Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TM4C123GH6PM
TM4C1294NCPDT CAN BUS Error
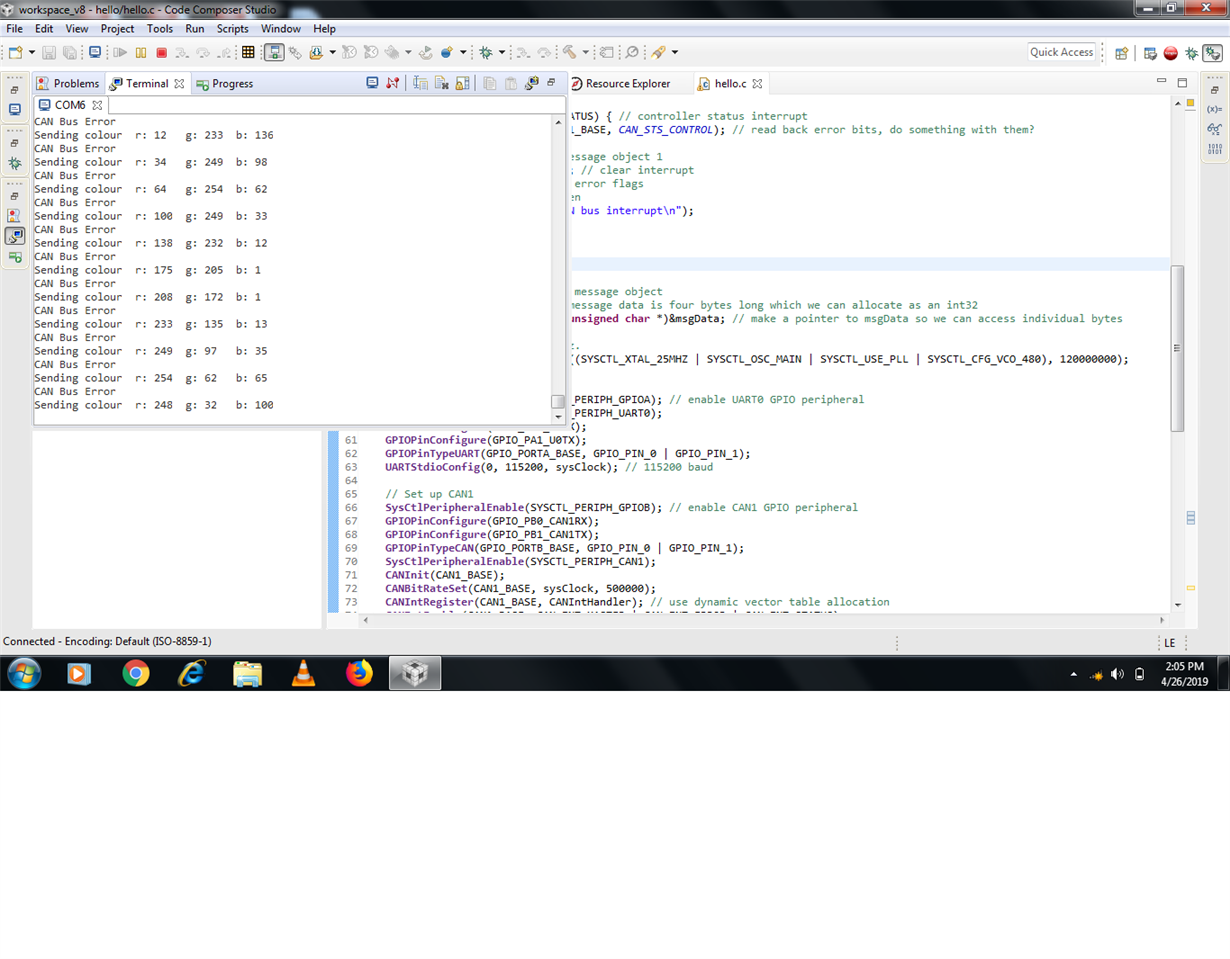
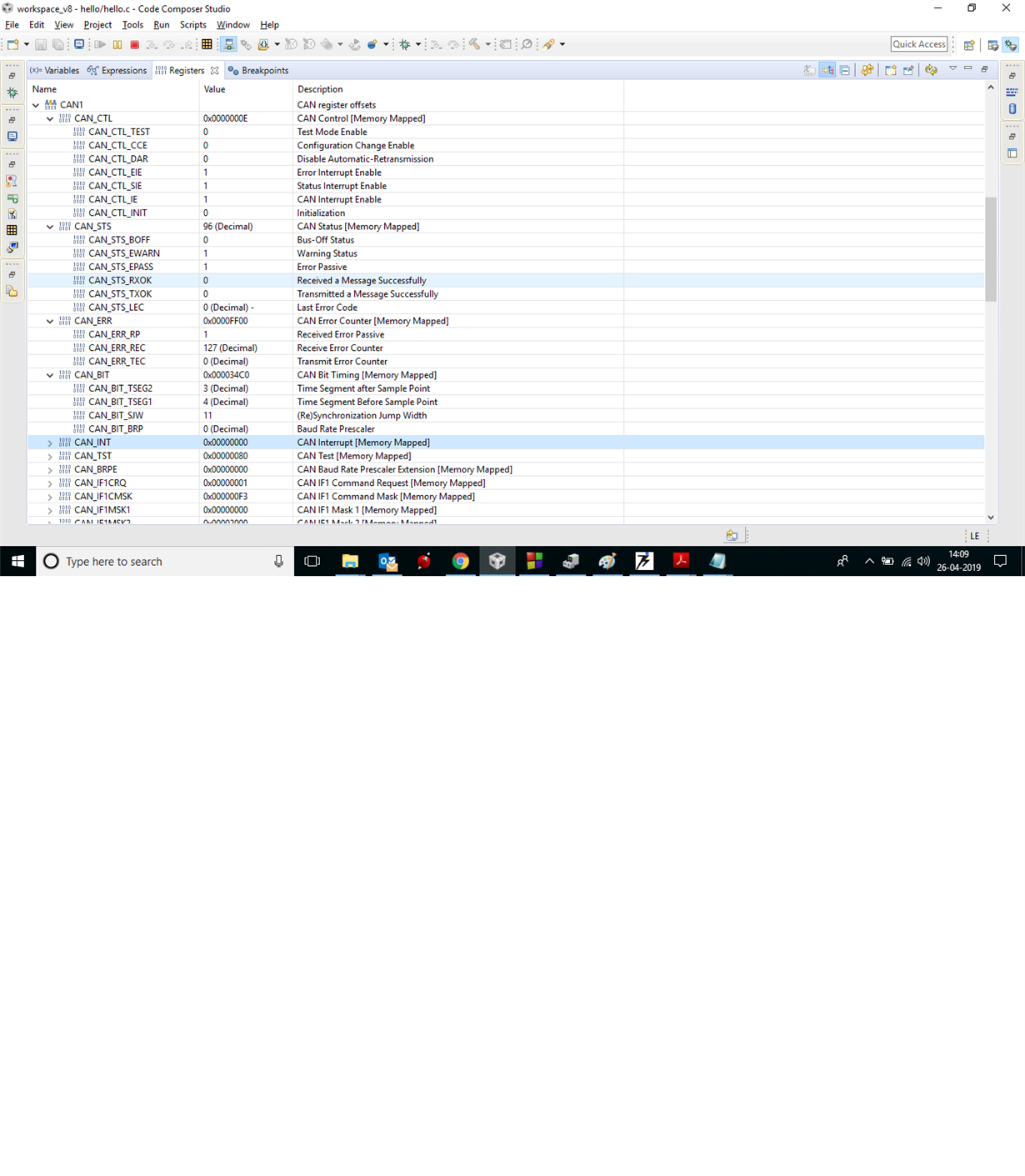
I am new to CAN interface programming. I tried to establish CAN communication between 2 TIVAC boards using MCP2551 transceiver. I got some help from ohmninja website for basic CAN programming. my basic idea is to read sensor value through ADC in one TIVAC and send the same to other TIVAC through CAN interface. The transmit and receive programs gets compiled successfully and I can able to build the project. But once I check the UART for output I end up with CAN BUS error. I post my program and output screenshot plz do help
Transmit Code
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "driverlib/debug.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/adc.h"
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "driverlib/uart.h"
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "utils/uartstdio.h"
#include "inc/hw_can.h"
#include "inc/hw_ints.h"
#include "driverlib/can.h"
#include "driverlib/interrupt.h"
#include "utils/uartstdio.h"
unsigned int sysClock;
volatile bool errFlag = 0; // transmission error flag
unsigned int sysClock; // clockspeed in hz
// CAN interrupt handler
void CANIntHandler(void) {
unsigned long status = CANIntStatus(CAN1_BASE, CAN_INT_STS_CAUSE); // read interrupt status
if(status == CAN_INT_INTID_STATUS) { // controller status interrupt
status = CANStatusGet(CAN1_BASE, CAN_STS_CONTROL); // read back error bits, do something with them?
errFlag = 1;
} else if(status == 1) { // message object 1
CANIntClear(CAN1_BASE, 1); // clear interrupt
errFlag = 0; // clear any error flags
} else { // should never happen
UARTprintf("Unexpected CAN bus interrupt\n");
}
}
void delay(unsigned int milliseconds) {
SysCtlDelay((sysClock / 3) * (milliseconds / 1000.0f));
}
int main(void)
{
uint32_t ui32ACCValues[4];
volatile uint32_t ui32AccX;
volatile uint32_t ui32AccY;
volatile uint32_t ui32AccZ;
tCANMsgObject msg; // the CAN message object
unsigned int msgData; // the message data is four bytes long which we can allocate as an int32
unsigned char *msgDataPtr = (unsigned char *)&msgData; // make a pointer to msgData so we can access individual bytes
SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_USE_PLL | SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_480), 120000000);
sysClock = SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_USE_PLL | SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_480), 120000000);
// Set up debugging UART
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA); // enable UART0 GPIO peripheral
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART0);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA0_U0RX);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA1_U0TX);
GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
UARTStdioConfig(0, 115200, sysClock); // 115200 baud
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_ADC0);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOE);
GPIOPinTypeADC(GPIO_PORTE_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1 | GPIO_PIN_2 );
ADCSequenceConfigure(ADC0_BASE, 1, ADC_TRIGGER_PROCESSOR, 0);
ADCSequenceStepConfigure(ADC0_BASE, 1, 0, ADC_CTL_CH3);
ADCSequenceStepConfigure(ADC0_BASE, 1, 1, ADC_CTL_CH2);
ADCSequenceStepConfigure(ADC0_BASE, 1, 2, ADC_CTL_CH1|ADC_CTL_IE|ADC_CTL_END);
ADCSequenceEnable(ADC0_BASE, 1);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOB); // enable CAN1 GPIO peripheral
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB0_CAN1RX);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB1_CAN1TX);
GPIOPinTypeCAN(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_CAN1);
CANInit(CAN1_BASE);
CANBitRateSet(CAN1_BASE, sysClock, 500000);
CANIntRegister(CAN1_BASE, CANIntHandler); // use dynamic vector table allocation
CANIntEnable(CAN1_BASE, CAN_INT_MASTER | CAN_INT_ERROR | CAN_INT_STATUS);
IntEnable(INT_CAN1);
CANEnable(CAN1_BASE);
// Set up msg object
msgData = 0;
msg.ui32MsgID = 1;
msg.ui32MsgIDMask = 0;
msg.ui32Flags = MSG_OBJ_TX_INT_ENABLE;
msg.ui32MsgLen = sizeof(msgDataPtr);
msg.pui8MsgData = msgDataPtr;
while(1)
{
ADCIntClear(ADC0_BASE, 1);
ADCProcessorTrigger(ADC0_BASE, 1);
while(!ADCIntStatus(ADC0_BASE, 1, false))
{
}
ADCSequenceDataGet(ADC0_BASE, 1, ui32ACCValues);
ui32AccX = ui32ACCValues[0];
ui32AccY = ui32ACCValues[1];
ui32AccZ = ui32ACCValues[2];
UARTprintf("Analog Voltage\tR: %d\tY: %d\tB: %d\n",ui32AccX, ui32AccY,ui32AccZ); // write colour to UART for debugging
CANMessageSet(CAN1_BASE, 1, &msg, MSG_OBJ_TYPE_TX); // send as msg object 1
delay(100); // wait 100ms
if(errFlag) { // check for errors
UARTprintf("CAN Bus Error\n");
}
delay(1000); // wait 100ms
}
return 0;
}
receive code
* CAN bus LED controller slave firmware
* Written for TI Tiva TM4C123GH6PM
*/
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "driverlib/debug.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/adc.h"
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "driverlib/uart.h"
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "utils/uartstdio.h"
#include "inc/hw_can.h"
#include "inc/hw_ints.h"
#include "driverlib/can.h"
#include "driverlib/interrupt.h"
#include "utils/uartstdio.h"
volatile bool errFlag = 0; // error flag
void CANIntHandler(void) {
status = CANStatusGet(CAN1_BASE, CAN_STS_CONTROL);
errFlag = 1;
} else if(status == 1) { // msg object 1
CANIntClear(CAN1_BASE, 1); // clear interrupt
rxFlag = 1; // set rx flag
errFlag = 0; // clear any error flags
} else { // should never happen
UARTprintf("Unexpected CAN bus interrupt\n");
}
}
unsigned char msgData[8]; // 8 byte buffer for rx message data
SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_USE_PLL | SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_480), 120000000);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART0);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA0_U0RX);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA1_U0TX);
GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
UARTStdioConfig(0, 115200, SysCtlClockGet());
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB0_CAN1RX);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB1_CAN1TX);
GPIOPinTypeCAN(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_CAN1);
CANInit(CAN1_BASE);
CANBitRateSet(CAN1_BASE, SysCtlClockGet(), 500000);
CANIntRegister(CAN1_BASE, CANIntHandler); // use dynamic vector table allocation
CANIntEnable(CAN1_BASE, CAN_INT_MASTER | CAN_INT_ERROR | CAN_INT_STATUS);
CANIntClear(CAN1_BASE,CAN_INT_STATUS);
IntEnable(INT_CAN1);
CANEnable(CAN1_BASE);
// Use ID and mask 0 to recieved messages with any CAN ID
msg.ui32MsgID = 0;
msg.ui32MsgIDMask = 0;
msg.ui32Flags = MSG_OBJ_RX_INT_ENABLE | MSG_OBJ_USE_ID_FILTER;
msg.ui32MsgLen = 8; // allow up to 8 bytes
CANMessageSet(CAN1_BASE, 1, &msg, MSG_OBJ_TYPE_RX);
float intensity;
CANMessageGet(CAN1_BASE, 1, &msg, 0); // read CAN message object 1 from CAN peripheral
UARTprintf("CAN message loss detected\n");
}
colour[0] = msgData[0] * 0xFF;
colour[1] = msgData[1] * 0xFF;
colour[2] = msgData[2] * 0xFF;
intensity = msgData[3] / 255.0f; // scale from 0-255 to float 0-1
UARTprintf("Received colour\tr: %d\tg: %d\tb: %d\ti: %d\n", msgData[0], msgData[1], msgData[2], msgData[3]);
//RGBSet(colour, intensity);
}
}
}
receive error