Hi,
I am transmitting multiple CAN messages with different ID and try to receive only particular CAN message with a particular CAN ID. Can able to transmit multiple messages with different ID. but while receiving I cant able to receive the desired CAN message with a particular CAN ID. Plz help
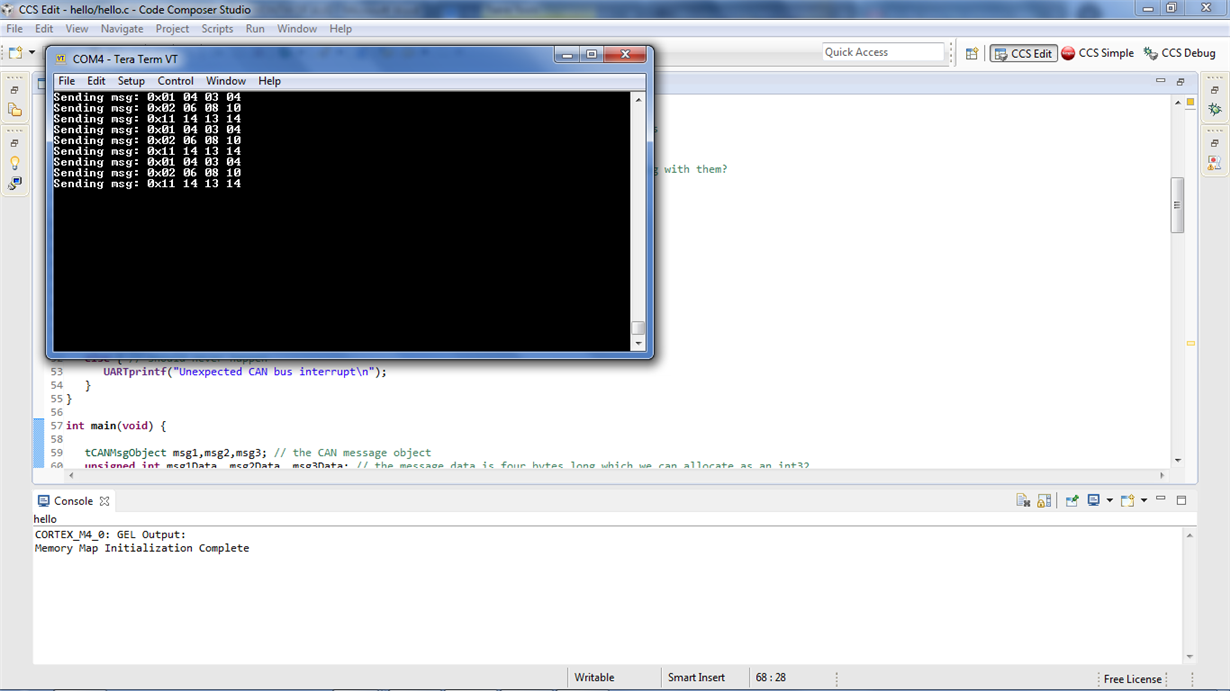
Transmitter Code:
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <math.h>
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "inc/hw_can.h"
#include "inc/hw_ints.h"
#include "driverlib/can.h"
#include "driverlib/interrupt.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/uart.h"
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "utils/uartstdio.h"
volatile bool errFlag = 0; // transmission error flag
unsigned int sysClock; // clockspeed in hz
void delay(unsigned int milliseconds) {
SysCtlDelay((sysClock / 3) * (milliseconds / 1000.0f));
}
// CAN interrupt handler
void CANIntHandler(void) {
unsigned long status = CANIntStatus(CAN1_BASE, CAN_INT_STS_CAUSE); // read interrupt status
if(status == CAN_INT_INTID_STATUS) { // controller status interrupt
status = CANStatusGet(CAN1_BASE, CAN_STS_CONTROL); // read back error bits, do something with them?
errFlag = 1;
} else if(status == 1) { // message object 1
CANIntClear(CAN1_BASE, 1); // clear interrupt
errFlag = 0; // clear any error flags
}
else if(status == 2) { // message object 1
CANIntClear(CAN1_BASE, 2); // clear interrupt
errFlag = 0; // clear any error flags
}
else if(status == 3) { // message object 1
CANIntClear(CAN1_BASE, 3); // clear interrupt
errFlag = 0; // clear any error flags
}
else { // should never happen
UARTprintf("Unexpected CAN bus interrupt\n");
}
}
int main(void) {
tCANMsgObject msg1,msg2,msg3; // the CAN message object
unsigned int msg1Data, msg2Data, msg3Data; // the message data is four bytes long which we can allocate as an int32
unsigned char *msg1DataPtr = (unsigned char *)&msg1Data;
unsigned char *msg2DataPtr = (unsigned char *)&msg2Data;
unsigned char *msg3DataPtr = (unsigned char *)&msg3Data;
// Run from the PLL at 120 MHz.
sysClock = SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_USE_PLL | SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_480), 120000000);
// Set up debugging UART
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA); // enable UART0 GPIO peripheral
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART0);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA0_U0RX);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA1_U0TX);
GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
UARTStdioConfig(0, 115200, sysClock); // 115200 baud
// Set up CAN1
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOB); // enable CAN1 GPIO peripheral
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB0_CAN1RX);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB1_CAN1TX);
GPIOPinTypeCAN(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_CAN1);
CANInit(CAN1_BASE);
CANBitRateSet(CAN1_BASE, sysClock, 500000);
CANIntRegister(CAN1_BASE, CANIntHandler); // use dynamic vector table allocation
CANIntEnable(CAN1_BASE, CAN_INT_MASTER | CAN_INT_ERROR | CAN_INT_STATUS);
IntEnable(INT_CAN1);
CANEnable(CAN1_BASE);
// Set up msg object
msg1Data = 0;
msg1.ui32MsgID = 1;
// msg1.ui32MsgIDMask = 0;
msg1.ui32Flags = MSG_OBJ_TX_INT_ENABLE;
msg1.ui32MsgLen = sizeof(msg1DataPtr);
msg1.pui8MsgData = msg1DataPtr;
msg2Data = 0;
msg2.ui32MsgID = 2;
// msg2.ui32MsgIDMask = 0;
msg2.ui32Flags = MSG_OBJ_TX_INT_ENABLE;
msg2.ui32MsgLen = sizeof(msg2DataPtr);
msg2.pui8MsgData = msg2DataPtr;
msg3Data = 0;
msg3.ui32MsgID = 3;
//msg3.ui32MsgIDMask = 0;
msg3.ui32Flags = MSG_OBJ_TX_INT_ENABLE;
msg3.ui32MsgLen = sizeof(msg3DataPtr);
msg3.pui8MsgData = msg3DataPtr;
unsigned int t = 0; // loop counter
float freq = 0.3; // frequency scaler
while(1)
{
msg1DataPtr[0] = 0x01;
msg1DataPtr[1] = 0x04;
msg1DataPtr[2] = 0x03;
msg1DataPtr[3] = 0x04;
msg2DataPtr[0] = 0x02;
msg2DataPtr[1] = 0x06;
msg2DataPtr[2] = 0x08;
msg2DataPtr[3] = 0x10;
msg3DataPtr[0] = 0x11;
msg3DataPtr[1] = 0x14;
msg3DataPtr[2] = 0x13;
msg3DataPtr[3] = 0x14;
if (UARTCharsAvail(UART0_BASE))
{
if(UARTCharGetNonBlocking (UART0_BASE)=='a')
{
UARTprintf("Sending msg: 0x%02X %02X %02X %02X\n", msg1DataPtr[0], msg1DataPtr[1], msg1DataPtr[2], msg1DataPtr[3]); // write colour to UART for debugging
UARTprintf("Sending msg: 0x%02X %02X %02X %02X\n", msg2DataPtr[0], msg2DataPtr[1], msg2DataPtr[2], msg2DataPtr[3]); // write colour to UART for debugging
UARTprintf("Sending msg: 0x%02X %02X %02X %02X\n", msg3DataPtr[0], msg3DataPtr[1], msg3DataPtr[2], msg3DataPtr[3]); // write colour to UART for debugging
IntMasterDisable();
CANMessageSet(CAN1_BASE, 1, &msg1, MSG_OBJ_TYPE_TX); // send as msg object 1
CANMessageSet(CAN1_BASE, 2, &msg2, MSG_OBJ_TYPE_TX); // send as msg object 1
CANMessageSet(CAN1_BASE, 3, &msg3, MSG_OBJ_TYPE_TX); // send as msg object 1
delay(100); // wait 100ms
IntMasterEnable();
if(errFlag) { // check for errors
UARTprintf("CAN Bus Error\n");
}
}
}
t++; // overflow is fine
}
}
Output:
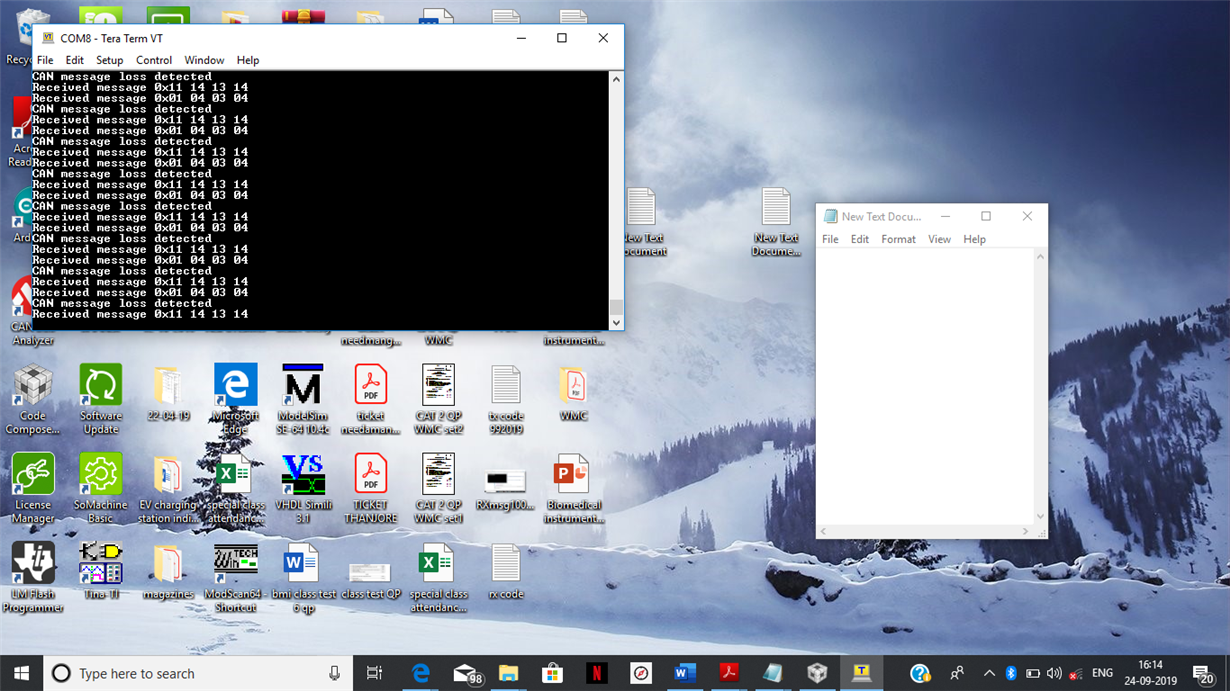
Receiver Code:
/*
* CAN bus LED controller slave firmware
* Written for TI Tiva TM4C123GH6PM
*/
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "inc/hw_can.h"
#include "inc/hw_ints.h"
#include "driverlib/can.h"
#include "driverlib/interrupt.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/uart.h"
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "utils/uartstdio.h"
volatile bool rxFlag = 0; // msg recieved flag
volatile bool errFlag = 0; // error flag
unsigned int sysClock; // clockspeed in hz
// CAN interrupt handler
void CANIntHandler(void) {
unsigned long status = CANIntStatus(CAN1_BASE, CAN_INT_STS_CAUSE); // read interrupt status
if(status == CAN_INT_INTID_STATUS) { // controller status interrupt
status = CANStatusGet(CAN1_BASE, CAN_STS_CONTROL);
errFlag = 1;
} else if(status == 1) { // msg object 1
CANIntClear(CAN1_BASE, 1); // clear interrupt
rxFlag = 1; // set rx flag
errFlag = 0; // clear any error flags
}
else if(status == 2) { // msg object 1
CANIntClear(CAN1_BASE, 2); // clear interrupt
rxFlag = 1; // set rx flag
errFlag = 0; // clear any error flags
}
else if(status == 3) { // msg object 1
CANIntClear(CAN1_BASE, 3); // clear interrupt
rxFlag = 1; // set rx flag
errFlag = 0; // clear any error flags
}else { // should never happen
UARTprintf("Unexpected CAN bus interrupt\n");
}
}
int main(void) {
tCANMsgObject msg1,msg2,msg3;// the CAN msg object
unsigned char msg1Data[8]; // 8 byte buffer for rx message data
unsigned char msg2Data[8]; // 8 byte buffer for rx message data
unsigned char msg3Data[8]; // 8 byte buffer for rx message data
// Run from crystal at 50Mhz
sysClock = SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_USE_PLL | SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_480), 120000000);
// Set up debugging UART
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART0);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA0_U0RX);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA1_U0TX);
GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
UARTStdioConfig(0, 115200, sysClock); // 115200 baud
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOB); // enable CAN1 GPIO peripheral
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB0_CAN1RX);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB1_CAN1TX);
GPIOPinTypeCAN(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_CAN1);
CANInit(CAN1_BASE);
CANBitRateSet(CAN1_BASE, sysClock, 500000);
CANIntRegister(CAN1_BASE, CANIntHandler); // use dynamic vector table allocation
CANIntEnable(CAN1_BASE, CAN_INT_MASTER | CAN_INT_ERROR | CAN_INT_STATUS);
IntEnable(INT_CAN1);
CANEnable(CAN1_BASE);
//IntMasterEnable();
// Set up LED driver
// RGBInit(1);
// Use ID and mask 0 to recieved messages with any CAN ID
msg1.ui32MsgID = 1;
//msg.ui32MsgIDMask = 0;
msg1.ui32Flags = MSG_OBJ_RX_INT_ENABLE | MSG_OBJ_USE_ID_FILTER;
msg1.ui32MsgLen = 8; // allow up to 8 bytes
// Use ID and mask 0 to recieved messages with any CAN ID
msg2.ui32MsgID = 2;
//msg.ui32MsgIDMask = 0;
msg2.ui32Flags = MSG_OBJ_RX_INT_ENABLE | MSG_OBJ_USE_ID_FILTER;
msg2.ui32MsgLen = 8; // allow up to 8 bytes
// Use ID and mask 0 to recieved messages with any CAN ID
msg3.ui32MsgID = 3;
//msg.ui32MsgIDMask = 0;
msg3.ui32Flags = MSG_OBJ_RX_INT_ENABLE | MSG_OBJ_USE_ID_FILTER;
msg3.ui32MsgLen = 8; // allow up to 8 bytes
// Load msg into CAN peripheral message object 1 so it can trigger interrupts on any matched rx messages
//CANMessageSet(CAN1_BASE, 1, &msg1, MSG_OBJ_TYPE_RX);
CANMessageSet(CAN1_BASE, 2, &msg2, MSG_OBJ_TYPE_RX);
//CANMessageSet(CAN1_BASE, 3, &msg3, MSG_OBJ_TYPE_RX);
// unsigned int colour[3];
// float intensity;
unsigned int rcv1msg[4];
unsigned int rcv2msg[4];
unsigned int rcv3msg[4];
while(1) {
//IntMasterEnable();
if(rxFlag) { // rx interrupt has occured
msg2.pui8MsgData = msg2Data; // set pointer to rx buffer
CANMessageGet(CAN1_BASE, 2, &msg2, 0); // read CAN message object 1 from CAN peripheral
rxFlag = 0; // clear rx flag
if(msg2.ui32Flags & MSG_OBJ_DATA_LOST)
{ // check msg flags for any lost messages
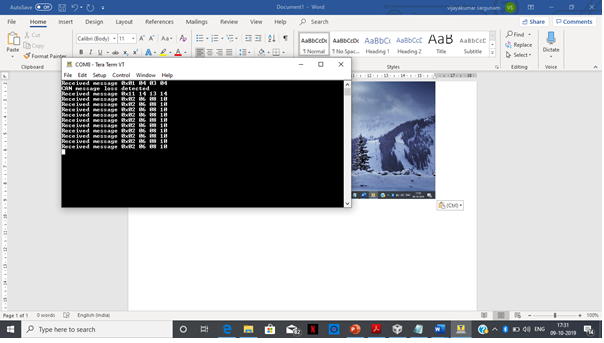
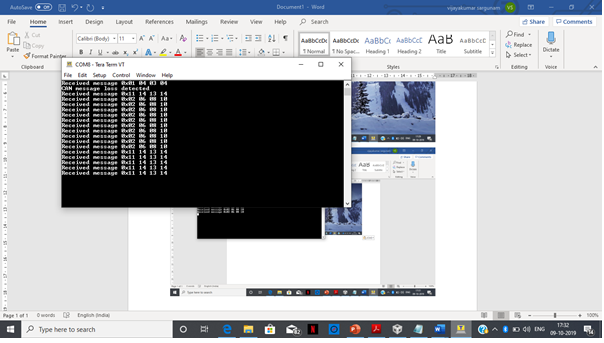
UARTprintf("CAN message loss detected\n");
msg2.ui32Flags &= ~MSG_OBJ_DATA_LOST;
// Set the new state of the message object.
CANMessageSet(CAN1_BASE, 2, &msg2, MSG_OBJ_TYPE_RX);
}
rcv2msg[0] = msg2Data[0] ;
rcv2msg[1] = msg2Data[1] ;
rcv2msg[2] = msg2Data[2] ;
rcv2msg[3] = msg2Data[3] ;
// write to UART for debugging
UARTprintf("Received message 0x%02X %02X %02X %02X\n", rcv2msg[0], rcv2msg[1],rcv2msg[2],rcv2msg[3]);
}
else
{
#if DEBUG
if(bMsgFlag == 0)
{
UARTPrintf("cant able to receive message");
bMsgFlag = 1;
}
#endif
}
}
}
Output: