removing these lines, its working fine.
float k,a; unsigned long ulPeriod,p; k=0.8; ulPeriod = SysCtlClockGet() / 50000; a=k*ulPeriod; p=(long)a;
regards
Prashant