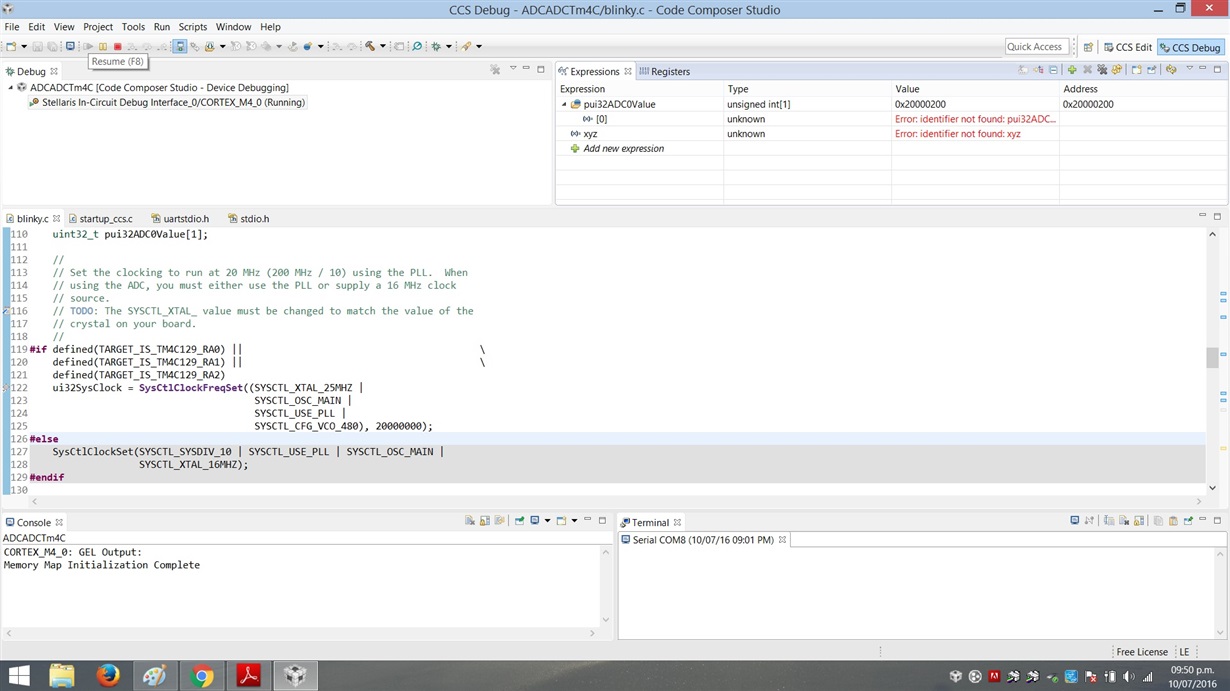
Hello, I just get a TM4C129exl launchpad, I load the blinky sample proyect and then I copied an ADC sample code from TivaWare, the problem is that when I want to see the result from the ADC conversion after I "resume" the code I got this problem:
The code is from Tiva Ware examples:
#include <stdbool.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <stdio.h> #include "inc/hw_memmap.h" #include "driverlib/adc.h" #include "driverlib/gpio.h" #include "driverlib/pin_map.h" #include "driverlib/sysctl.h" #include "driverlib/uart.h" #include "utils/uartstdio.h" //*****************************************************************************
//! This example uses the following interrupt handlers. To use this example
//! in your own application you must add these interrupt handlers to your
//! vector table.
//! - None.
//*****************************************************************************
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This function sets up UART0 to be used for a console to display information
// as the example is running.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void InitConsole(void)
{
//
// Enable GPIO port A which is used for UART0 pins.
// TODO: change this to whichever GPIO port you are using.
//
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
//
// Configure the pin muxing for UART0 functions on port A0 and A1.
// This step is not necessary if your part does not support pin muxing.
// TODO: change this to select the port/pin you are using.
//
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA0_U0RX);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA1_U0TX);
//
// Enable UART0 so that we can configure the clock.
//
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART0);
//
// Use the internal 16MHz oscillator as the UART clock source.
//
UARTClockSourceSet(UART0_BASE, UART_CLOCK_PIOSC);
//
// Select the alternate (UART) function for these pins.
// TODO: change this to select the port/pin you are using.
//
GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
//
// Initialize the UART for console I/O.
//
UARTStdioConfig(0, 115200, 16000000);
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Configure ADC0 for a differential input and a single sample. Once the
// sample is ready, an interrupt flag will be set. Using a polling method,
// the data will be read then displayed on the console via UART0.
//
//*****************************************************************************
int
main(void)
{
#if defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA0) || \
defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA1) || \
defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA2)
uint32_t ui32SysClock;
#endif
//
// This array is used for storing the data read from the ADC FIFO. It
// must be as large as the FIFO for the sequencer in use. This example
// uses sequence 3 which has a FIFO depth of 1. If another sequence
// was used with a deeper FIFO, then the array size must be changed.
//
uint32_t pui32ADC0Value[1];
//
// Set the clocking to run at 20 MHz (200 MHz / 10) using the PLL. When
// using the ADC, you must either use the PLL or supply a 16 MHz clock
// source.
// TODO: The SYSCTL_XTAL_ value must be changed to match the value of the
// crystal on your board.
//
#if defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA0) || \
defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA1) || \
defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA2)
ui32SysClock = SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ |
SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN |
SYSCTL_USE_PLL |
SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_480), 20000000);
#else
SysCtlClockSet(SYSCTL_SYSDIV_10 | SYSCTL_USE_PLL | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN |
SYSCTL_XTAL_16MHZ);
#endif
//
// Set up the serial console to use for displaying messages. This is just
// for this example program and is not needed for ADC operation.
//
InitConsole();
//
// Display the setup on the console.
//
UARTprintf("ADC ->\n");
UARTprintf(" Type: differential\n");
UARTprintf(" Samples: One\n");
UARTprintf(" Update Rate: 250ms\n");
UARTprintf(" Input Pin: (AIN0/PE7 - AIN1/PE6)\n\n");
//
// The ADC0 peripheral must be enabled for use.
//
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_ADC0);
//
// For this example ADC0 is used with AIN0/1 on port E7/E6.
// The actual port and pins used may be different on your part, consult
// the data sheet for more information. GPIO port E needs to be enabled
// so these pins can be used.
// TODO: change this to whichever GPIO port you are using.
//
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOE);
//
// Select the analog ADC function for these pins.
// Consult the data sheet to see which functions are allocated per pin.
// TODO: change this to select the port/pin you are using.
//
GPIOPinTypeADC(GPIO_PORTE_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7 | GPIO_PIN_6);
//
// Enable sample sequence 3 with a processor signal trigger. Sequence 3
// will do a single sample when the processor sends a signal to start the
// conversion. Each ADC module has 4 programmable sequences, sequence 0
// to sequence 3. This example is arbitrarily using sequence 3.
//
ADCSequenceConfigure(ADC0_BASE, 3, ADC_TRIGGER_PROCESSOR, 0);
//
// Configure step 0 on sequence 3. Sample channel 0 (ADC_CTL_CH0) in
// differential mode (ADC_CTL_D) and configure the interrupt flag
// (ADC_CTL_IE) to be set when the sample is done. Tell the ADC logic
// that this is the last conversion on sequence 3 (ADC_CTL_END). Sequence
// 3 has only one programmable step. Sequence 1 and 2 have 4 steps, and
// sequence 0 has 8 programmable steps. Since we are only doing a single
// conversion using sequence 3 we will only configure step 0. For more
// information on the ADC sequences and steps, refer to the datasheet.
//
ADCSequenceStepConfigure(ADC0_BASE, 3, 0, ADC_CTL_D | ADC_CTL_CH0 |
ADC_CTL_IE | ADC_CTL_END);
//
// Since sample sequence 3 is now configured, it must be enabled.
//
ADCSequenceEnable(ADC0_BASE, 3);
//
// Clear the interrupt status flag. This is done to make sure the
// interrupt flag is cleared before we sample.
//
ADCIntClear(ADC0_BASE, 3);
//
// Sample AIN0/1 forever. Display the value on the console.
//
while(1)
{
//
// Trigger the ADC conversion.
//
ADCProcessorTrigger(ADC0_BASE, 3);
//
// Wait for conversion to be completed.
//
while(!ADCIntStatus(ADC0_BASE, 3, false))
{
}
//
// Clear the ADC interrupt flag.
//
ADCIntClear(ADC0_BASE, 3);
//
// Read ADC Value.
//
ADCSequenceDataGet(ADC0_BASE, 3, pui32ADC0Value);
//
// Display the [AIN0(PE7) - AIN1(PE6)] digital value on the console.
//
UARTprintf("AIN0 - AIN1 = %4d\r", pui32ADC0Value[0]);
//
// This function provides a means of generating a constant length
// delay. The function delay (in cycles) = 3 * parameter. Delay
// 250ms arbitrarily.
//
#if defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA0) || \
defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA1) || \
defined(TARGET_IS_TM4C129_RA2)
SysCtlDelay(ui32SysClock / 12);
#else
SysCtlDelay(SysCtlClockGet() / 12);
#endif
}
}
The UART does not seen to work properly, the terminal dont show me the ADC value, I have been working with the MSP432, and I use to declare the interruptions in the startup file for UART and ADC (not when using DMA), the ADC example from TIVAware tells me to not declare the interruptions in the startup, why??.
Also is weird that there are not project examples for ADC :D.
Thanks in advance