Hello,
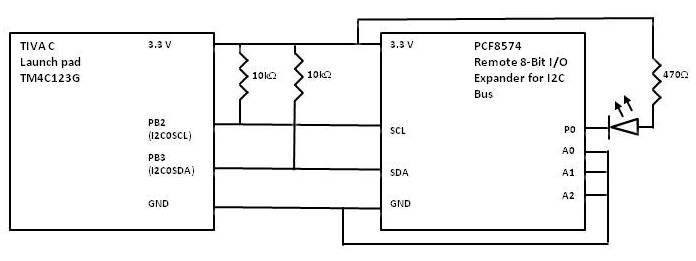
I am using TIVA C launch pad for my experiment. With reference to TIVA ware I2C example (loopback) mode I am configuring my application. Below is my schematic for the application.
SCL and SDA line continuously stay low. Please let me is there any corrections I need to do in hardware.
Below is my code. Reference is taken from Tiwaware example , I'm kind of stuck in it.
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include "inc/hw_i2c.h"
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/i2c.h"
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/uart.h"
#include "utils/uartstdio.h"
//*****************************************************************************
//
//! \addtogroup i2c_examples_list
//! <h1>I2C Master Loopback (i2c_master_slave_loopback)</h1>
//!
//! This example shows how to configure the I2C0 module for loopback mode.
//! This includes setting up the master and slave module. Loopback mode
//! internally connects the master and slave data and clock lines together.
//! The address of the slave module is set in order to read data from the
//! master. Then the data is checked to make sure the received data matches
//! the data that was transmitted. This example uses a polling method for
//! sending and receiving data.
//!
//! This example uses the following peripherals and I/O signals. You must
//! review these and change as needed for your own board:
//! - I2C0 peripheral
//! - GPIO Port B peripheral (for I2C0 pins)
//! - I2C0SCL - PB2
//! - I2C0SDA - PB3
//
// Number of I2C data packets to send.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#define NUM_I2C_DATA 3
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Set the address for slave module. This is a 7-bit address sent in the
// following format:
// [A6:A5:A4:A3:A2:A1:A0:RS]
//
// A zero in the "RS" position of the first byte means that the master
// transmits (sends) data to the selected slave, and a one in this position
// means that the master receives data from the slave.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#define SLAVE_ADDRESS 0x40
int
main(void)
{
//
// Set the clocking to run directly from the external crystal/oscillator.
// TODO: The SYSCTL_XTAL_ value must be changed to match the value of the
// crystal on your board.
//
SysCtlClockSet(SYSCTL_SYSDIV_1 | SYSCTL_USE_OSC | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN |
SYSCTL_XTAL_16MHZ);
//
// The I2C0 peripheral must be enabled before use.
//
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_I2C0);
//
// For this example I2C0 is used with PortB[3:2]. The actual port and
// pins used may be different on your part, consult the data sheet for
// more information. GPIO port B needs to be enabled so these pins can
// be used.
// TODO: change this to whichever GPIO port you are using.
//
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOB);
//
// Configure the pin muxing for I2C0 functions on port B2 and B3.
// This step is not necessary if your part does not support pin muxing.
// TODO: change this to select the port/pin you are using.
//
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB2_I2C0SCL);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB3_I2C0SDA);
//
// Select the I2C function for these pins. This function will also
// configure the GPIO pins pins for I2C operation, setting them to
// open-drain operation with weak pull-ups. Consult the data sheet
// to see which functions are allocated per pin.
// TODO: change this to select the port/pin you are using.
//
GPIOPinTypeI2CSCL(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2);
GPIOPinTypeI2C(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3);
//
// Enable loopback mode. Loopback mode is a built in feature that is
// useful for debugging I2C operations. It internally connects the I2C
// master and slave terminals, which effectively let's you send data as
// a master and receive data as a slave.
// NOTE: For external I2C operation you will need to use external pullups
// that are stronger than the internal pullups. Refer to the datasheet for
// more information.
//
HWREG(I2C0_BASE + I2C_O_MCR) |= 0x00;
//
// Enable and initialize the I2C0 master module. Use the system clock for
// the I2C0 module. The last parameter sets the I2C data transfer rate.
// If false the data rate is set to 100kbps and if true the data rate will
// be set to 400kbps. For this example we will use a data rate of 100kbps.
//
I2CMasterInitExpClk(I2C0_BASE, SysCtlClockGet(), false);
// Tell the master module what address it will place on the bus when
// communicating with the slave. Set the address to SLAVE_ADDRESS
// (as set in the slave module). The receive parameter is set to false
// which indicates the I2C Master is initiating a writes to the slave. If
// true, that would indicate that the I2C Master is initiating reads from
// the slave.
//
I2CMasterSlaveAddrSet(I2C0_BASE, SLAVE_ADDRESS, false);
// Place the data to be sent in the data register
//
I2CMasterDataPut(I2C0_BASE,0x00);
//
// Initiate send of data from the master. Since the loopback
// mode is enabled, the master and slave units are connected
// allowing us to receive the same data that we sent out.
//
I2CMasterControl(I2C0_BASE, I2C_MASTER_CMD_SINGLE_SEND);
// Wait until master module is done transferring.
//
while(I2CMasterBusy(I2C0_BASE))
{
}
while(1)
{
}
}