Other Parts Discussed in Thread: PCF8574A
I added 10 K pullup resistors to the I2C lines. Yesterday, the CLK and data lines were clearly visible from the scope. The eval board I used yesterday blew up and I brought in a new one today. I hooked it up and I am running the I2C loopback example (no slave connected, UART printf commented out) and the I2C clock won't show up on the scope. The pullups still measure 10 K. The eval board is OK, it runs blinky. I am out of ideas.
Thanks,
Priya
CLK came back. I made some multimeter measurements
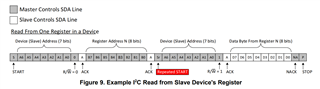
The clock issue is resolved. However, I need to understand how the slave ACK works. The part is pcf8574a, an 8 bit I2C I/O expander chip with no registers. If I write the address and wait, I don't see any I2C CLK trigger on the scope. I2C activity is visible only when after I2CMasterControl(I2C0_BASE, I2C_MASTER_CMD_SINGLE_SEND);
Do you have any pointers on what to do about the ACK signal?
Thanks
Priya
uint32_t g_ui32SysClock;
int main(void)
{
volatile uint32_t ui32Loop;
//
// The I2C0 peripheral must be enabled before use.
//
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_I2C0);
//
// For this example I2C0 is used with PortB[3:2]. The actual port and
// pins used may be different on your part, consult the data sheet for
// more information. GPIO port B needs to be enabled so these pins can
// be used.
// TODO: change this to whichever GPIO port you are using.
//
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOB);
//
// Configure the pin muxing for I2C0 functions on port B2 and B3.
// This step is not necessary if your part does not support pin muxing.
// TODO: change this to select the port/pin you are using.
//
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB2_I2C0SCL);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB3_I2C0SDA);
//
// Select the I2C function for these pins. This function will also
// configure the GPIO pins pins for I2C operation, setting them to
// open-drain operation with weak pull-ups. Consult the data sheet
// to see which functions are allocated per pin.
// TODO: change this to select the port/pin you are using.
//
GPIOPinTypeI2CSCL(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2);
GPIOPinTypeI2C(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3);
g_ui32SysClock = SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ |
SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN |
SYSCTL_USE_PLL |
SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_480), 120000000);
//Initialise relevent peripherals and ports
while (!SysCtlPeripheralReady(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOB));
SysCtlPeripheralDisable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_I2C0);
SysCtlPeripheralReset(SYSCTL_PERIPH_I2C0);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_I2C0);
// Initialize Master and slave for 400 kbps //extern uint32_t g_ui32SysClock;
I2CMasterInitExpClk(I2C0_BASE, g_ui32SysClock, false); //fast mode = true (400 kb/s)
I2CMasterEnable(I2C0_BASE);
while(1)
{
I2CMasterSlaveAddrSet(I2C0_BASE, MOSFET_ADDRESS, 1);
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 200000; ui32Loop++)
{
}
I2CMasterDataPut(I2C0_BASE, RED);
I2CMasterControl(I2C0_BASE, I2C_MASTER_CMD_SINGLE_SEND);
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 200000; ui32Loop++)
{
}
/*
I2CMasterSlaveAddrSet(I2C0_BASE, MOSFET_ADDRESS, 0);
I2CMasterDataPut(I2C0_BASE, GREEN);
I2CMasterControl(I2C0_BASE, I2C_MASTER_CMD_SINGLE_SEND);
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 200000; ui32Loop++)
{
}
I2CMasterSlaveAddrSet(I2C0_BASE, MOSFET_ADDRESS, 0);
I2CMasterDataPut(I2C0_BASE, AMBER);
I2CMasterControl(I2C0_BASE, I2C_MASTER_CMD_SINGLE_SEND);
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 200000; ui32Loop++)
{
}
*/
}
}